Androgen Insensitivity Syndrome
Article Sections
Introduction
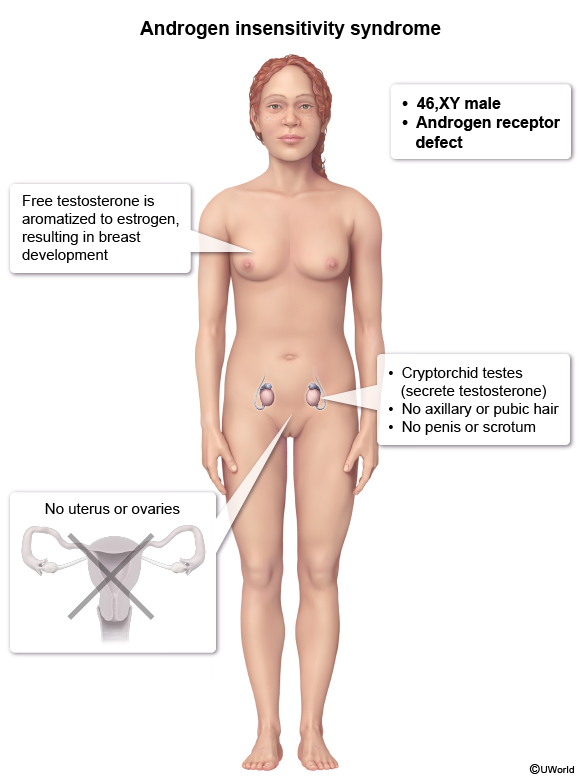
Androgen insensitivity syndrome (AIS) is a rare, X-linked recessive disorder of sex development caused by defective androgen receptors. Patients with complete AIS have a 46,XY genotype yet have a female phenotype (ie, female external genitalia, breast development) despite the presence of testes and male-range androgen production (Figure 1).
Pathogenesis
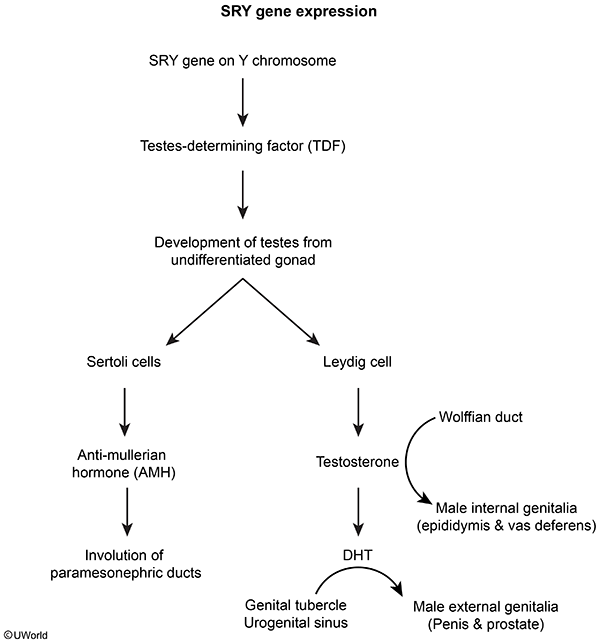
Testosterone and dihydrotestosterone (DHT) normally interact with androgen receptors in target tissues to induce androgenic effects (ie, virilization).
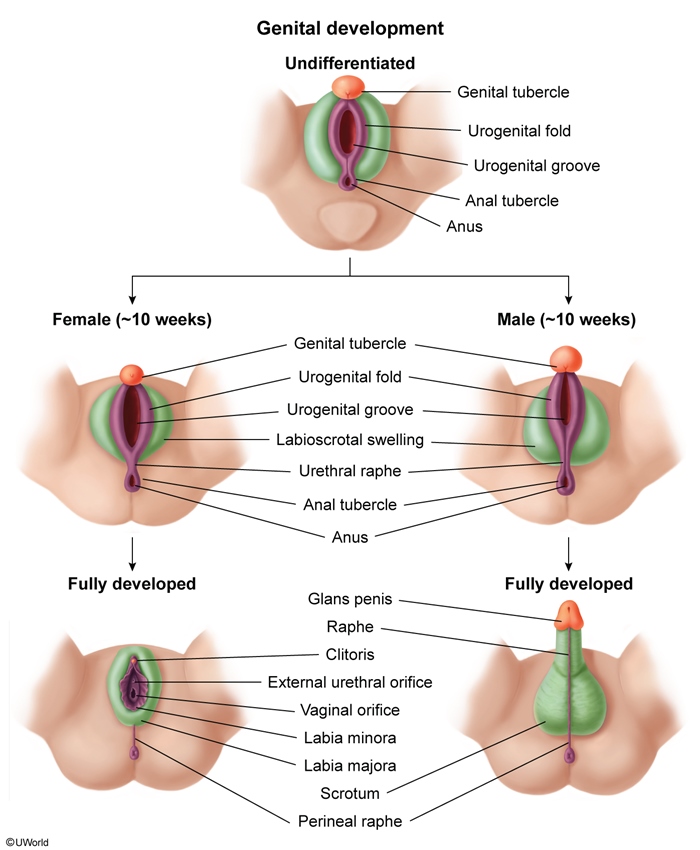
AIS, an X-linked recessive disorder, is caused by loss-of-function mutations in the androgen receptor gene on the X chromosome. These mutations lead to a lack of response to androgens, resulting in abnormal sexual development (ie, undervirilization) beginning in utero:
Development of internal genitalia- 46,XY patients with AIS have an intact
Continue Learning with UWorld
Get the full Androgen Insensitivity Syndrome article plus rich visuals, real-world cases, and in-depth insights from medical experts, all available through the UWorld Medical Library.
Unlock Full AccessFigures