Evaluation Of Abnormal Liver Function Tests (LFTs)
Article Sections
Introduction
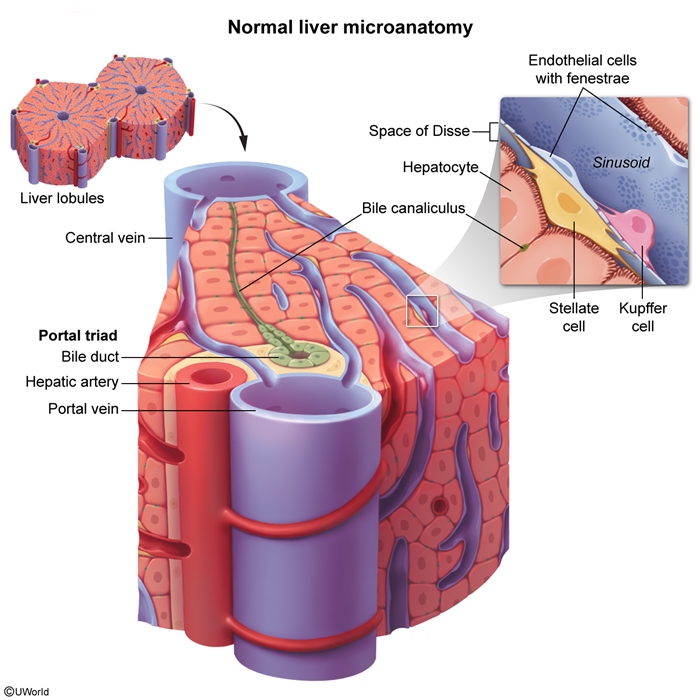
Liver functions include metabolism, detoxification, protein synthesis, and digestion, with hepatocytes carrying out most metabolic and detoxification processes and cholangiocytes (which line the bile ducts) aiding in bile secretion and modification. Abnormal liver function tests (LFTs) can be the first indication of liver injury or dysfunction, often before clinical symptoms appear. Elevated LFTs may result from benign or severe hepatobiliary conditions. Commonly measured tests include the following:
- Liver enzymes: Alanine aminotransferase (ALT), aspartate aminotransferase (AST), alkaline phosphatase, gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase (GGT), and lactate dehydrogenase
- Synthetic function tests: Serum albumin and prothrombin time (PT) (also named international normalized ratio [INR])
A systematic approach based on the pattern of injury is helpful in the evaluation of elevated LFTs.
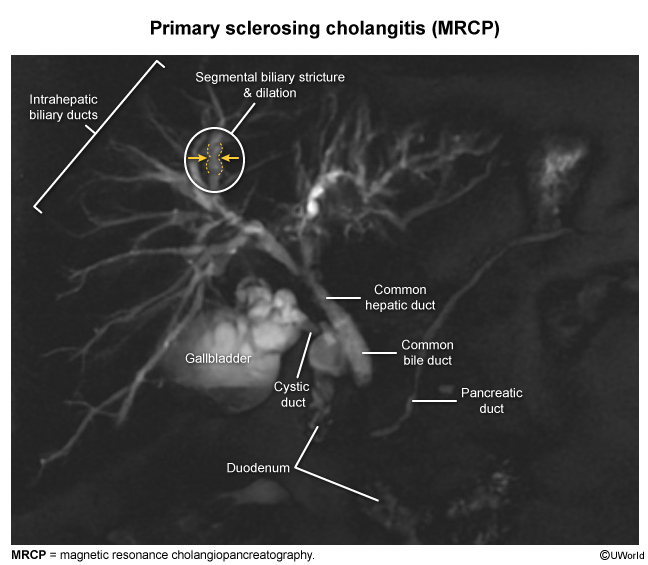
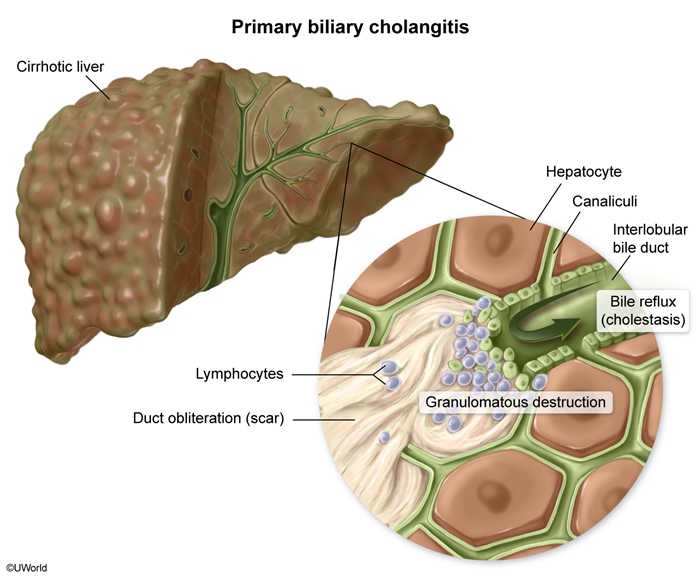
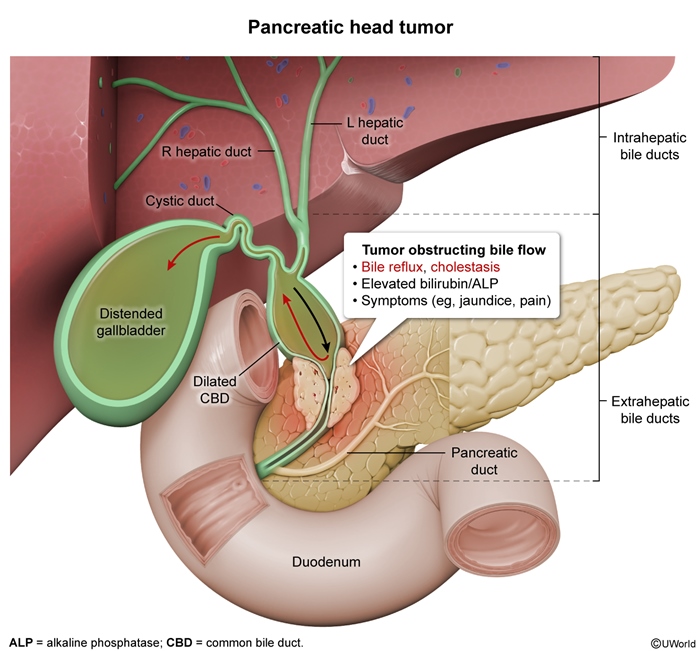
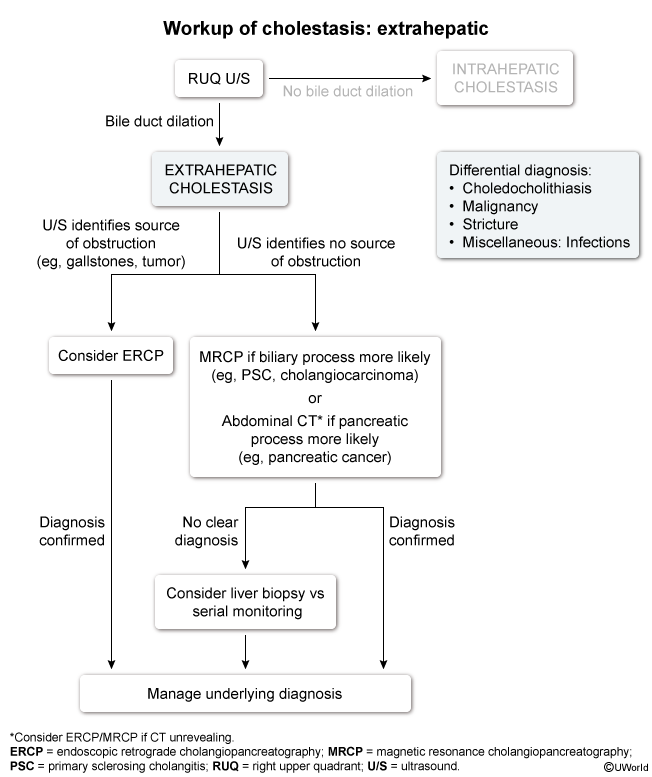
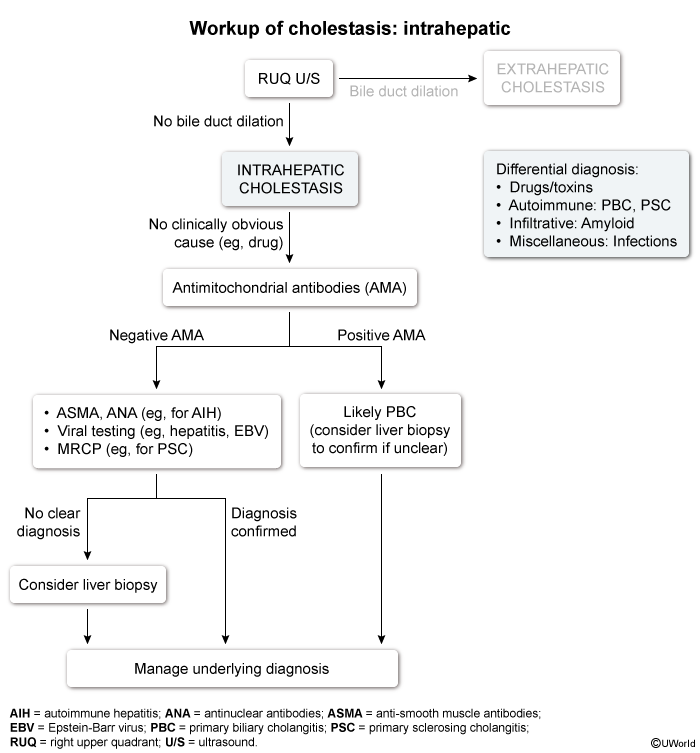
Patterns of liver injury
Elevated LFTs typically follow 1 of 3 patterns of liver injury depending on the predominant structures involved (
Continue Learning with UWorld
Get the full Evaluation Of Abnormal Liver Function Tests (LFTs) article plus rich visuals, real-world cases, and in-depth insights from medical experts, all available through the UWorld Medical Library.
Unlock Full AccessFigures
Images