Food Protein-Induced Allergic Proctocolitis (FPIAP)
Article Sections
Introduction
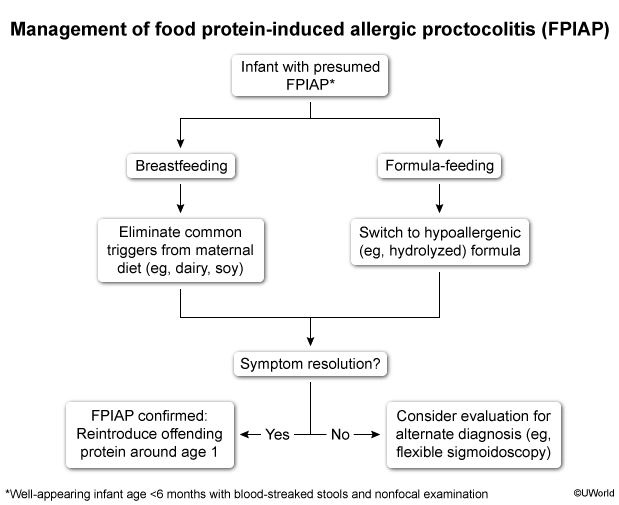
Food protein-induced allergic proctocolitis (FPIAP) is a benign, non–IgE-mediated reaction in young infants that is triggered by dietary proteins (eg, casein, whey) found in standard formula and/or breast milk. It is characterized by blood-streaked stools in otherwise healthy infants and managed by dietary elimination of the offending protein.
Pathogenesis
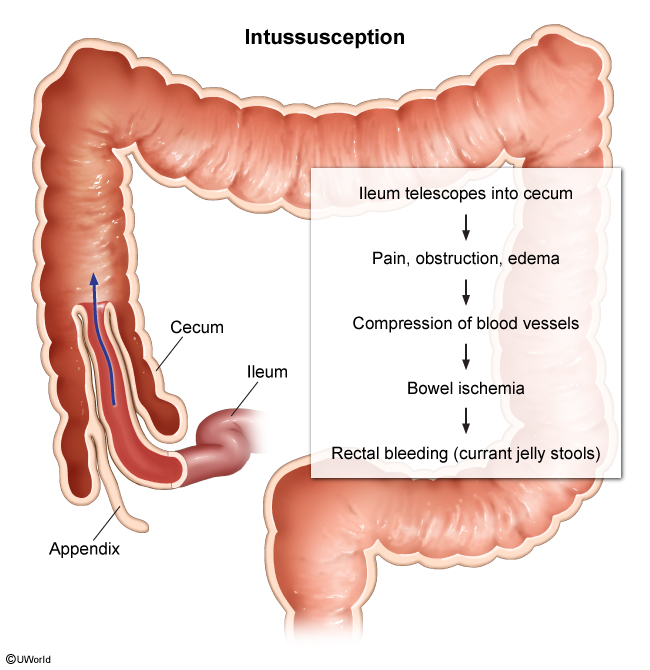
FPIAP is a benign, self-limited, non–IgE-mediated reaction that occurs in infancy. The exact mechanism is unclear but is likely due to a delayed-type hypersensitivity to dietary proteins that may be exaggerated due to an immature neonatal intestinal barrier, allowing increased antigen absorption. Eosinophilic infiltration of the distal colon and rectum results in mucosal friability and rectal bleeding.
The most common dietary triggers are cow's milk proteins
Continue Learning with UWorld
Get the full Food Protein-Induced Allergic Proctocolitis (FPIAP) article plus rich visuals, real-world cases, and in-depth insights from medical experts, all available through the UWorld Medical Library.
Unlock Full AccessFigures