GnRH Agonists (Leuprolide)
Article Sections
Introduction
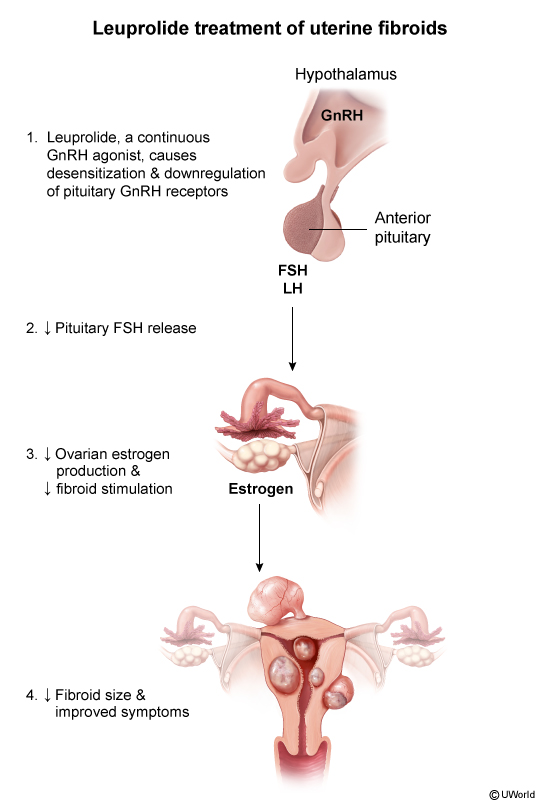
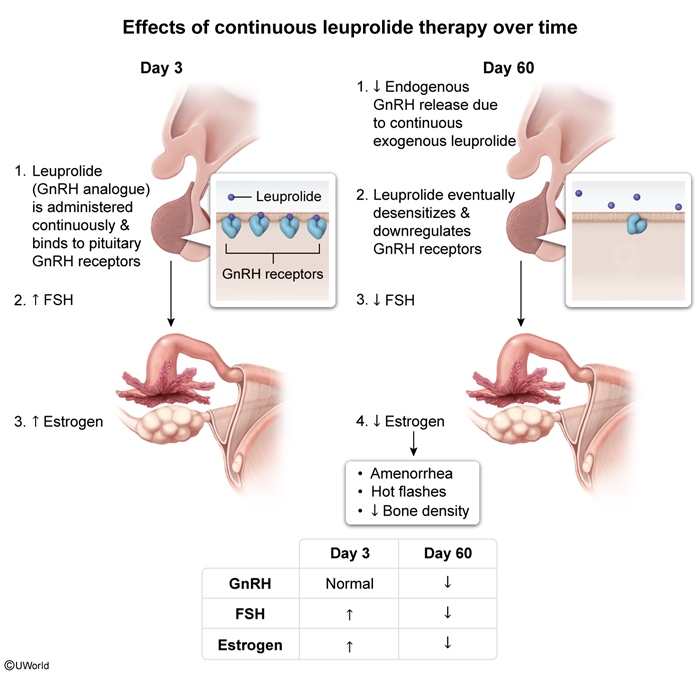
Leuprolide is a synthetic gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH) agonist (ie, GnRH analogue) used to modulate the hypothalamic-pituitary-gonadal (HPG) axis. It functions by initially stimulating, then profoundly suppressing, pituitary gonadotropic secretion (eg, LH, FSH) with continuous administration. This results in decreased production of gonadal sex steroids (testosterone in men, estradiol in women), leading to a reversible hypogonadal state.
HPG axis physiology
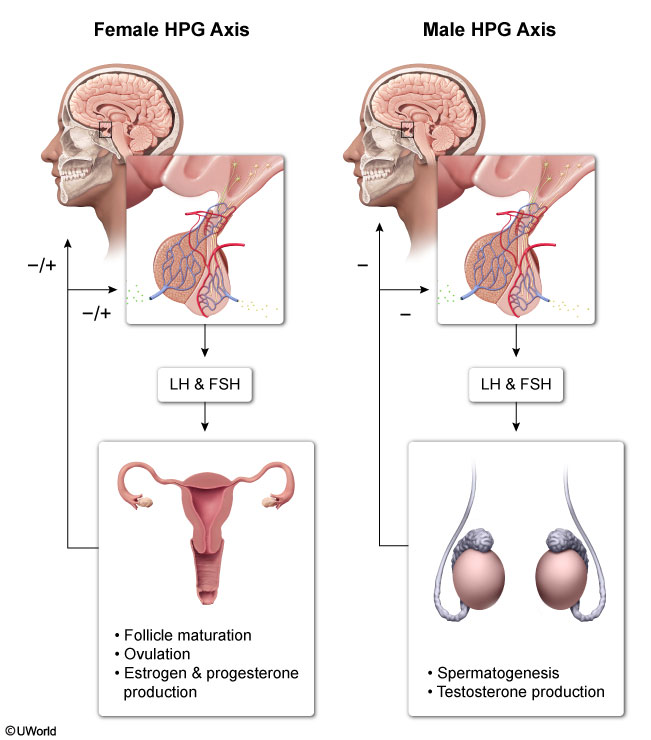
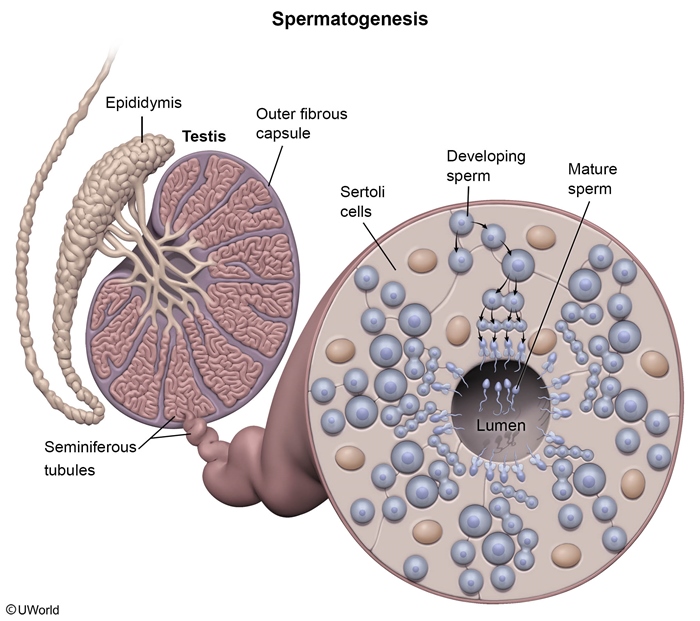
The HPG axis is a hormonal feedback loop that regulates reproductive function in men and women (Figure 1). At puberty, the hypothalamus begins periodic, pulsatile releases of GnRH, which stimulate the pituitary to release the gonadotropins LH and FSH, which act on the gonads.
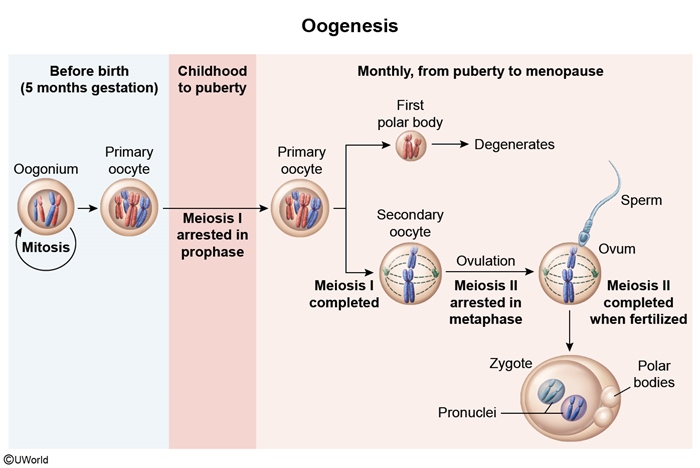
- In women, this stimulates the ovary to release estrogen and progesterone, which regulate follicular development, the uterine endometrium, and menses (
Continue Learning with UWorld
Get the full GnRH Agonists (Leuprolide) article plus rich visuals, real-world cases, and in-depth insights from medical experts, all available through the UWorld Medical Library.
Unlock Full AccessFigures