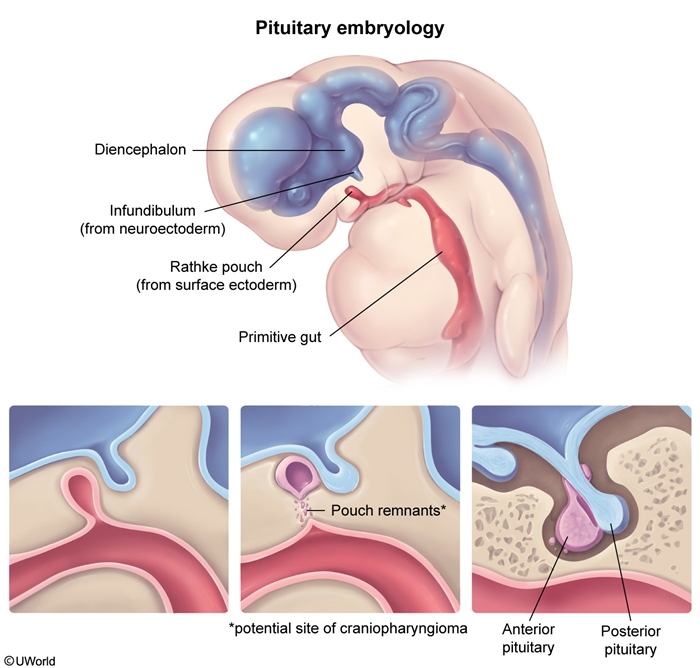
Embryologic Derivatives: Gastrulation, Neurulation, And The Primary Germ Layers
Article Sections
Introduction
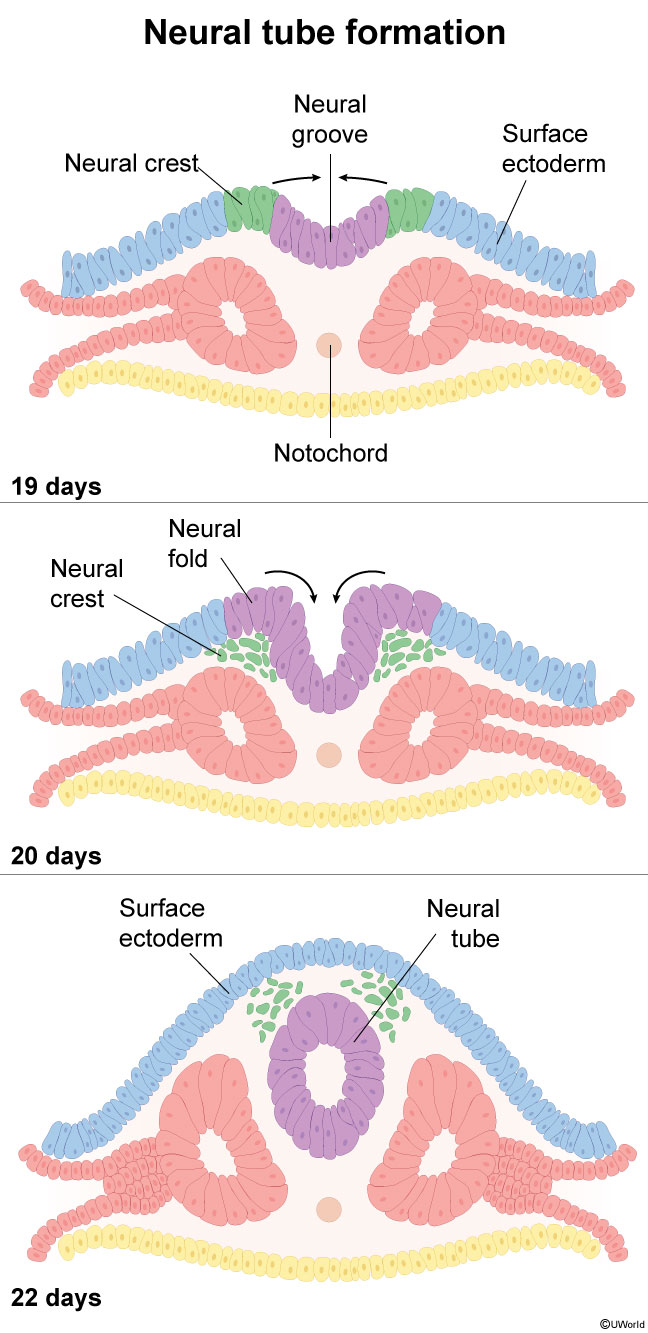
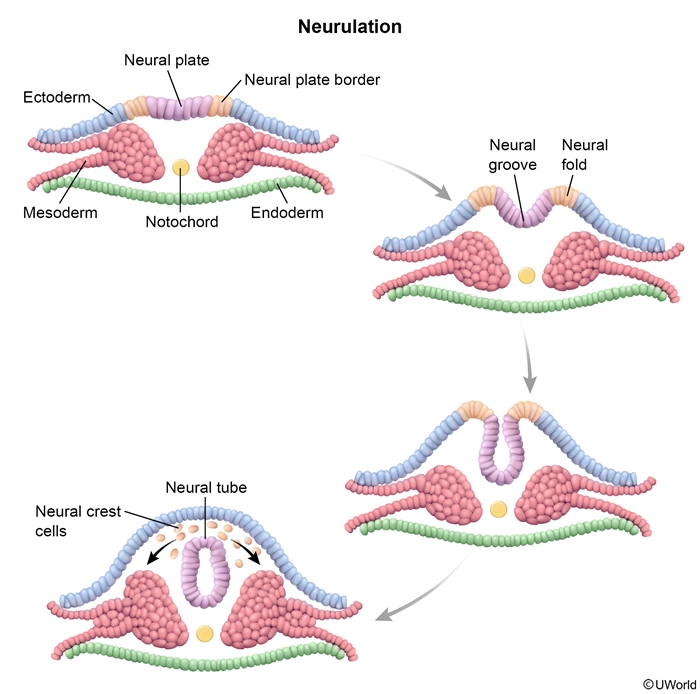
The embryonic stage of fetal development, which occurs 3-8 weeks after fertilization (ie, weeks 5-10 of gestation), involves the differentiation of specialized tissues and organs from a single fertilized egg. Key to this process are gastrulation and neurulation, which lead to the formation of the 3 primary germ layers—ectoderm, mesoderm, and endoderm—and the subsequent development of the central nervous system.
Gastrulation
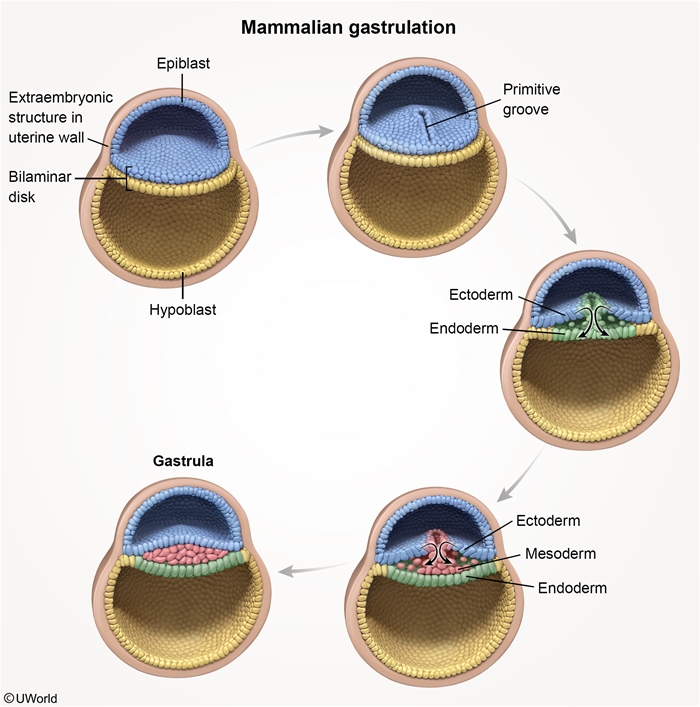
Gastrulation (Figure 1) marks the beginning of the embryonic stage of development. It is the process by which the blastocyst, a hollow ball of cells, reorganizes from a bilaminar disc into a trilaminar (3-layered) disc (ectoderm, mesoderm, endoderm), from which all tissues and organs are derived. This process occurs during week 3 postfertilization and begins with the formation of the
Continue Learning with UWorld
Get the full Embryologic Derivatives: Gastrulation, Neurulation, And The Primary Germ Layers article plus rich visuals, real-world cases, and in-depth insights from medical experts, all available through the UWorld Medical Library.
Unlock Full AccessFigures