Labial Adhesions
Article Sections
Introduction
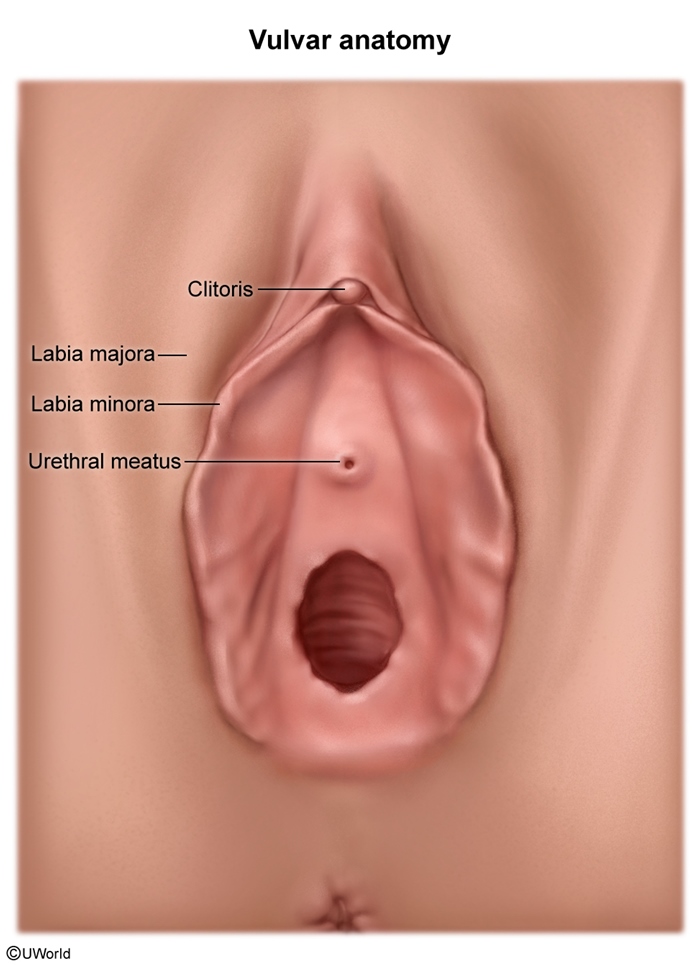
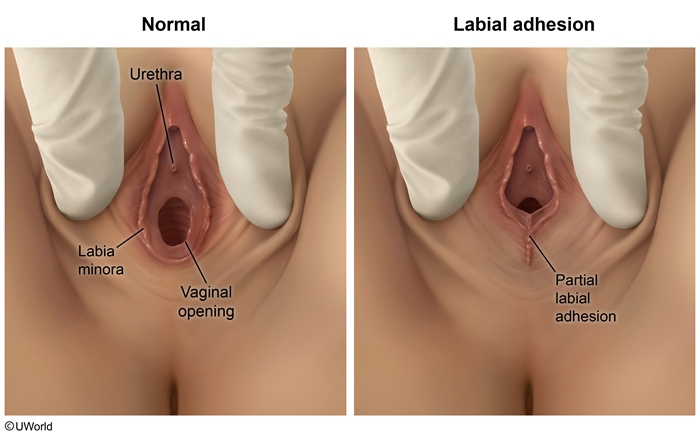
Labial adhesion refers to the fusion of the labia minora (Figure 1). This condition most commonly occurs in prepubertal girls (peak incidence at age 2-3) and postmenopausal women due to a combination of low estrogen levels and local irritation or inflammation. Although often asymptomatic and discovered incidentally, labial adhesions can sometimes lead to urinary or vaginal symptoms.
Pathophysiology and risk factors
The cause of labial adhesions is not fully understood, but the underlying mechanism likely involves low estrogen levels, resulting in thin and delicate genital tissues that are more susceptible to microtrauma followed by local inflammation or irritation that denudes the epithelial surface. As the inflamed and injured tissues attempt to heal, the lack of lubrication (also caused by low estrogen levels) results in the formation of a thin fibrous bridge of tissue between the labia minora, leading the tissues to fuse (
Continue Learning with UWorld
Get the full Labial Adhesions article plus rich visuals, real-world cases, and in-depth insights from medical experts, all available through the UWorld Medical Library.
Unlock Full AccessFigures