Pelvic Inflammatory Disease
Article Sections
Introduction
Pelvic inflammatory disease (PID) is an acute infection of any part of the upper female reproductive tract, which includes the uterus, fallopian tubes, and ovaries. It is classically a result of sexually transmitted infections (STIs) and can lead to serious and lasting sequelae if not treated promptly.
Pathophysiology
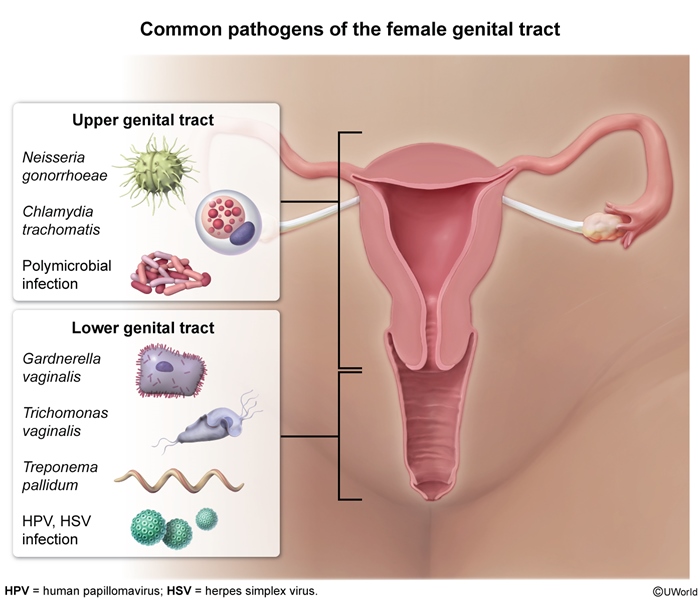
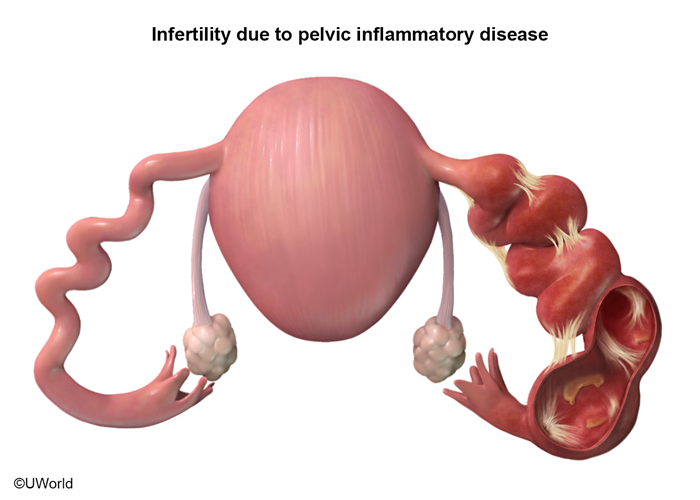
The female genital tract can be divided into the lower genital tract (ie, vagina), which contains anaerobic, gram-negative, and gram-positive bacteria, and the upper genital tract (ie, cervix, uterus, fallopian tubes, ovaries), which is sterile. The upper genital tract is isolated from normal, but potentially pathogenic, vaginal flora by the endocervical canal, which creates a barrier between the upper and lower genital tracts.
When this barrier is disrupted (often by sexually transmitted infections), pathogens ascend from the lower genital tract and infect the uterus, resulting in pelvic inflammatory disease (PID) (
Continue Learning with UWorld
Get the full Pelvic Inflammatory Disease article plus rich visuals, real-world cases, and in-depth insights from medical experts, all available through the UWorld Medical Library.
Unlock Full AccessFigures
Images