Rare Ovarian Tumors
Article Sections
Introduction
Ovarian tumors can be benign or malignant and are classified based on their predominant cell type, which determines their clinical symptoms and gross appearance (Figure 1).
Ovarian tumor types include (Table 1):
- Epithelial: composed of surface epithelial cells and include serous and mucinous subtypes. Epithelial carcinomas are the most common type of ovarian cancer and are reviewed in detail in a separate article.
- Germ cell: derived from primordial germ cells of the ovary; they can broadly be divided into cell populations that differentiate towards embryo-like tumors (eg, teratomas, dysgerminomas) and those that differentiate towards extraembryonic (ie, placenta) tumors (eg, yolk sac tumors).
- Sex cord-stromal: tumors composed of cells from either the sex cord (eg, granulosa cell tumors), stromal cells (eg, fibroma, thecoma), or both (eg, Sertoli-Leydig tumors).
Continue Learning with UWorld
Get the full Rare Ovarian Tumors article plus rich visuals, real-world cases, and in-depth insights from medical experts, all available through the UWorld Medical Library.
Unlock Full AccessFigures
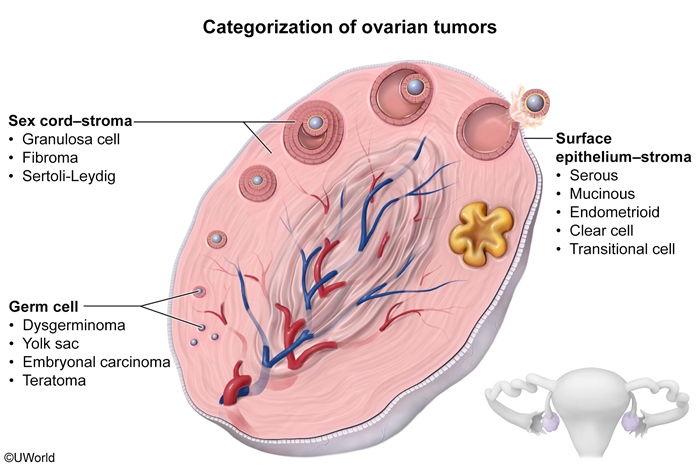
Figure 1
Images
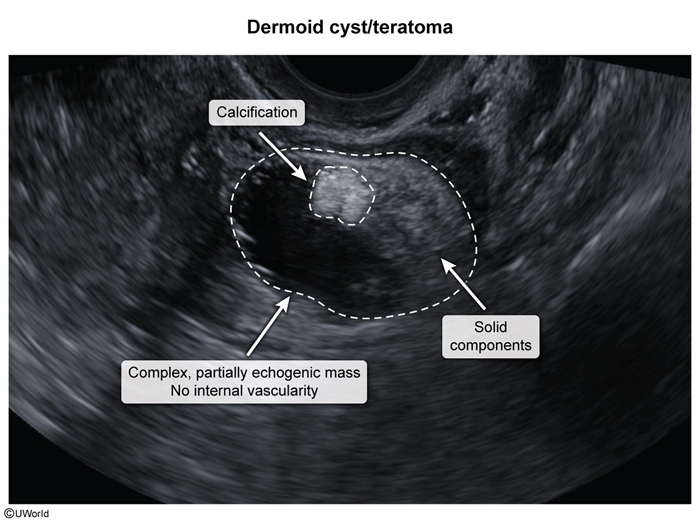
Image 1
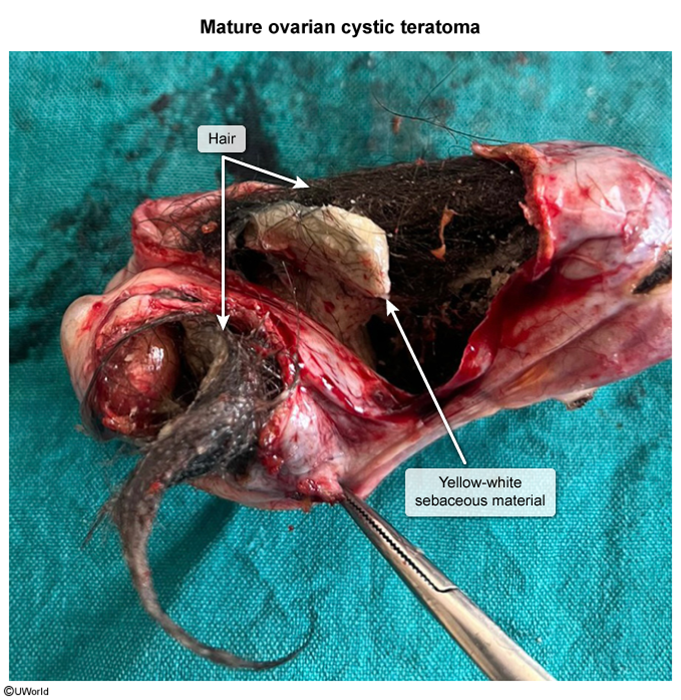
Image 2
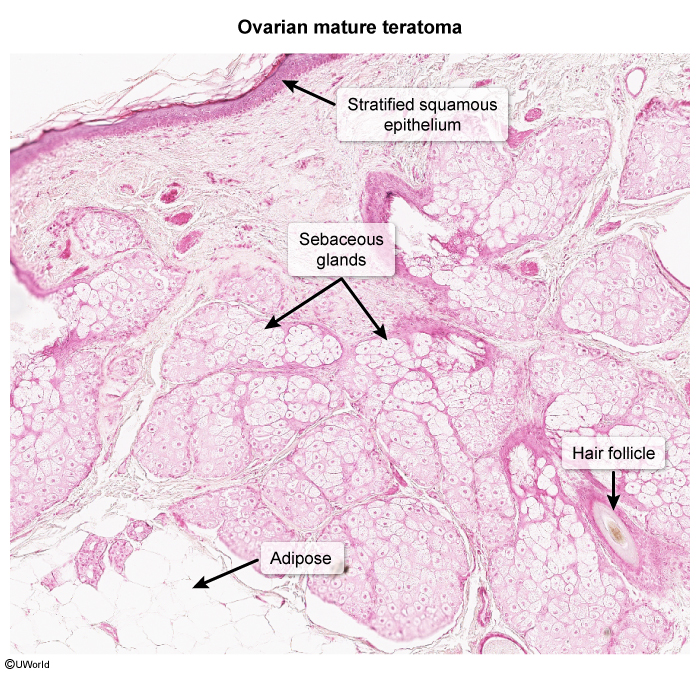
Image 3
Tables
Table 1
Table 2