Endometriosis
Article Sections
Introduction
Endometriosis is a chronic gynecologic condition affecting approximately 10% of reproductive-aged women and is characterized by the presence of extrauterine (or ectopic) endometrial glands and stroma. It is often found within the pelvic cavity and, less commonly, distant organs (eg, diaphragm). Endometriosis has a variety of clinical presentations, ranging from an asymptomatic, incidental finding to severe pelvic pain and infertility.
Pathophysiology
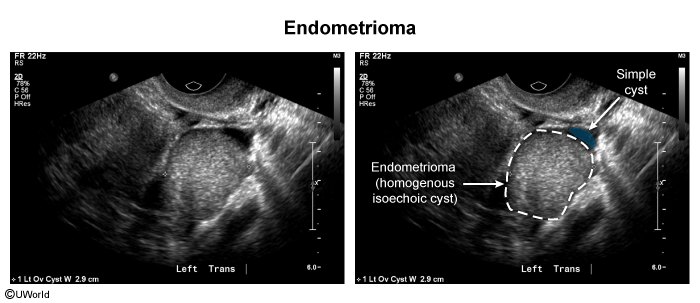
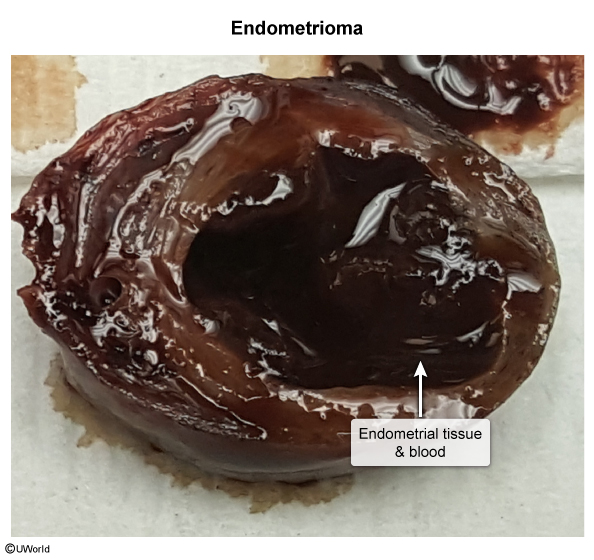
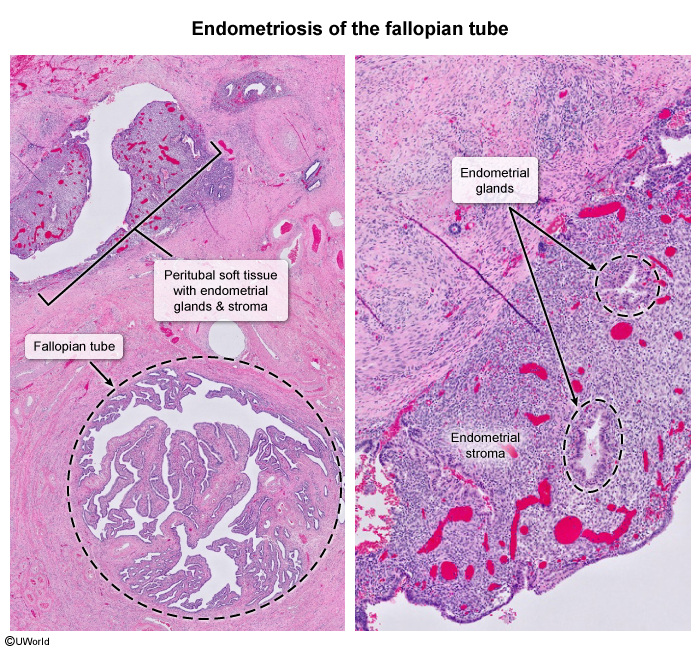
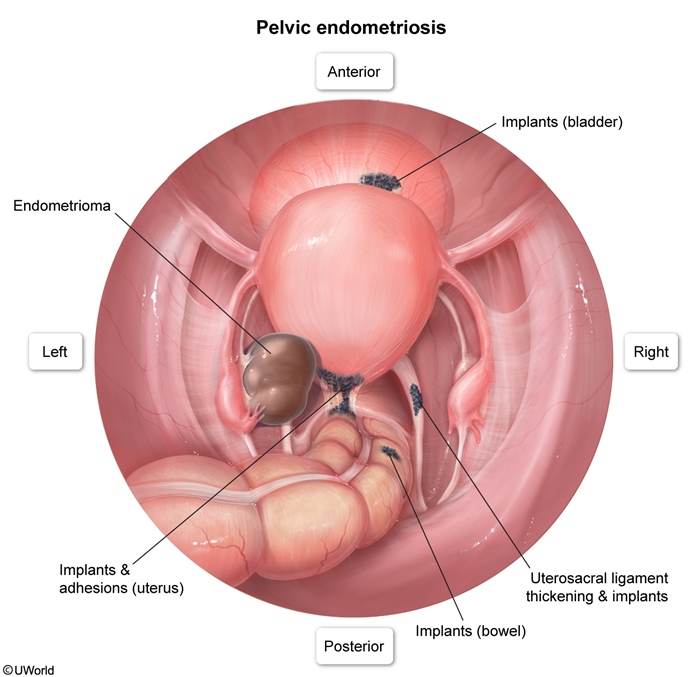
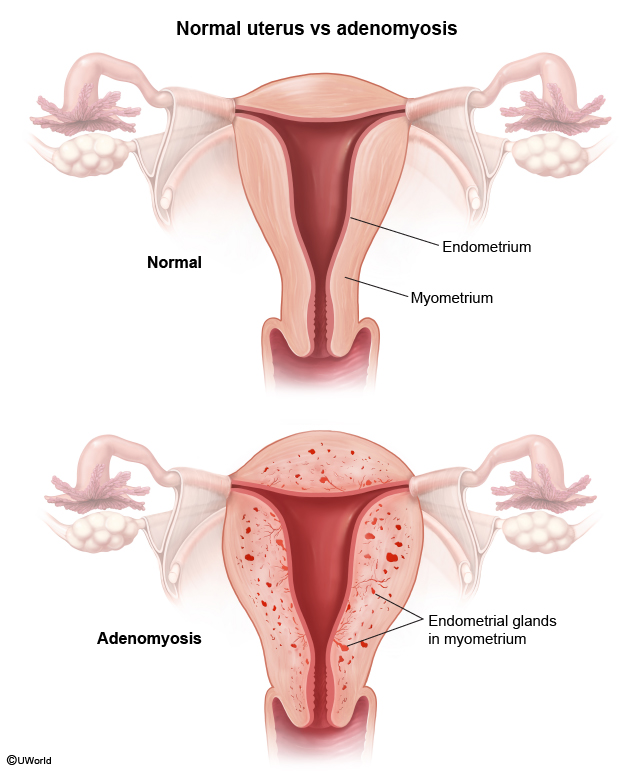
Endometriosis is characterized by ectopic (Figure 1) endometrial glands and stroma typically found in the pelvis, most commonly on the ovaries, anterior and posterior cul-de-sacs, and broad and uterosacral ligaments. They can also be found on the bladder, fallopian tubes, bowel, and peritoneum. Several theories have been proposed to explain the appearance of endometrial tissue in extrauterine locations; these include:
Continue Learning with UWorld
Get the full Endometriosis article plus rich visuals, real-world cases, and in-depth insights from medical experts, all available through the UWorld Medical Library.
Unlock Full AccessFigures
Images