Cavernous Sinus Thrombosis
Article Sections
Introduction
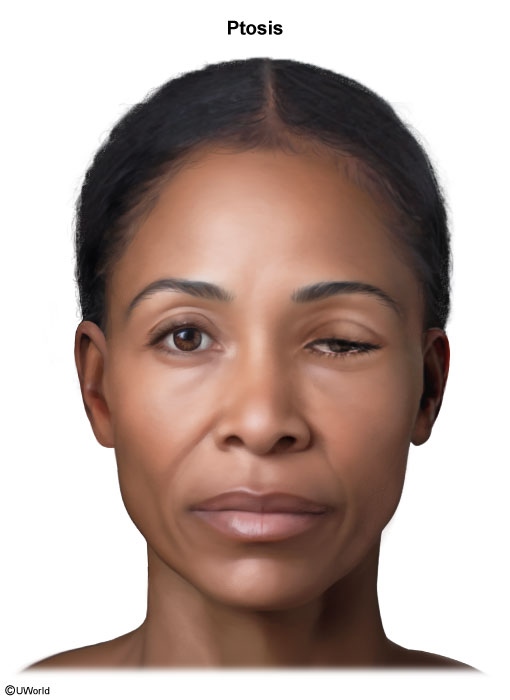
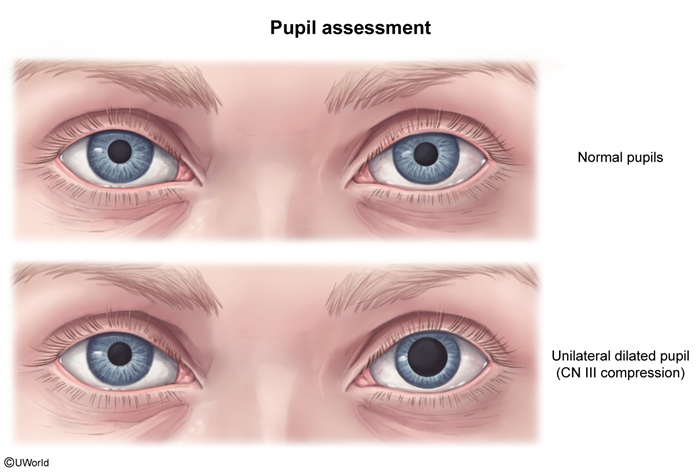
Cavernous sinus thrombosis is a rare but life-threatening condition characterized by thrombus formation within the cavernous sinus, a portion of the dural venous network of the brain. It most commonly arises due to the retrograde spread of infection from the face, sinuses, or orbit. Clinical presentation includes headache, fever, periorbital edema and pain, and varying degrees of cranial nerve abnormalities (eg, ophthalmoplegia).
Anatomy
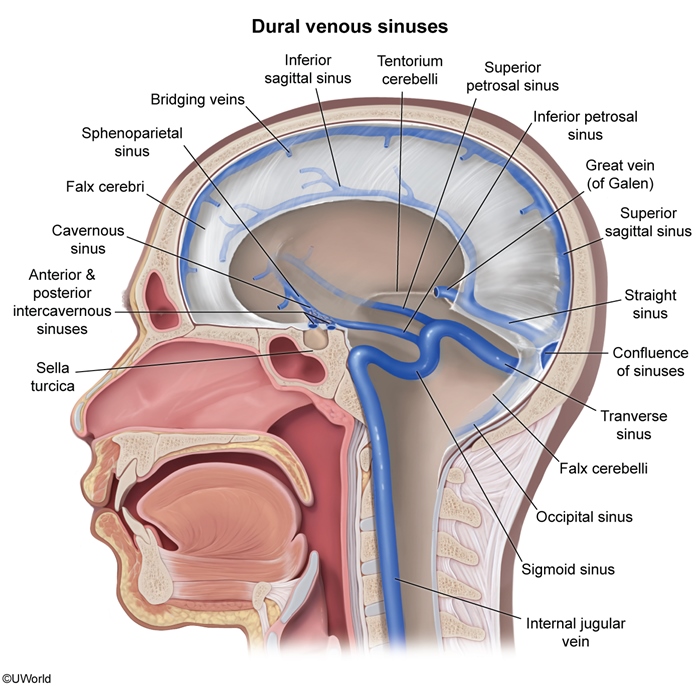
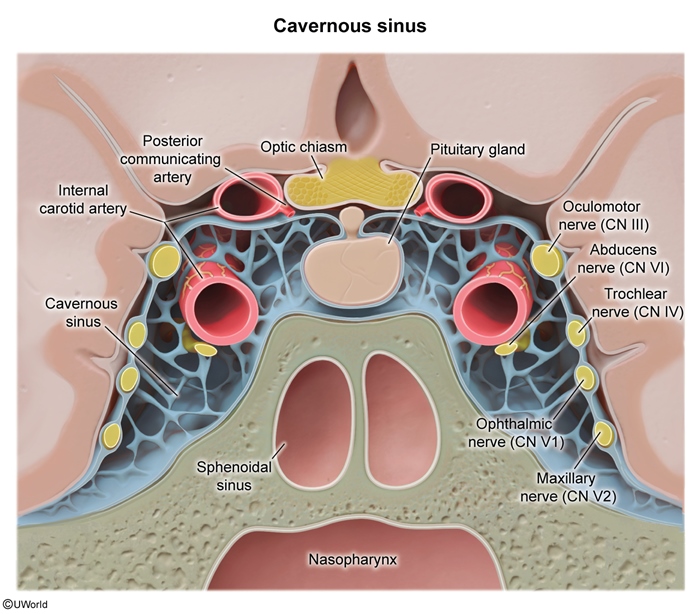
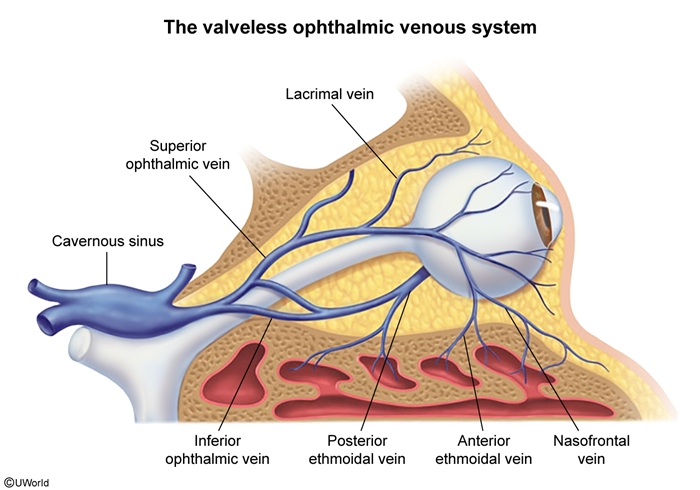
The dural sinuses are a network of veins that drain blood from the brain into the internal jugular vein (Figure 1). The cavernous sinus lies on each side of the sella turcica posterior to the optic chiasm (Figure 2) and is unique among the dural sinuses for several reasons. It is the only dural sinus that receives venous blood not only from the cerebral veins, but also from the facial veins (via the superior and inferior ophthalmic veins) (
Continue Learning with UWorld
Get the full Cavernous Sinus Thrombosis article plus rich visuals, real-world cases, and in-depth insights from medical experts, all available through the UWorld Medical Library.
Unlock Full AccessFigures