Insulin Therapy In Diabetes Mellitus Management
Article Sections
Introduction
This article provides an overview of insulin therapy in diabetes mellitus (DM), including indications for insulin use, pharmacology, and administration.
Physiology of insulin
Insulin, a polypeptide hormone synthesized by pancreatic beta cells, is released in response to elevated glucose levels (Figure 1). It is formed through a multistep process involving the following (Figure 2):
- Insulin mRNA codes for preproinsulin, a larger precursor molecule that begins with a hydrophobic N-terminal signal peptide.
- The signal sequence guides preproinsulin to the rough endoplasmic reticulum (RER) during translation, where it is cleaved to yield proinsulin.
- Proinsulin undergoes further protein folding and disulfide bond formation in the RER.
- Proinsulin is then transported to the Golgi apparatus and packed with endopeptidases into secretory granules.
- Endopeptidases cleave proinsulin into insulin
Continue Learning with UWorld
Get the full Insulin Therapy In Diabetes Mellitus Management article plus rich visuals, real-world cases, and in-depth insights from medical experts, all available through the UWorld Medical Library.
Unlock Full AccessFigures
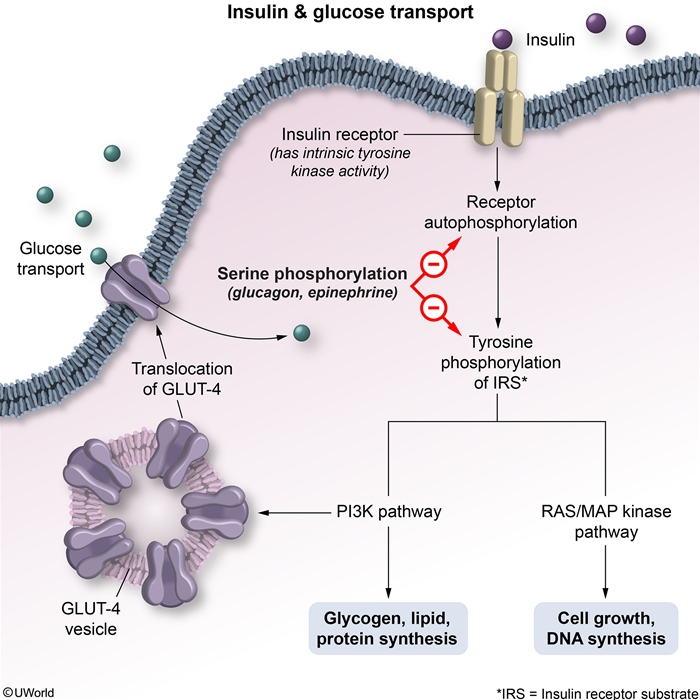
Figure 1
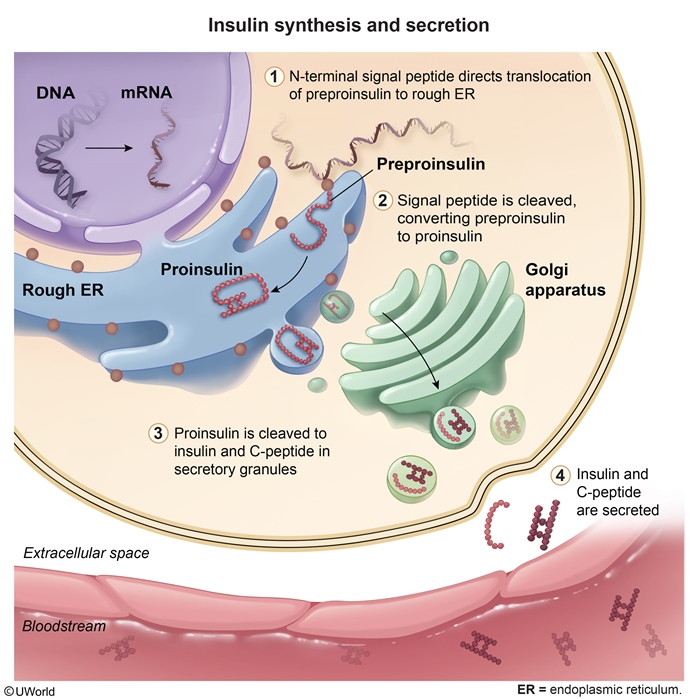
Figure 2
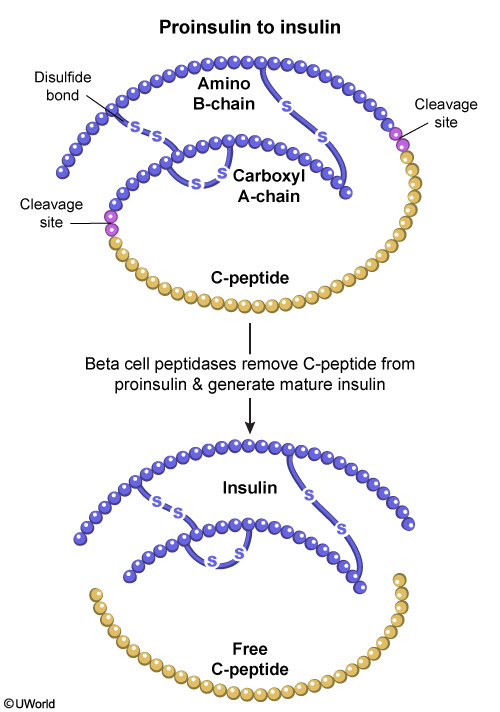
Figure 3
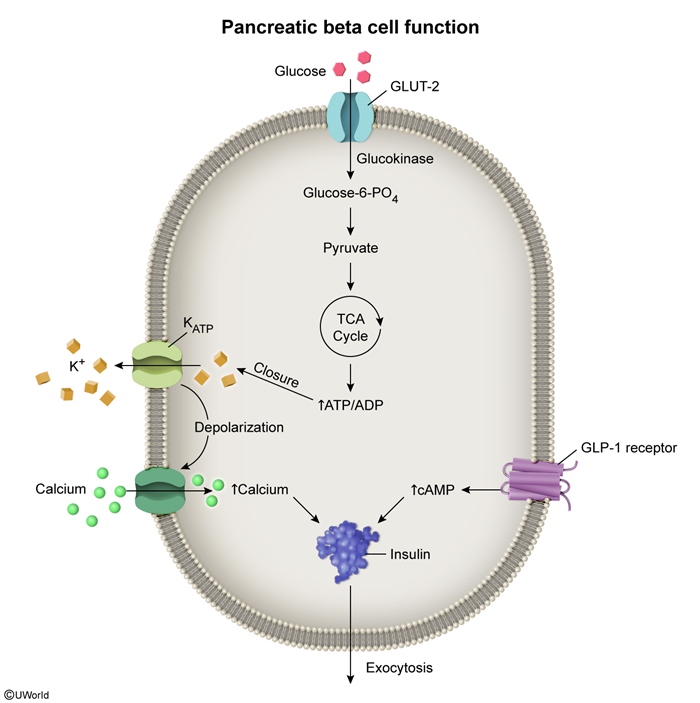
Figure 4
Tables
Table 1
Table 2