Condyloma Acuminata
Article Sections
Introduction
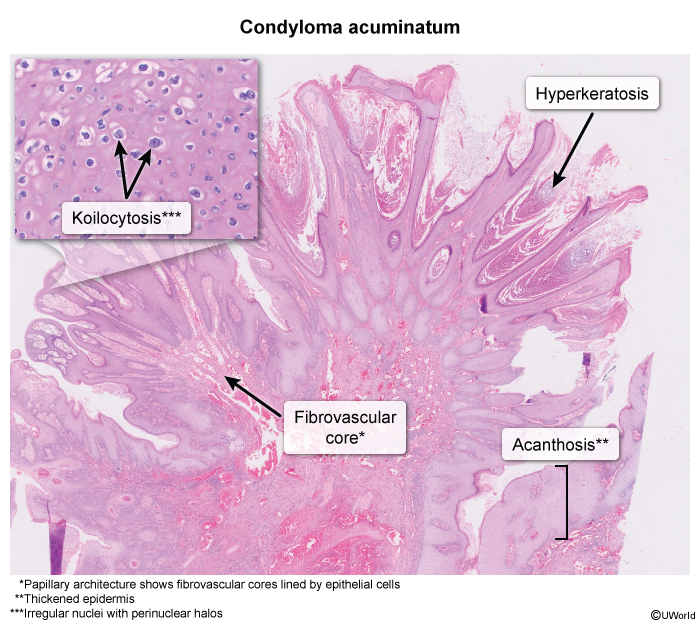
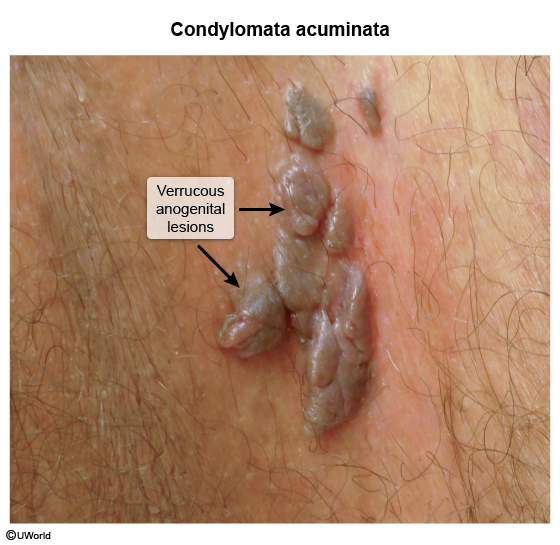
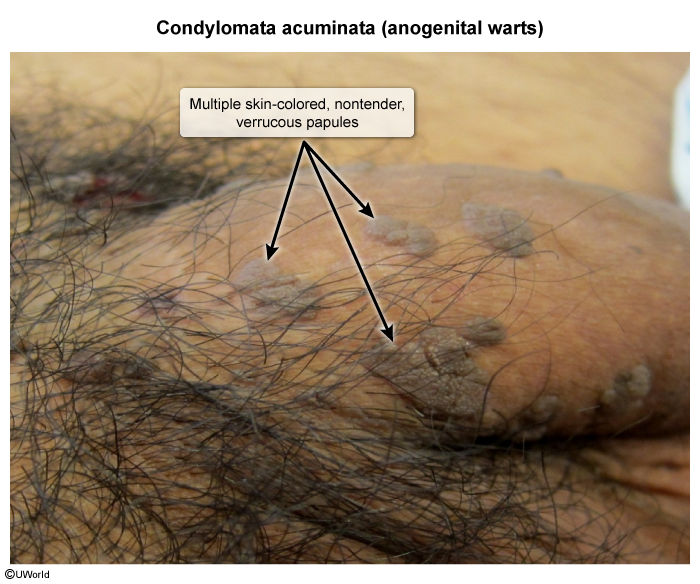
Condyloma acuminata, also known as anogenital warts, are a common sexually transmitted infection (STI) caused by human papillomavirus (HPV), most often types 6 and 11. HPV infection is common and is spread by direct skin-to-skin contact. Anogenital warts can develop in both men and women in the genital, perineal, and perianal areas.
Risk factors
- Multiple sexual partners with no barrier contraception
- Younger age (20-24)
- Immunosuppression (eg, HIV/AIDS, immunosuppressive therapy)
- Smoking
- Prior STIs
Pathophysiology
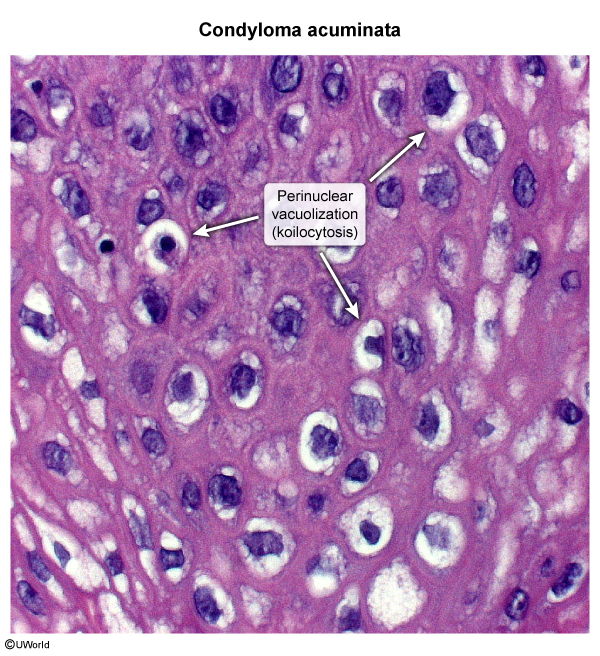
HPV is a nonenveloped, double-stranded DNA virus with multiple strands. HPV can be categorized as high or low risk based on the propensity to cause malignancy. Low-risk HPV types 6 and 11 are primarily responsible for the development of condyloma acuminata. The virus infects the basal cells of the epithelium through microabrasions or microtrauma. Once inside the cell, HPV DNA integrates into the host genome, leading to cellular proliferation and the formation of warty growths, which are benign but usually persistent and recurrent.
Continue Learning with UWorld
Get the full Condyloma Acuminata article plus rich visuals, real-world cases, and in-depth insights from medical experts, all available through the UWorld Medical Library.
Unlock Full AccessImages