Urethral Diverticulum
Article Sections
Introduction
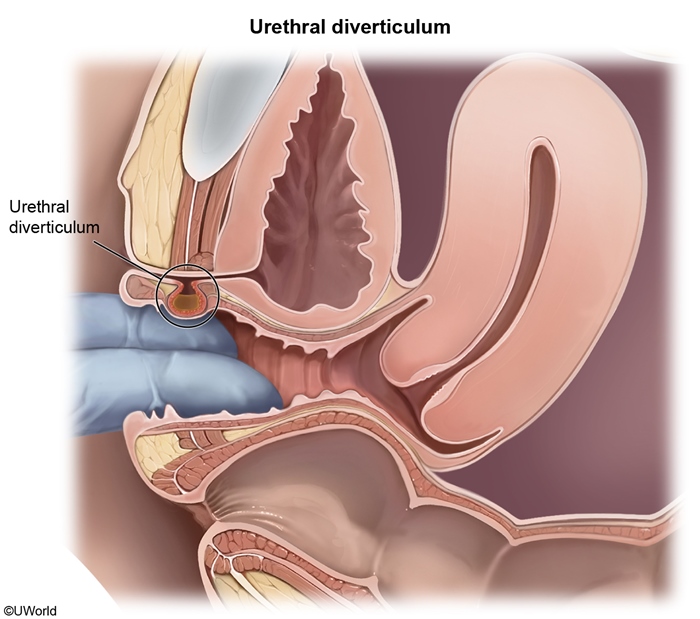
A urethral diverticulum is a localized outpouching of the urethral mucosa through the muscular wall of the urethra. It predominantly affects women and typically presents with dysuria, postvoid dribbling, dyspareunia, and an anterior vaginal wall mass.
Pathophysiology and risk factors
The exact pathogenesis of a urethral diverticulum is not entirely understood, but it likely arises from recurrent periurethral gland infections, which can develop into an abscess that eventually breaches the urethral mucosa. The persistent infection, inflammation, and increased tissue tension in the area can cause development of the diverticulum and a tender anterior vaginal wall mass. The diverticulum may collect urine and debris, resulting in purulent discharge, dysuria, or postvoid dribbling.
Other possible causes include recurrent urinary tract infections (because chronic inflammation can weaken the urethral wall), pelvic floor trauma or surgery (eg, vaginal delivery), and recurrent obstruction (eg, urethral stone).
Continue Learning with UWorld
Get the full Urethral Diverticulum article plus rich visuals, real-world cases, and in-depth insights from medical experts, all available through the UWorld Medical Library.
Unlock Full AccessFigures