Diabetic Eye Complications
Article Sections
Introduction
The major complications associated with diabetes mellitus (DM) include the following:
Macrovascular complicationsThese affect larger blood vessels and include:
- coronary artery disease
- cerebrovascular disease
- peripheral artery disease
These complications are driven by accelerated atherosclerosis, plaque formation, and vascular occlusion, as well as effects of comorbid risk factors (eg, hypertension, dyslipidemia, obesity).
Microvascular complicationsThese involve damage to small blood vessels (ie, microangiopathic damage) and include:
- diabetic retinopathy (DR) of the eye
- diabetic nephropathy
- diabetic neuropathy
These complications are driven by chronic hyperglycemia-induced endothelial dysfunction.
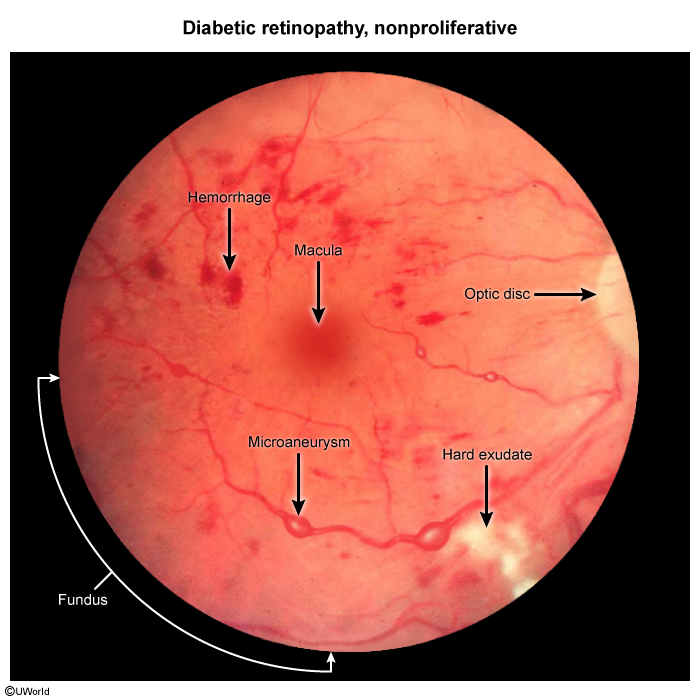
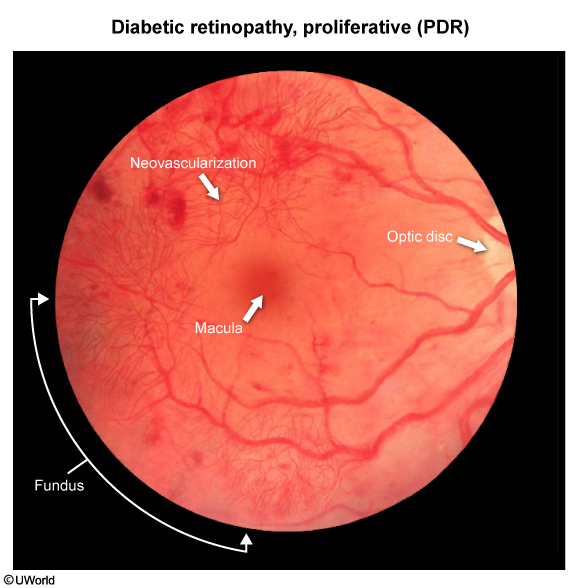
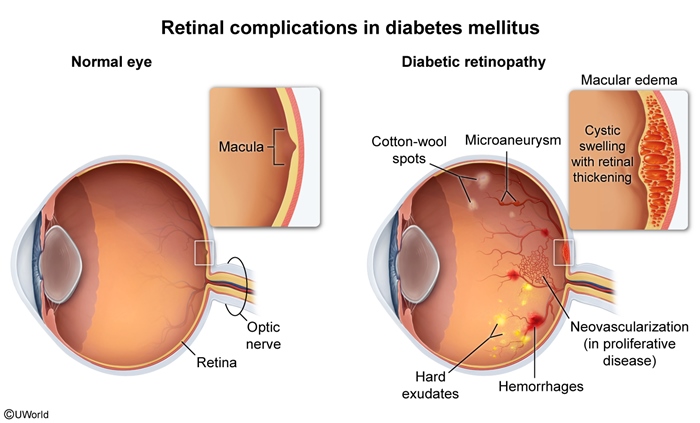
This article focuses on diabetic eye complications. Common eye complications (Table 1) in DM include DR (proliferative and nonproliferative), macular edema, and acute and subacute changes in vision due to osmotic lens changes. Cataracts and glaucoma are also seen with increased frequency in DM. Of note, DR (especially proliferative DR) and diabetic nephropathy share a similar pathophysiologic pathway; the presence of one of these conditions predicts the development of the other.
Continue Learning with UWorld
Get the full Diabetic Eye Complications article plus rich visuals, real-world cases, and in-depth insights from medical experts, all available through the UWorld Medical Library.
Unlock Full AccessFigures
Images