Failure To Thrive
Article Sections
Introduction
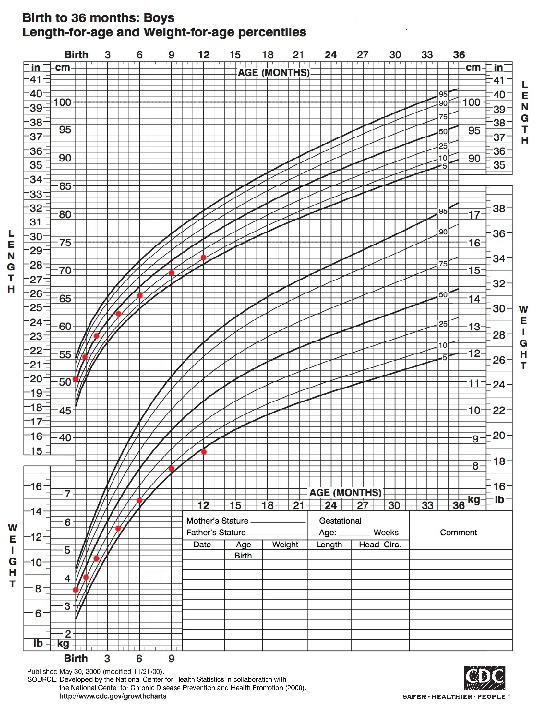
Failure to thrive (FTT) (ie, poor weight gain, weight faltering) describes a lack of appropriate weight gain relative to a patient's age, linear growth, sex, and genetic potential. Consensus criteria for FTT are not yet established, but proposed criteria include weight that crosses ≥2 major percentiles (eg, 25th, 10th, 5th) and is downtrending when plotted on an appropriate growth chart for gestation-corrected age and sex (Figure 1). FTT is typically a sign of underlying medical, nutritional, developmental, behavioral, and/or psychosocial issues that require further evaluation.
Pathogenesis and risk factors
FTT is common (affecting 5%-10% of children in resource-abundant settings) and occurs due to an imbalance between caloric intake, absorption, and expenditure, or a combination of these. Risk factors include:
Continue Learning with UWorld
Get the full Failure To Thrive article plus rich visuals, real-world cases, and in-depth insights from medical experts, all available through the UWorld Medical Library.
Unlock Full AccessFigures