Vulvovaginal Candidiasis
Article Sections
Introduction
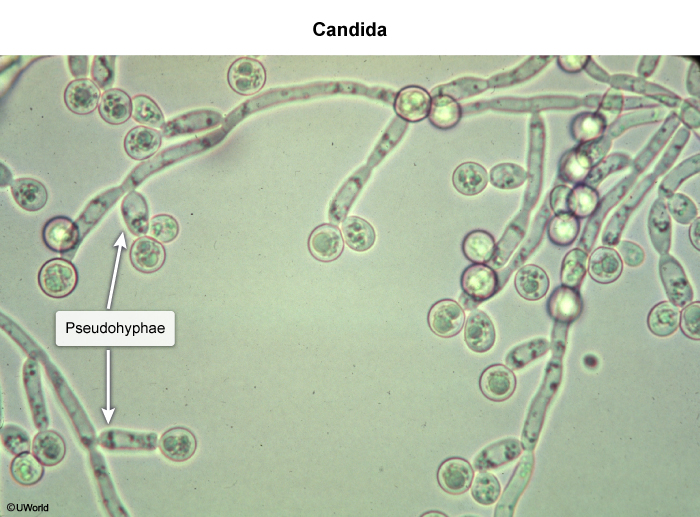
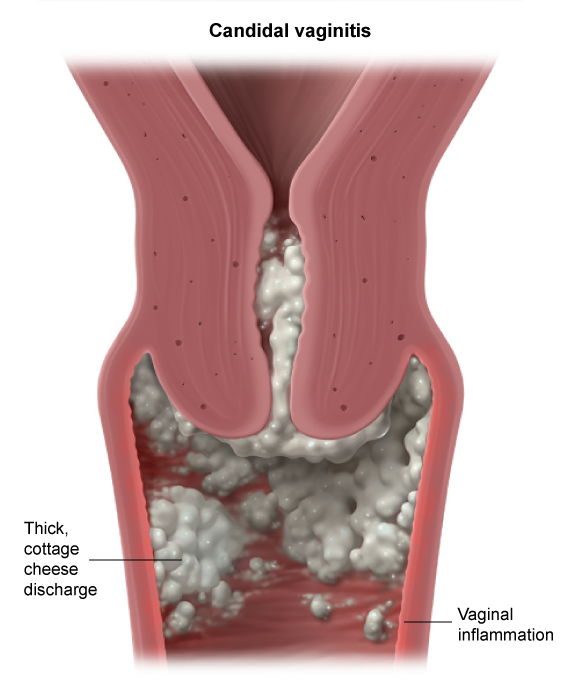
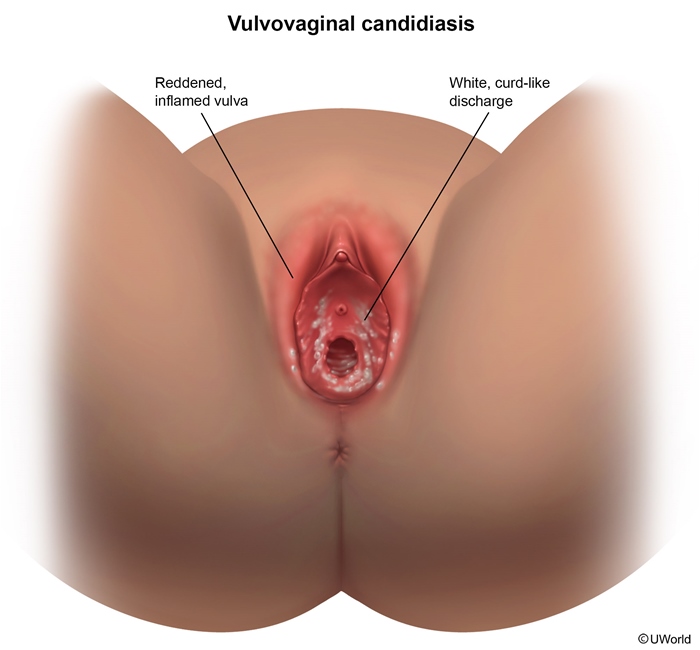
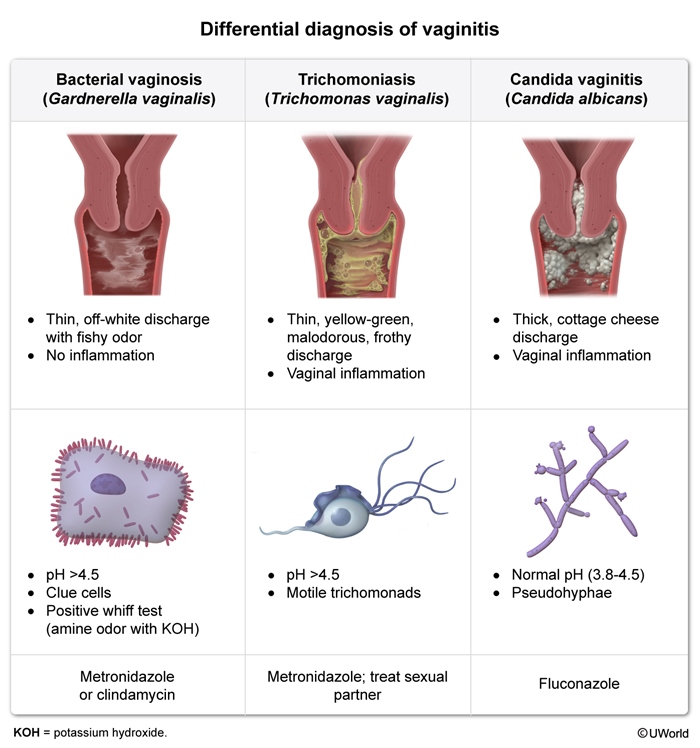
Vulvovaginal candidiasis (VVC), commonly known as a yeast infection, is an inflammatory vulvar and vaginal infection caused by overgrowth of fungal Candida species, most commonly Candida albicans. Although Candida spp. are part of the normal vaginal flora, overgrowth can lead to symptomatic infection.
Pathophysiology and risk factors
Candida fungal spp. are part of the normal vaginal flora and exist in balance with the predominant bacteria of the vaginal microbiome, gram-positive Lactobacillus spp. Alterations in immune function or in the balance of the vaginal microbiome allow for excessive Candida proliferation. Symptomatic infection develops when pseudohyphae invade the vaginal epithelium, leading to inflammation. Disruptions in the flora balance can occur sporadically or as a result of well-known risk factors that predispose to candidiasis:
- Antibiotic use
Continue Learning with UWorld
Get the full Vulvovaginal Candidiasis article plus rich visuals, real-world cases, and in-depth insights from medical experts, all available through the UWorld Medical Library.
Unlock Full AccessFigures
Images