5-Alpha Reductase Deficiency
Article Sections
Introduction
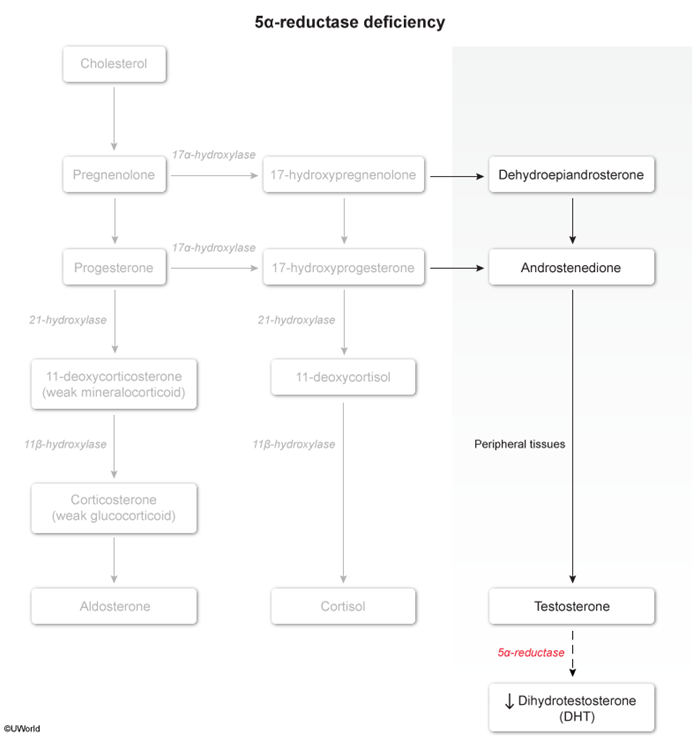
5-alpha reductase deficiency is a rare, autosomal recessive disorder of sex development impairing the conversion of testosterone to dihydrotestosterone (DHT) (Figure 1). Patients with 5-alpha reductase deficiency have a 46,XY genotype but have a female phenotype (eg, external female genitalia) at birth and experience virilization (eg, clitoromegaly, increased muscle mass) at puberty.
Pathogenesis
There are 2 types of 5-alpha reductase enzyme that convert testosterone to DHT: type 1 is present in postpubescent skin and type 2 is predominantly found in the genitals. 5-alpha reductase deficiency is caused exclusively by a defective type 2 enzyme. The lack of DHT leads to abnormal sexual development, beginning in utero:
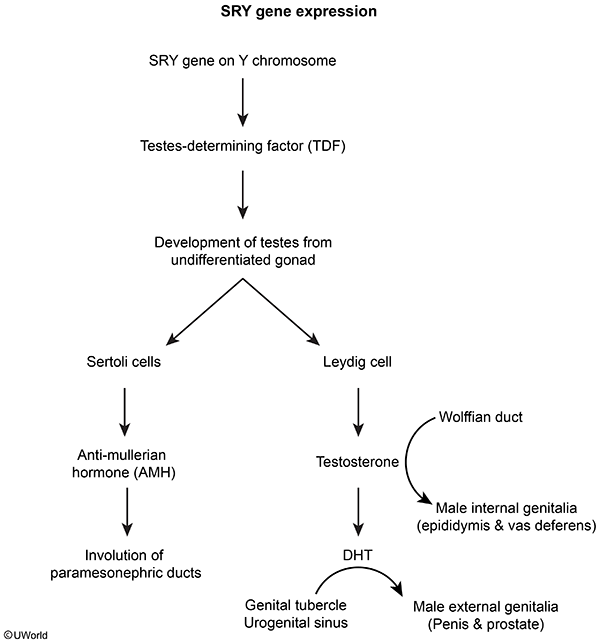
Development of internal genitalia- In utero, the gonads of genotypic males (46,XY
Continue Learning with UWorld
Get the full 5-Alpha Reductase Deficiency article plus rich visuals, real-world cases, and in-depth insights from medical experts, all available through the UWorld Medical Library.
Unlock Full AccessFigures