Acute Rhinosinusitis
Article Sections
Introduction
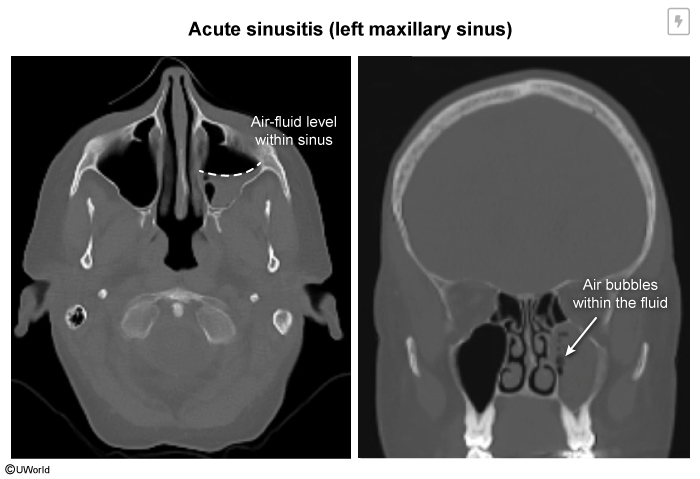
Acute sinusitis, also referred to as acute rhinosinusitis, is an inflammatory condition of the paranasal sinuses. It is usually precipitated by a viral upper respiratory infection (URI), which leads to subsequent infection of the sinuses. This leads to nasal congestion, facial pressure/pain, and rhinorrhea. Most cases have a viral etiology, but acute bacterial sinusitis can usually be differentiated based on clinical presentation.
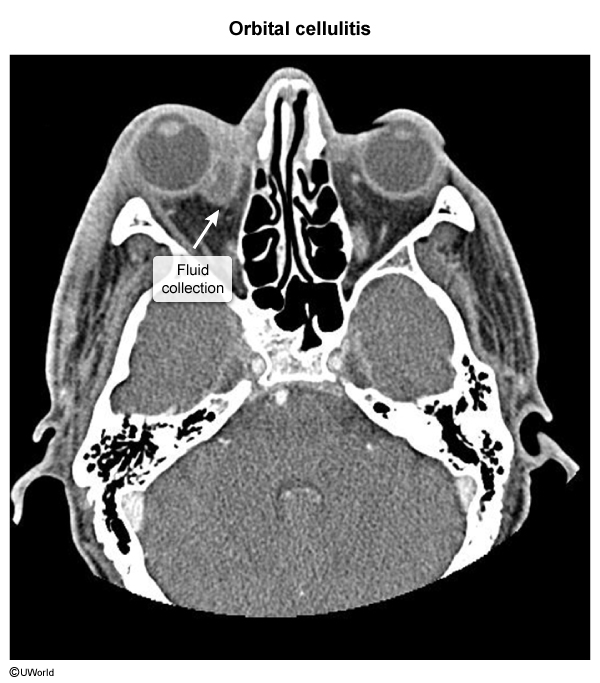
Acute sinusitis can also be caused by invasive fungal species (which is discussed in a separate article). Sinusitis lasting at least 12 weeks is considered chronic (discussed in a separate article).
Anatomy and pathophysiology
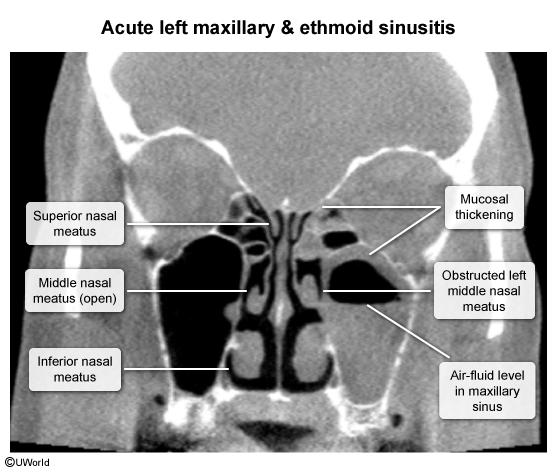
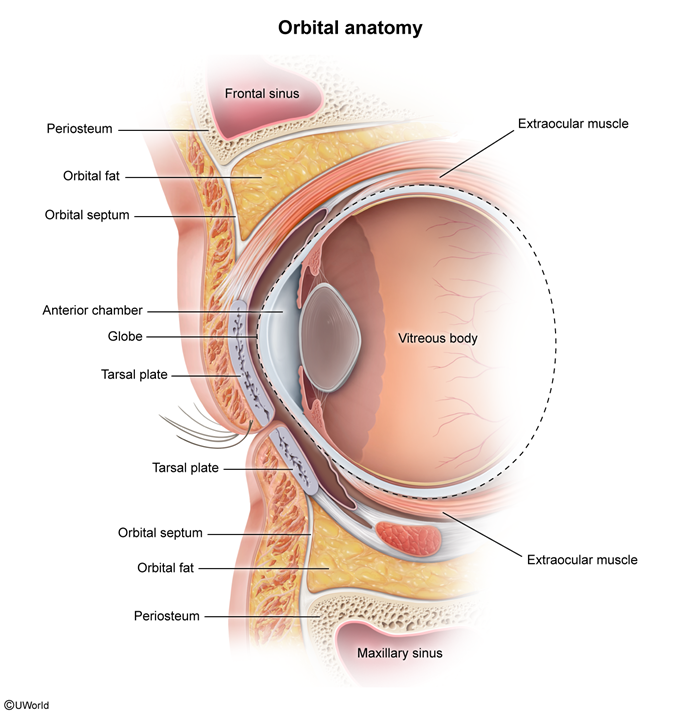
The paranasal sinuses are paired, air-filled spaces adjacent to the nose and lined with ciliated epithelium. They secrete mucus that is cleared by the cilia through openings from the sinuses into the nasal cavity. There are 3 openings (meatus) into the nasal cavity, opening just lateral to each of the nasal conchae (ie, superior, middle, and inferior) (
Continue Learning with UWorld
Get the full Acute Rhinosinusitis article plus rich visuals, real-world cases, and in-depth insights from medical experts, all available through the UWorld Medical Library.
Unlock Full AccessFigures
Images