Epithelial Ovarian Cancer
Article Sections
Introduction
Ovarian cancers include epithelial ovarian cancers (EOCs), germ cell tumors, and sex cord-stromal tumors. EOC is the most common type of ovarian cancer and includes primary epithelial cancers of the ovary, fallopian tube, and peritoneum. Because ovarian cancer causes only vague abdominal symptoms or no symptoms at all, it is often diagnosed at an advanced stage, and is therefore a leading cause of gynecologic mortality.
Pathogenesis
The ovary is composed of multiple different cell lineages, each of which can result in different malignancies:
- Surface epithelial stroma: composed of cells that support the normal ovarian structure for ovulation (eg, serous, mucinous epithelial cells).
- Sex cord stroma: composed of cells that surround and support the oocyte. These cells secrete sex hormones including estrogen (granulosa cells) and testosterone (Sertoli-Leydig cells).
Continue Learning with UWorld
Get the full Epithelial Ovarian Cancer article plus rich visuals, real-world cases, and in-depth insights from medical experts, all available through the UWorld Medical Library.
Unlock Full AccessImages
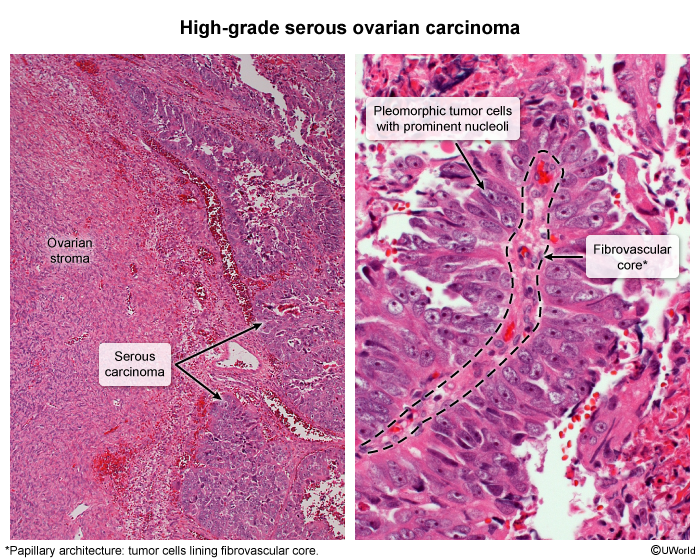
Image 1
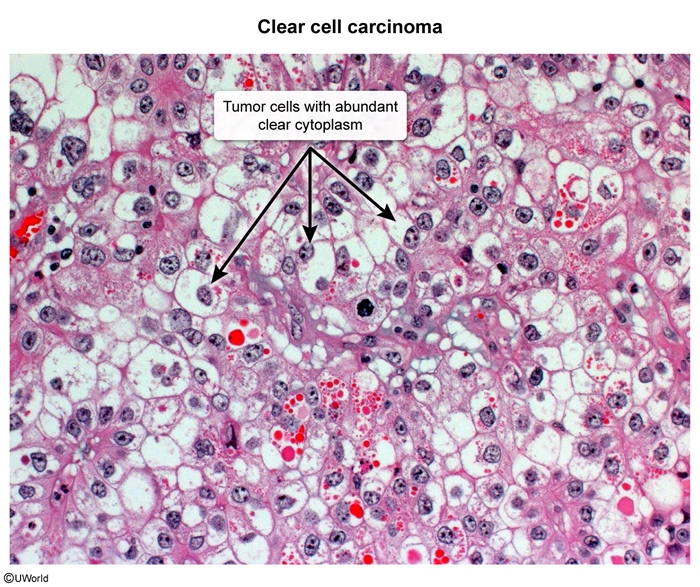
Image 2
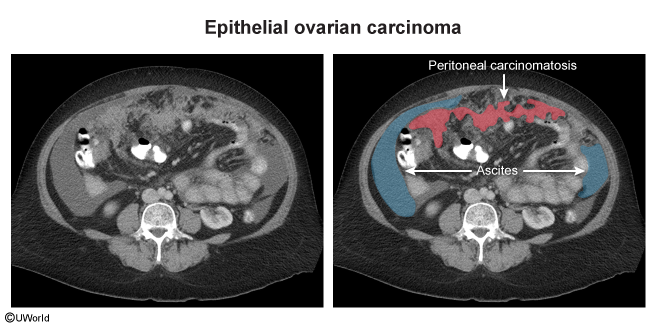
Image 3
Tables
Table 1
Table 2
Table 3