Hypothalamic-Pituitary Hormones
Article Sections
Introduction
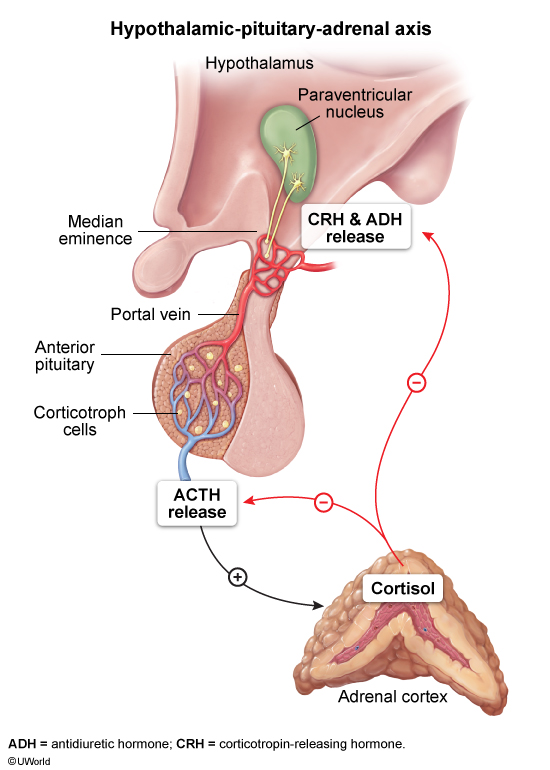
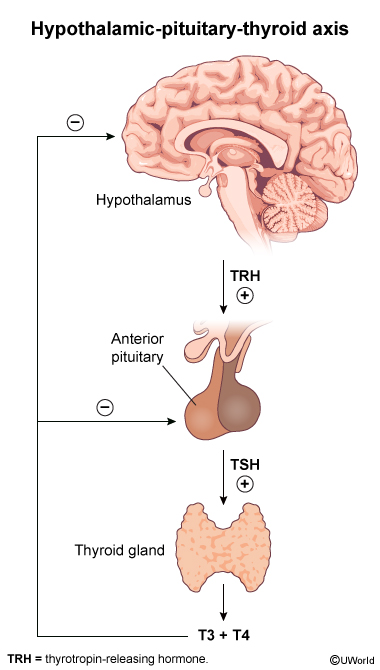
The hypothalamic-pituitary axis is a core component of the endocrine system, responsible for regulating various physiologic processes, including growth, metabolism, reproduction, and stress responses. The hypothalamus, located at the base of the brain, controls the release of hormones from the pituitary gland, which is divided into anterior and posterior lobes. The anterior pituitary releases several hormones that regulate peripheral endocrine glands, whereas the posterior pituitary stores and releases hormones synthesized in the hypothalamus. The interplay between these 2 organs is maintains homeostasis in the body. This article examines the hormones produced by both the hypothalamus and the pituitary gland and their functions, regulatory mechanisms, and physiologic effects.
Hypothalamic hormones
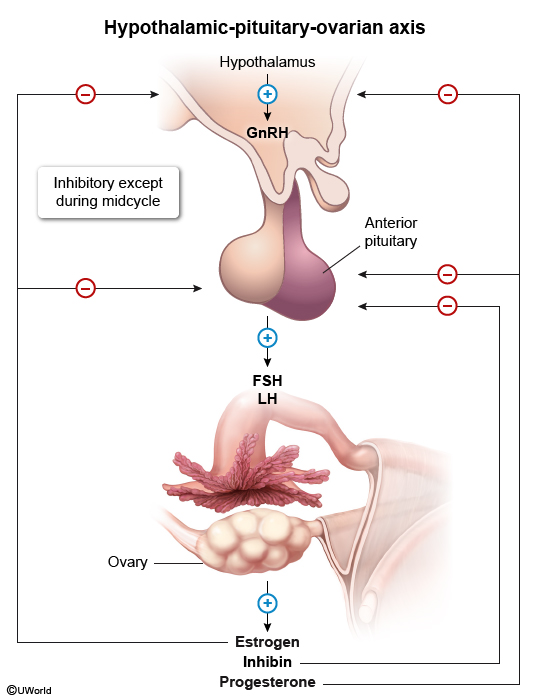
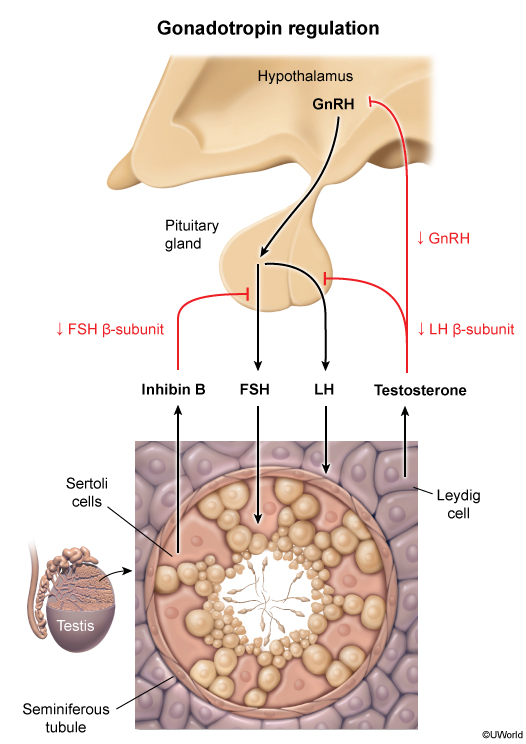
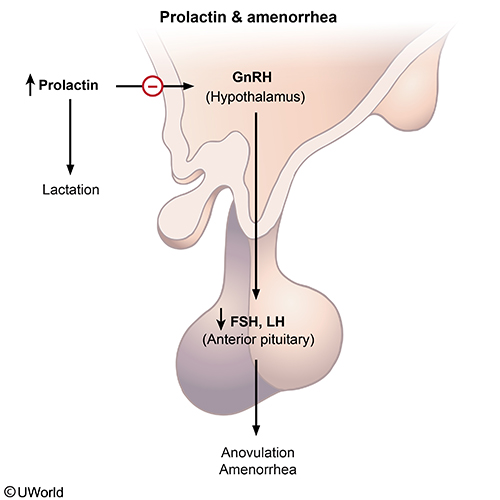
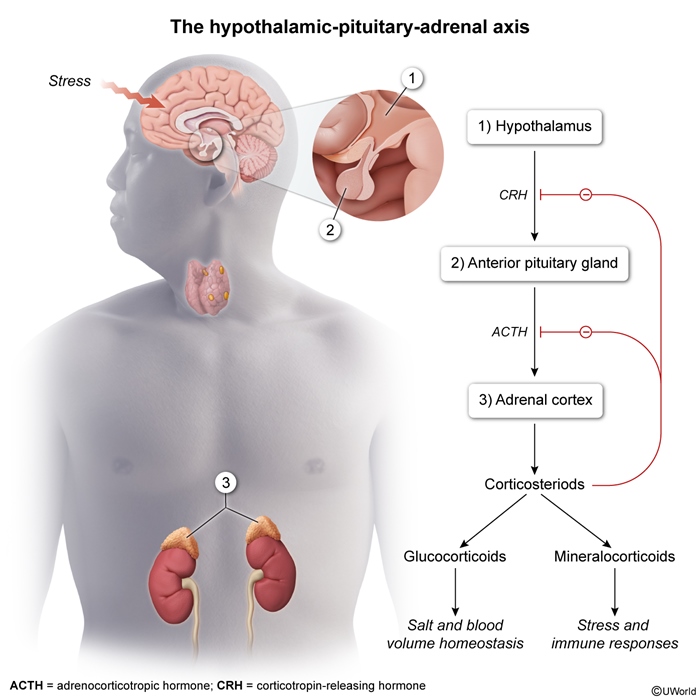
The hypothalamus produces releasing and inhibiting hormones that control the secretion of hormones from the anterior pituitary. These hormones help regulate a variety of bodily functions, including reproduction, stress response, and metabolism.
Continue Learning with UWorld
Get the full Hypothalamic-Pituitary Hormones article plus rich visuals, real-world cases, and in-depth insights from medical experts, all available through the UWorld Medical Library.
Unlock Full AccessFigures