Hearing Loss
Article Sections
Introduction
Hearing loss impacts almost 20% of adults and can have a profoundly morbid effect on patients and their families. It can result from a wide variety of etiologies and is commonly classified as conductive or sensorineural.
Physiology and pathophysiology
The pathway of sound transmission is as follows (Figure 1):
- Sound waves are collected by the external ear, then travel through the external auditory canal (EAC).
- Sound waves vibrate the tympanic membrane (Figure 2).
- Vibrations are amplified by the ossicular chain (Figure 3) (ie, malleus, incus, stapes) and transferred to the oval window of the cochlea.
- Vibration of the oval window causes vibration of the basilar membrane, which causes bending of the hair cell cilia against the tectorial membrane (Figure 4
Continue Learning with UWorld
Get the full Hearing Loss article plus rich visuals, real-world cases, and in-depth insights from medical experts, all available through the UWorld Medical Library.
Unlock Full AccessFigures
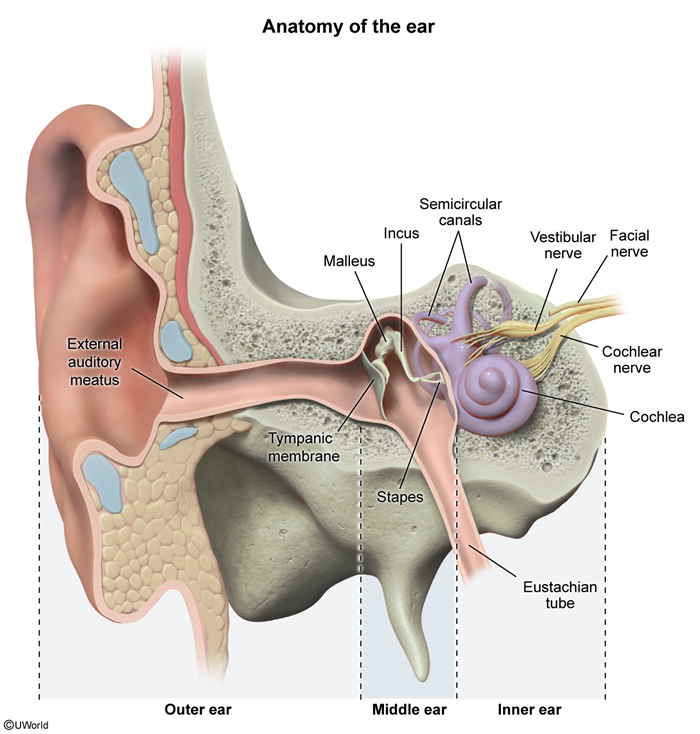
Figure 1
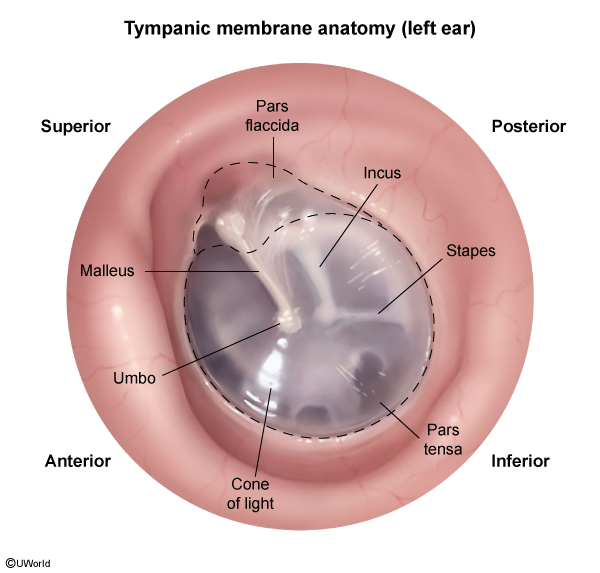
Figure 2
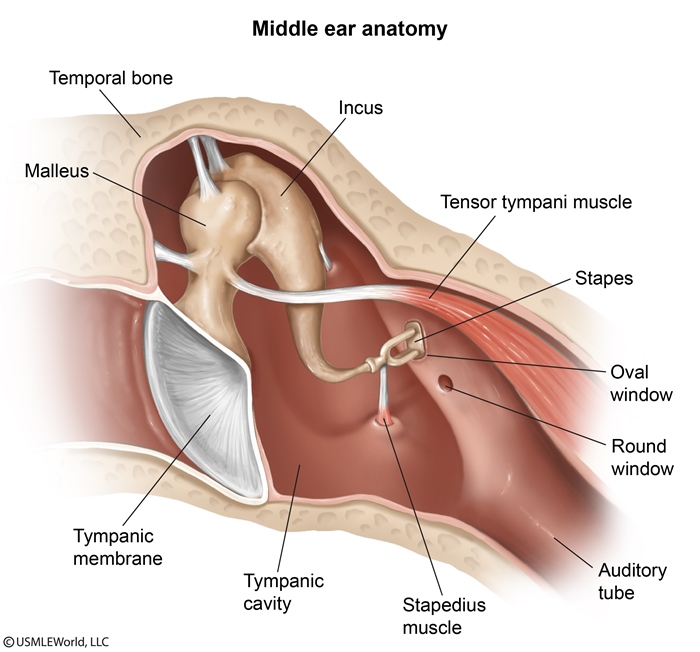
Figure 3
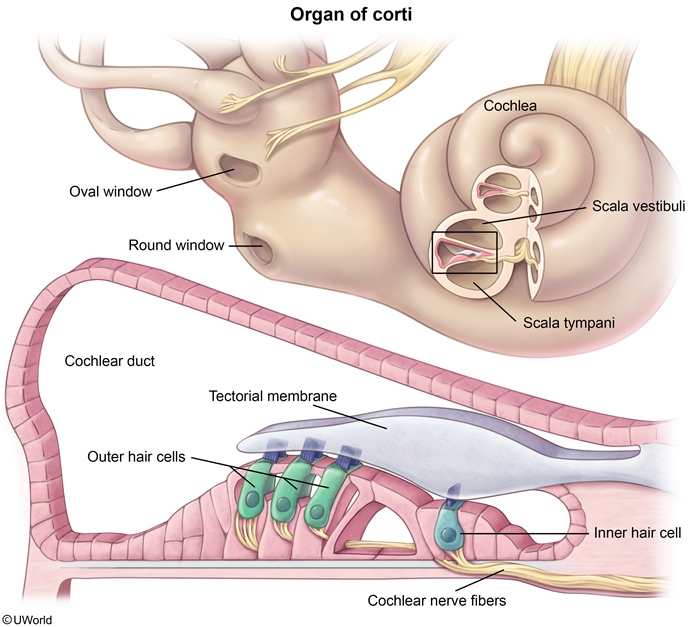
Figure 4
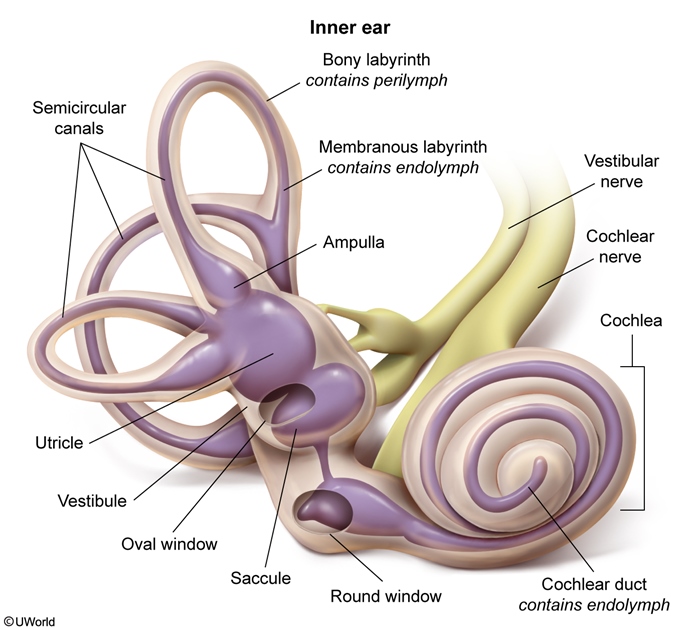
Figure 5
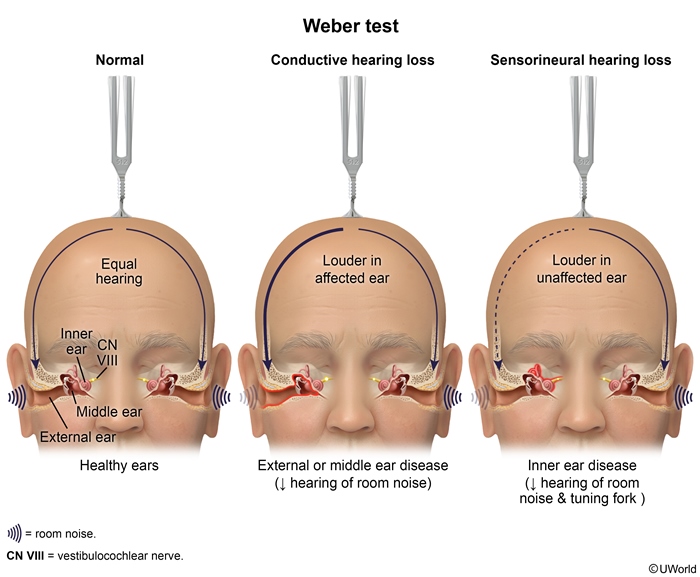
Figure 6