Peritonsillar Abscess
Article Sections
Introduction
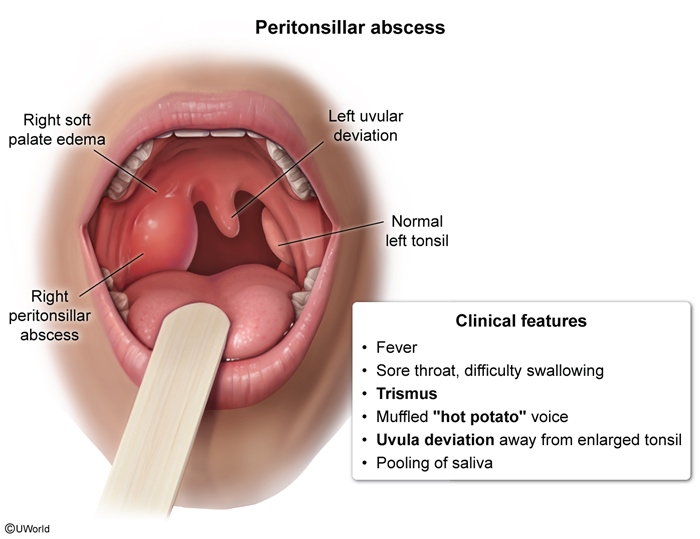
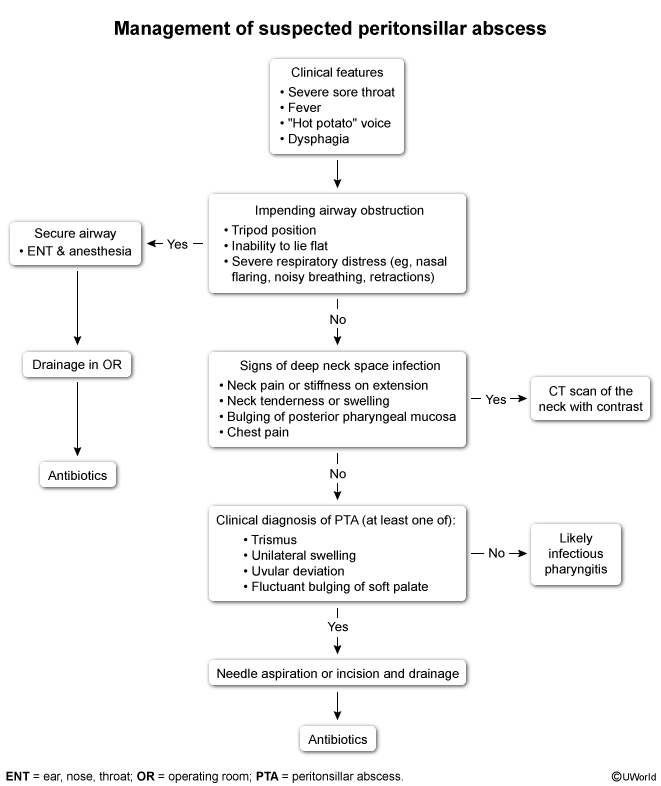
Peritonsillar abscess (PTA) is a localized collection of pus in the peritonsillar space between the tonsil and pharyngeal muscles. It typically occurs as a complication of tonsillitis. Symptoms include fever, severe sore throat, trismus, and a muffled voice. Unilateral tonsillar/palatal enlargement with uvular deviation to the unaffected side is the classic finding on examination. Treatment involves abscess drainage and antibiotic therapy.
Pathophysiology
PTA occurs most commonly in adolescents and young adults following an episode of acute tonsillitis. There are 2 proposed mechanisms of abscess formation:
- Infection begins within the tonsil, then bacteria spread into the loose connective tissue of the peritonsillar space. This progresses to peritonsillar cellulitis and eventually pus collects to form an abscess.
- Tonsillar inflammation causes obstruction of salivary glands located superior to the tonsils. Gland obstruction promotes bacterial overgrowth, which then infects the peritonsillar space and ultimately results in an abscess.
Continue Learning with UWorld
Get the full Peritonsillar Abscess article plus rich visuals, real-world cases, and in-depth insights from medical experts, all available through the UWorld Medical Library.
Unlock Full AccessFigures