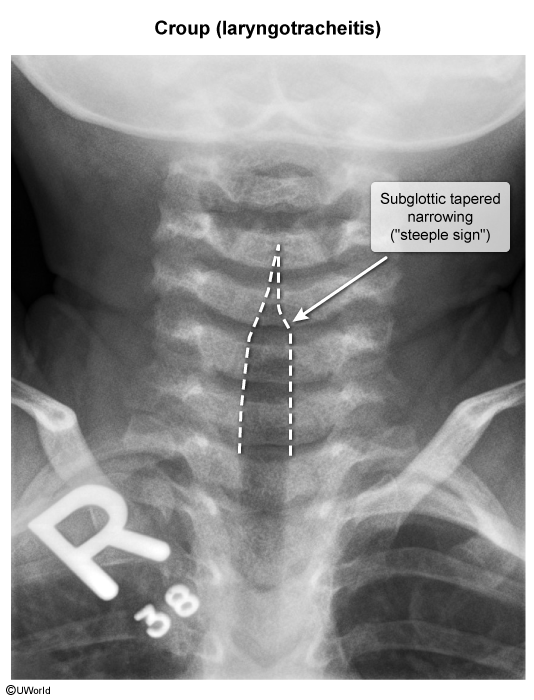
Croup
Article Sections
Introduction
Croup, also known as laryngotracheitis, is a common viral illness characterized by upper airway inflammation and obstruction of the larynx and proximal trachea. It typically presents in young children (peaking between age 6 months to 3 years) with a characteristic barking cough and inspiratory stridor.
Pathophysiology and risk factors
Parainfluenza virus is the most common cause of croup, although other viruses (eg, influenza virus, coronavirus) may present similarly. Parainfluenza virus is transmitted through infected respiratory secretions via direct contact (eg, hands, fomites) or inhalation of large droplets (eg, cough, sneeze). On exposure, the virus initially infects the nasopharynx, causing 1-2 days of fever and prodromal upper respiratory tract symptoms (eg, nasal congestion) before spreading to the larynx (particularly the subglottic portion) and trachea, causing subglottic edema and narrowing.
Continue Learning with UWorld
Get the full Croup article plus rich visuals, real-world cases, and in-depth insights from medical experts, all available through the UWorld Medical Library.
Unlock Full AccessFigures
Images