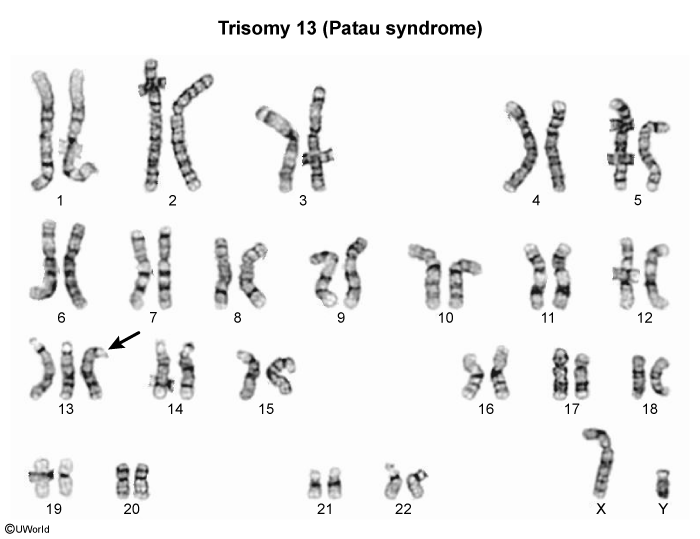
Trisomy 13 (Patau Syndrome)
Article Sections
Introduction
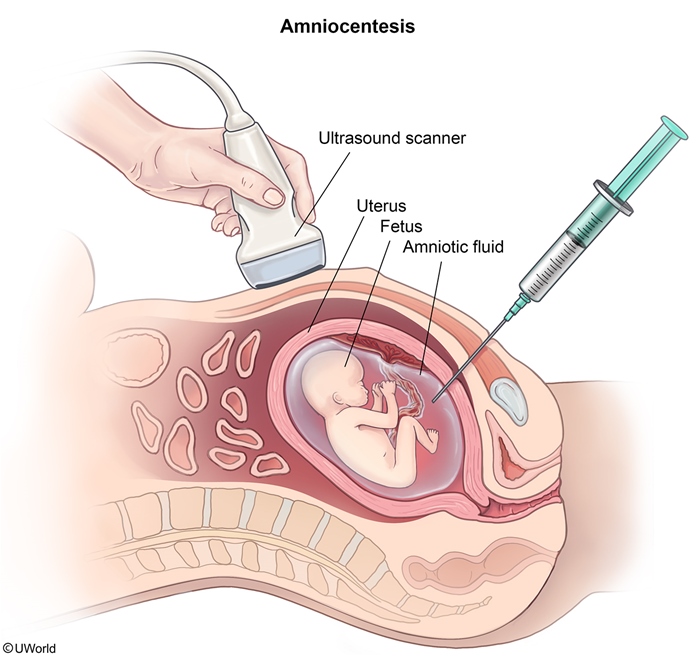
Trisomy 13 (Patau syndrome) is characterized by the presence of 3 copies of chromosome 13. It is the most severe and least common (ie, 1 in 7,000 live births) of the trisomy disorders (eg, 21, 18, 13). It is associated with severe congenital anomalies and a high mortality rate.
Pathogenesis
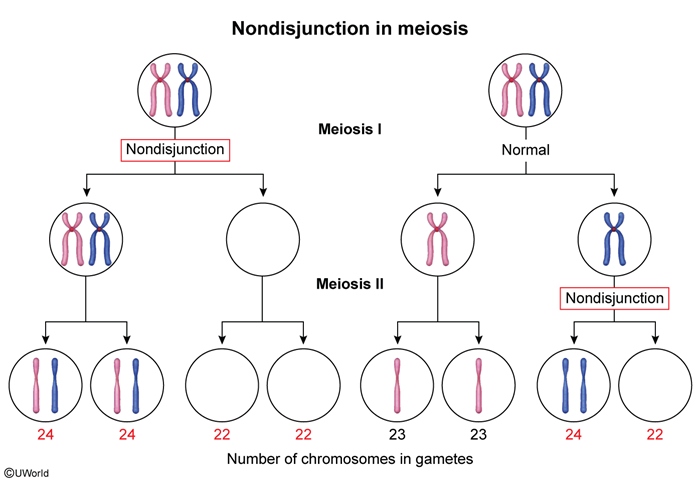
Normally, homologous chromosomes separate during meiosis, resulting in 4 gametes with 1 copy of each chromosome in each gamete. However, in meiotic nondisjunction, a pair of homologous chromosomes fails to separate, resulting in 4 gametes with 0, 1, or 2 copies of the chromosome in each gamete (Figure 1). If a gamete with 2 copies of the chromosome is fertilized by a gamete with 1 copy of the chromosome, then the zygote has 3 copies of the chromosome. Maternal
Continue Learning with UWorld
Get the full Trisomy 13 (Patau Syndrome) article plus rich visuals, real-world cases, and in-depth insights from medical experts, all available through the UWorld Medical Library.
Unlock Full AccessFigures
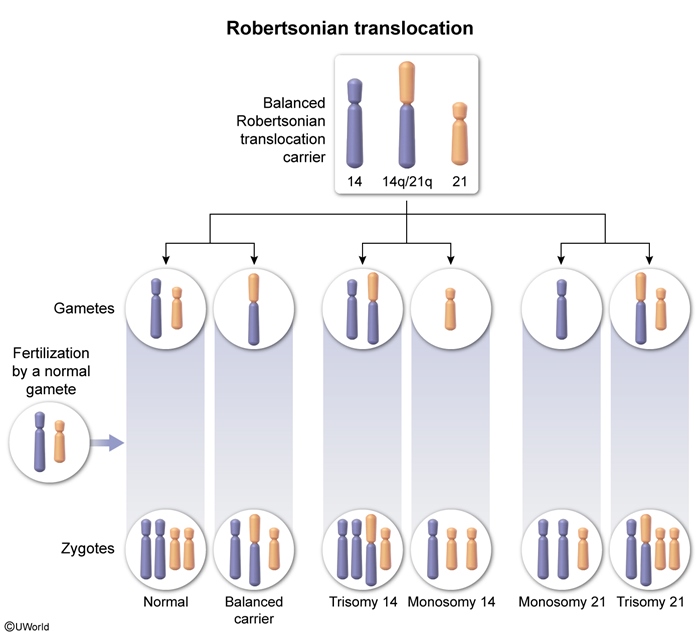
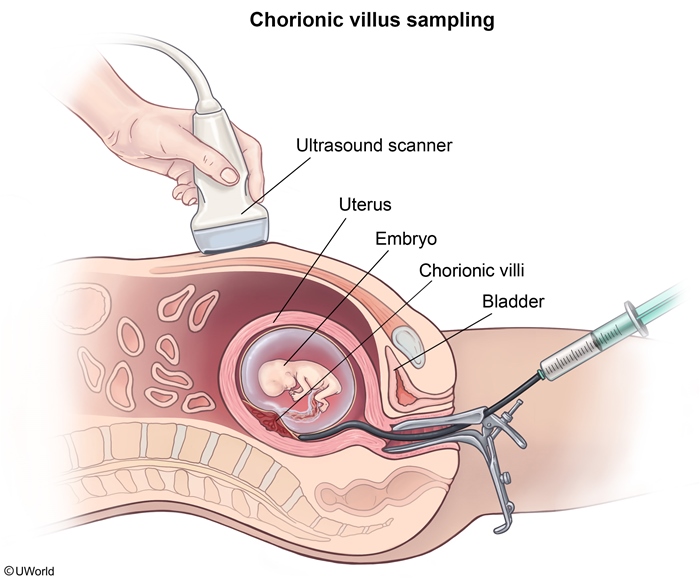
Images