Herpangina
Article Sections
Introduction
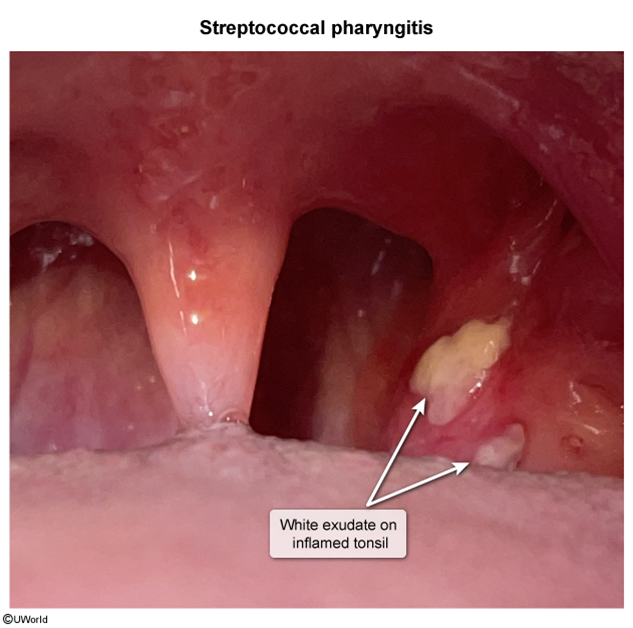
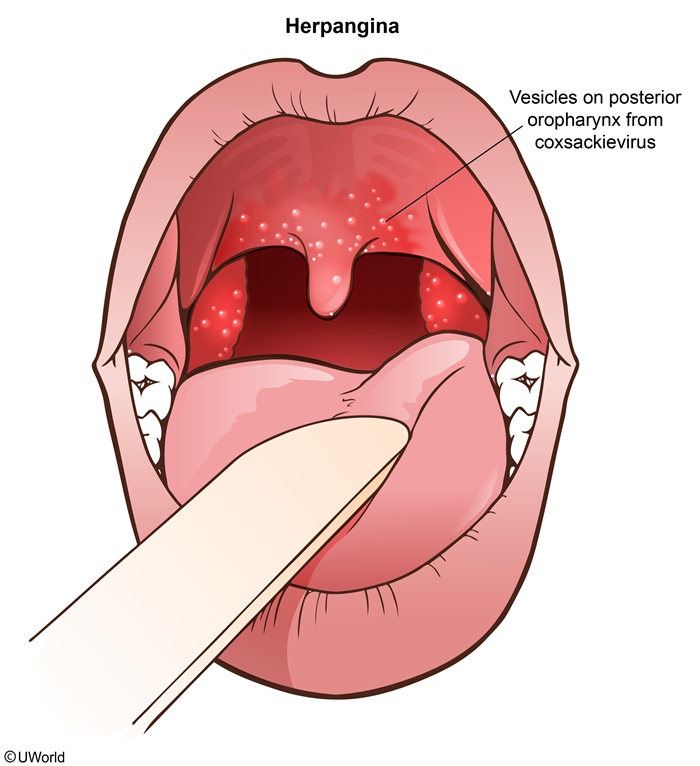
Herpangina is a benign, self-limited viral infection characterized by abrupt-onset high fever and a painful papular, vesicular, or ulcerative oral enanthem. It is caused by enteroviruses, most commonly coxsackievirus A. Herpangina primarily affects children age 3-10 in the late summer and early fall.
Pathophysiology and risk factors
Transmission of enteroviruses occurs through the ingestion of virus that is shed from the gastrointestinal or respiratory tracts of infected individuals. Once ingested, the virus replicates in the lymphoid tissues of the gastrointestinal and respiratory submucosa before spreading to the regional lymph nodes, leading to widespread viremia that can affect other organ systems (eg, myocarditis, aseptic meningitis).
Therefore, risk factors for herpangina include attendance in day care centers or schools, poor hygiene, and immune dysfunction.
Continue Learning with UWorld
Get the full Herpangina article plus rich visuals, real-world cases, and in-depth insights from medical experts, all available through the UWorld Medical Library.
Unlock Full AccessFigures
Images