Infectious Genital Ulcers
Article Sections
Introduction
Infectious genital ulcers are sores that appear on the genitalia due to sexually transmitted bacteria or viruses. Each condition that causes infectious genital ulcers has distinct characteristics and requires specific diagnostic and management strategies.
All share the common risk factors of:
- Unprotected sexual intercourse
- Multiple sexual partners
- History of other sexually transmitted infections (STIs)
- Immunosuppression
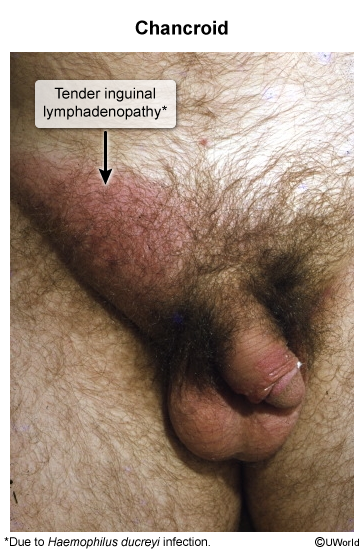
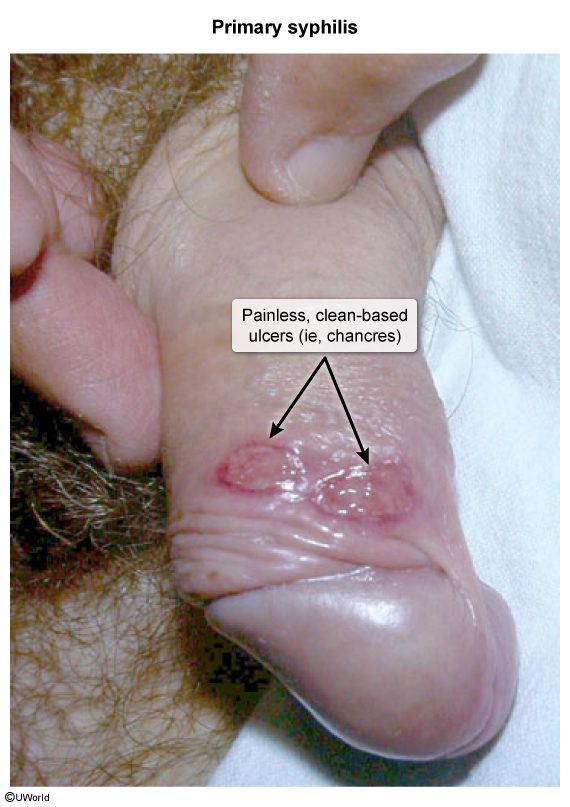
Depending on the underlying cause, infectious ulcers may differ in appearance, associated symptoms, and number of ulcers present (single or multiple). They can be further divided into painful (eg, herpes simplex virus [HSV], chancroid) and nonpainful (eg, syphilis, lymphogranuloma venereum, granuloma inguinale) lesions.
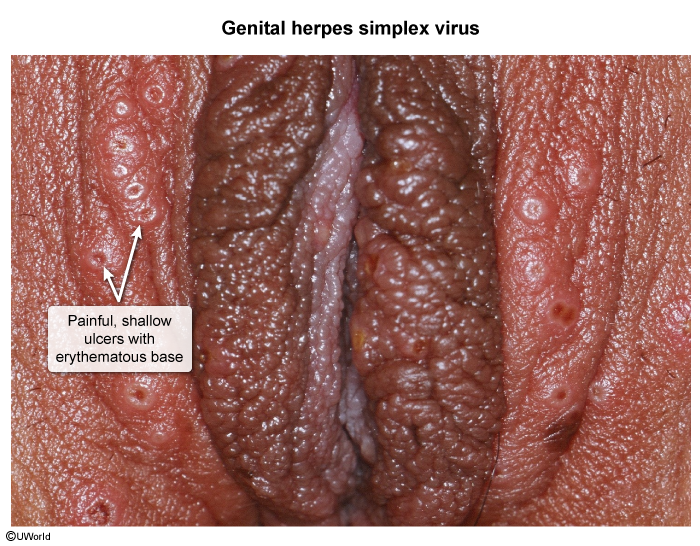
Herpes simplex virus (HSV)
HSV is an enveloped, double-stranded DNA virus with 2 serotypes: HSV-1 and HSV-2. Classically, HSV-1 is associated with gingivostomatitis (vesicles on the anterior oral mucosa), and HSV-2 is associated with genital infection. Infection with either serotype can occur at either location.
Continue Learning with UWorld
Get the full Infectious Genital Ulcers article plus rich visuals, real-world cases, and in-depth insights from medical experts, all available through the UWorld Medical Library.
Unlock Full AccessImages