Precocious Puberty
Article Sections
Introduction
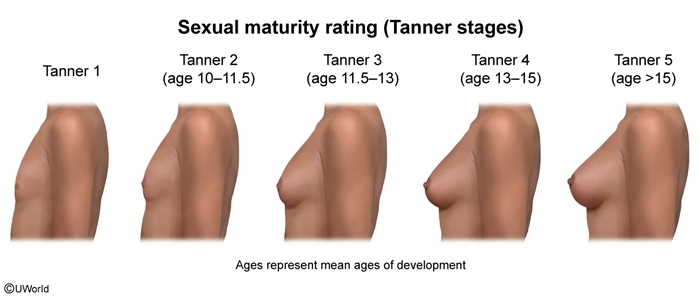
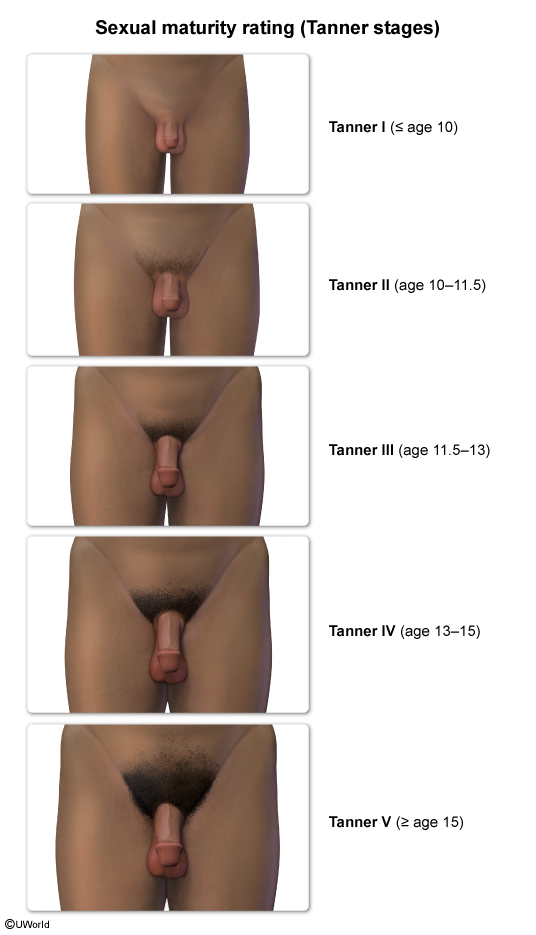
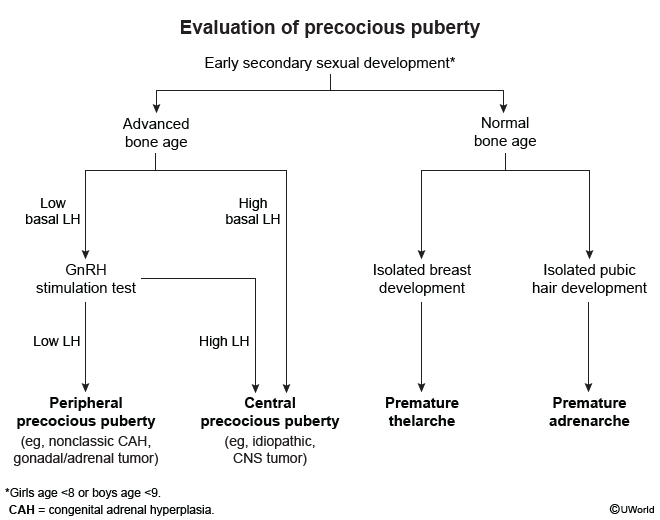
Precocious puberty is defined as the development of secondary sexual characteristics (eg, breasts, pubic hair) in girls age <8 or boys age <9. It can be categorized as central (gonadotropin-dependent) or peripheral (gonadotropin-independent). Benign variants can also occur and are characterized by nonprogressive, isolated secondary sexual characteristics.
Physiology
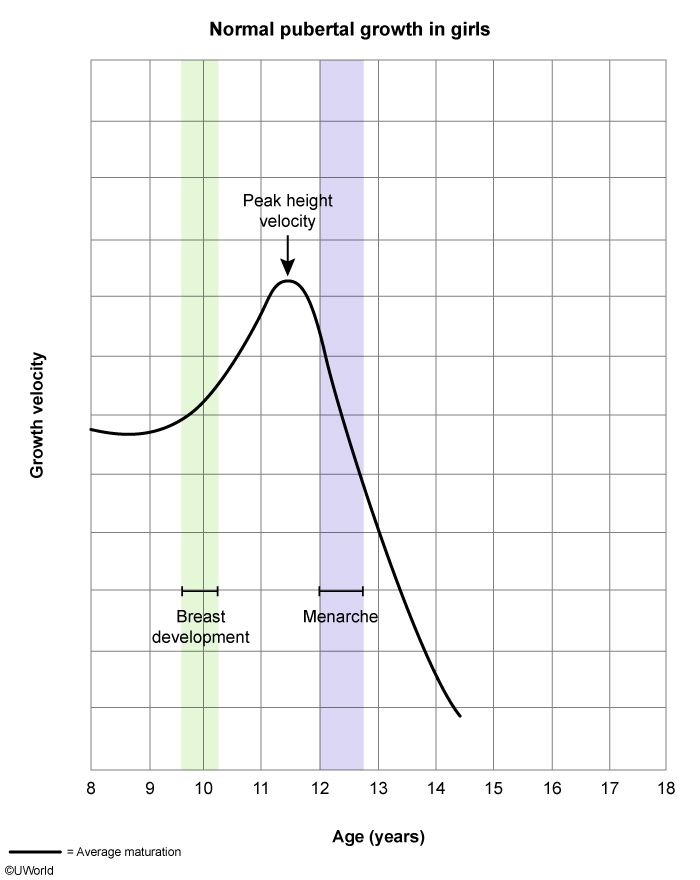
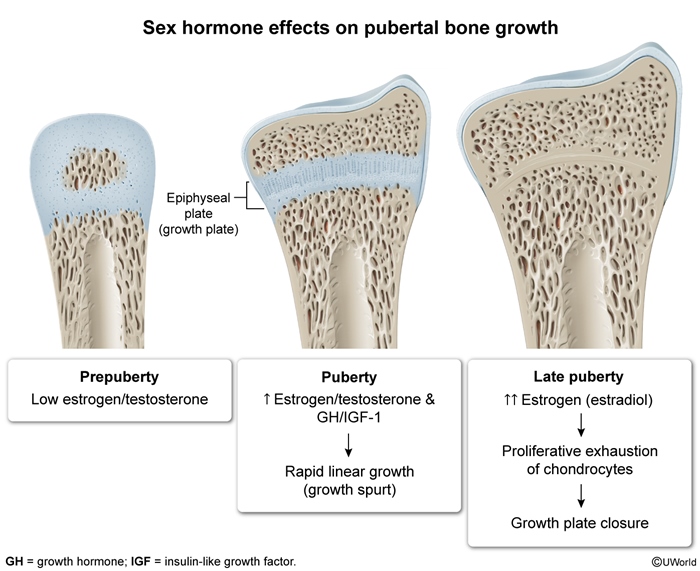
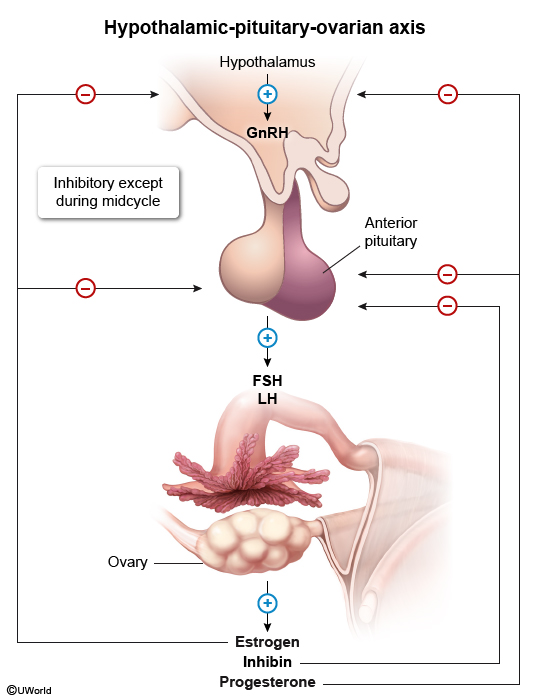
Normal pubertal development manifests with secondary sexual characteristics at age ≥8 for girls and at ≥9 in boys and is due to pulsatile GnRH secretion from the hypothalamus. This stimulates LH and FSH release from the pituitary, which triggers ovarian estrogen production in girls and testicular testosterone production in boys. Adrenal androgen production, which is not stimulated by GnRH, occurs in both sexes.
Secondary sexual characteristics are driven by these hormones as follows:
- Estrogens stimulate breast development (thelarche [
Continue Learning with UWorld
Get the full Precocious Puberty article plus rich visuals, real-world cases, and in-depth insights from medical experts, all available through the UWorld Medical Library.
Unlock Full AccessFigures