Thyroiditis
Article Sections
Introduction
Thyroiditis represents a diverse group of disorders characterized by inflammation or infection of the thyroid gland. Symptoms in thyroiditis can be due to metabolic dysfunction (ie, hyperthyroidism, hypothyroidism) and can include pain and tenderness in the gland itself and compressive or infiltrative effects on the surrounding structures (eg, trachea, esophagus).
The classification of thyroiditis is variable (eg, based on etiologies, symptoms) and can be confusing. In this article, thyroiditis is discussed according to broad etiologic categories:
- Autoimmune (symptoms predominantly related to metabolic dysfunction)
- Chronic autoimmune (Hashimoto) thyroiditis
- Painless (silent) thyroiditis, postpartum thyroiditis
- Nonautoimmune inflammatory and infectious (ie, symptoms predominantly related to local pain and systemic inflammation)
- Subacute granulomatous thyroiditis
- Acute (suppurative) thyroiditis
- Miscellaneous
- Fibrosing (Riedel) thyroiditis (ie, symptoms primarily related to effects on surrounding organs)
Continue Learning with UWorld
Get the full Thyroiditis article plus rich visuals, real-world cases, and in-depth insights from medical experts, all available through the UWorld Medical Library.
Unlock Full AccessFigures
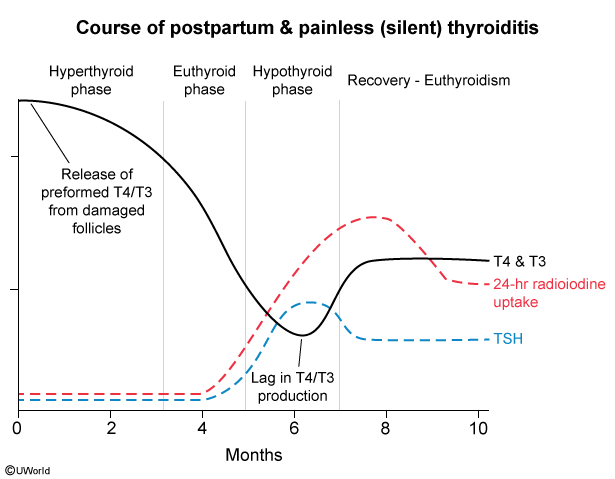
Figure 1
Images
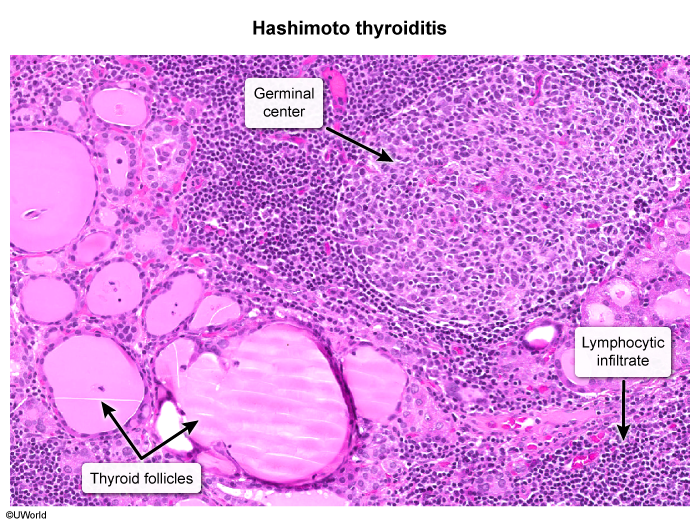
Image 1
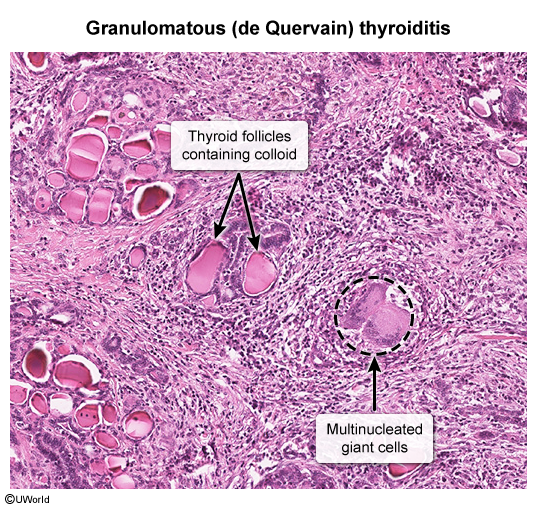
Image 2
Tables
Table 1