Adrenal Gland Anatomy And Physiology
Article Sections
Introduction
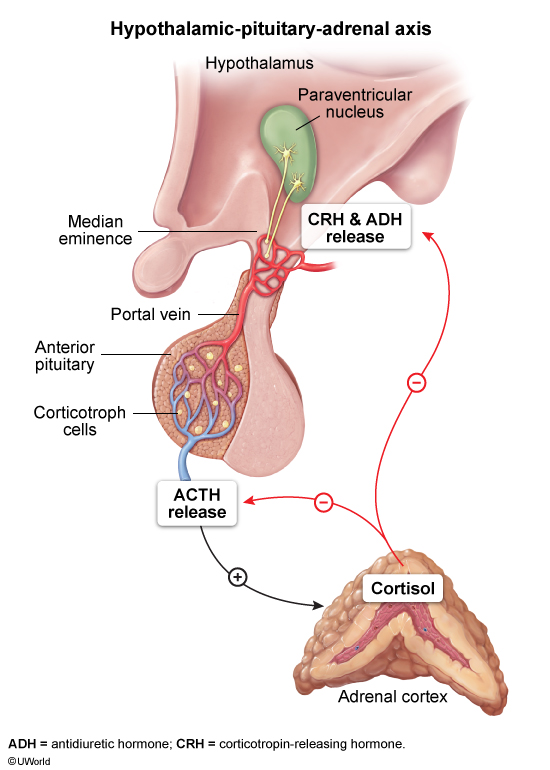
The adrenal glands are small, triangle-shaped endocrine organs that are located on top of each kidney that play a crucial role in metabolism, fluid and electrolyte balance, and stress response modulation. This article focuses on normal adrenal function. Pathologic adrenal conditions are discussed in detail in separate articles.
Anatomy
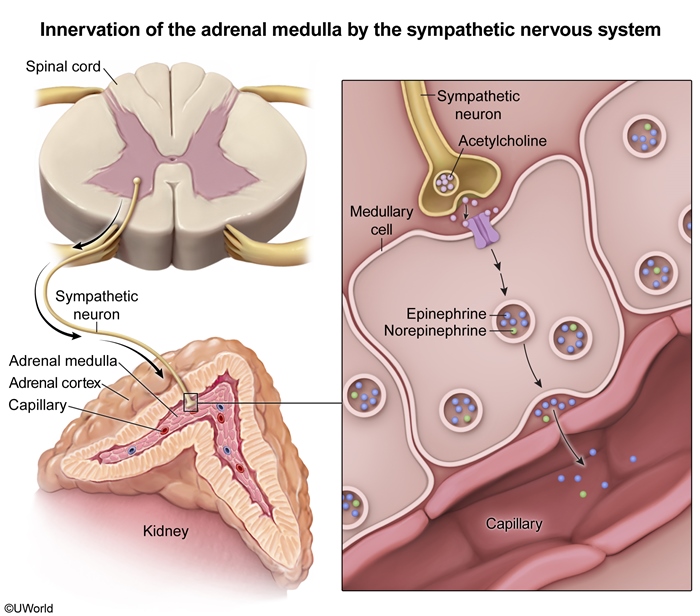
The adrenal glands are bilateral structures each weighing about 4-6 g in adults. They are composed of 2 distinct regions: the adrenal cortex and the adrenal medulla.
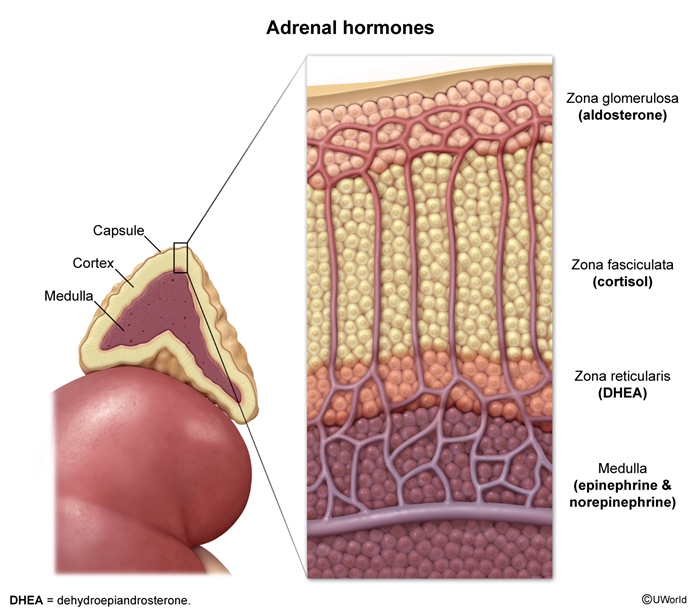
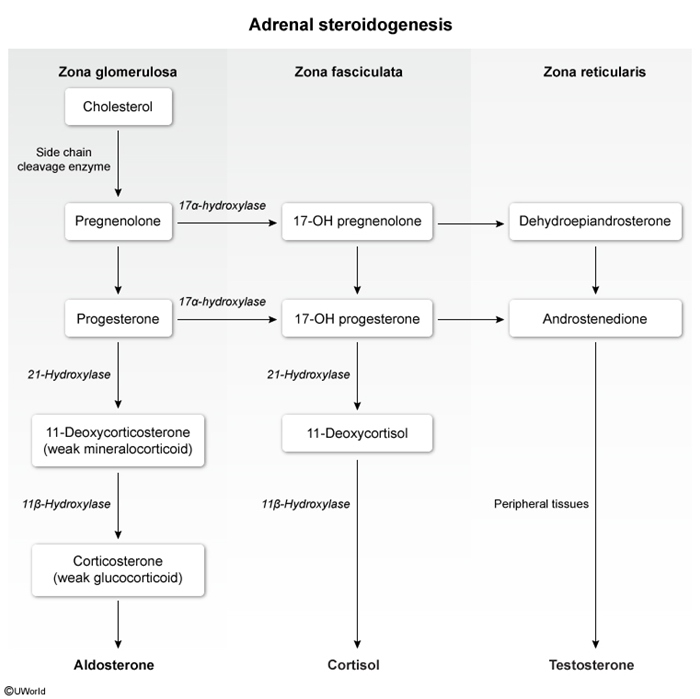
Adrenal cortexThe outer portion of the gland comprises about 80%-90% of its mass. It is further divided into 3 zones:
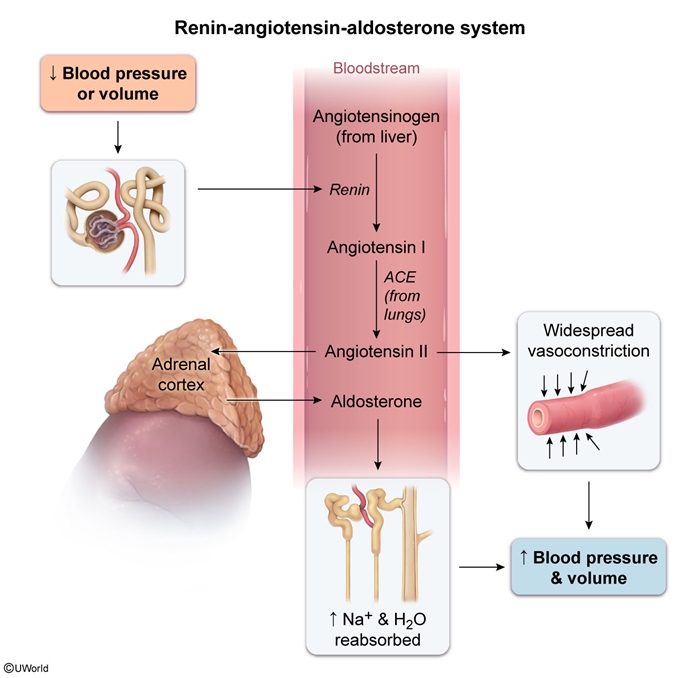
- Zona glomerulosa: The outermost layer, responsible for mineralocorticoid production (primarily aldosterone)
- Zona fasciculata: The middle and largest layer, responsible for glucocorticoid production (primarily cortisol)
Continue Learning with UWorld
Get the full Adrenal Gland Anatomy And Physiology article plus rich visuals, real-world cases, and in-depth insights from medical experts, all available through the UWorld Medical Library.
Unlock Full AccessFigures