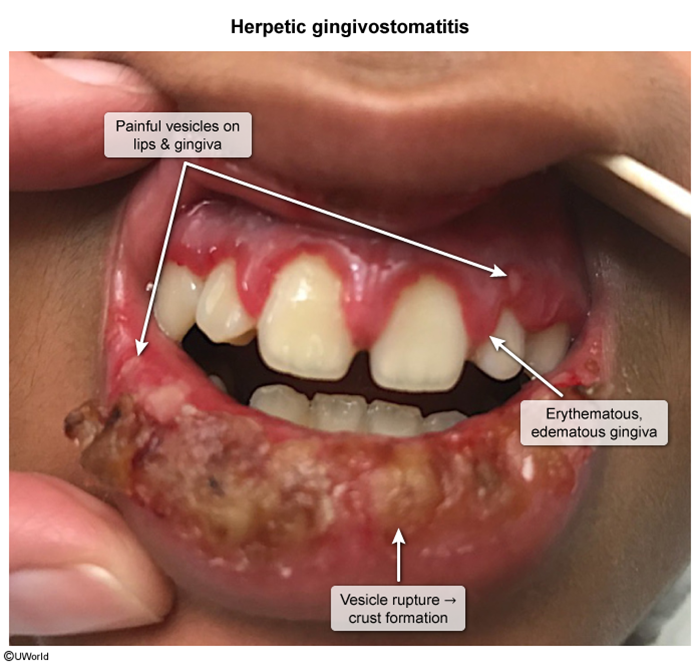
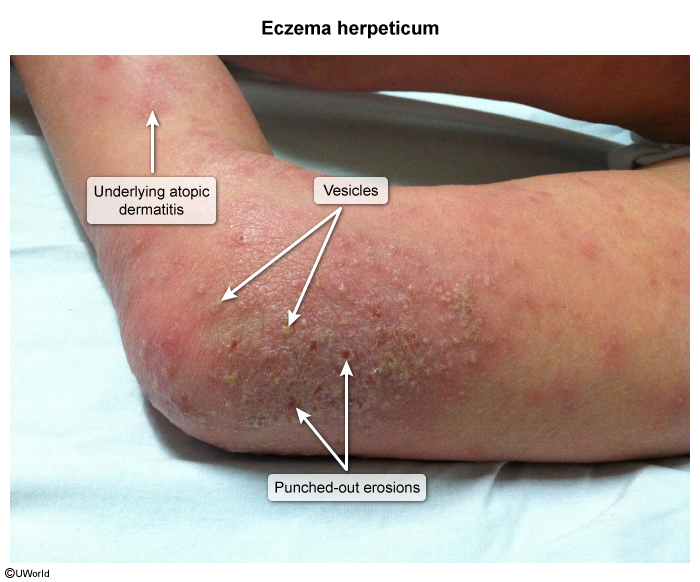
Hand-Foot-And-Mouth Disease
Article Sections
Introduction
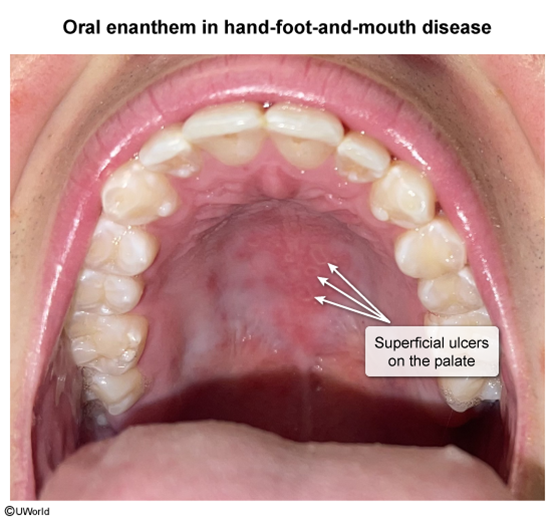
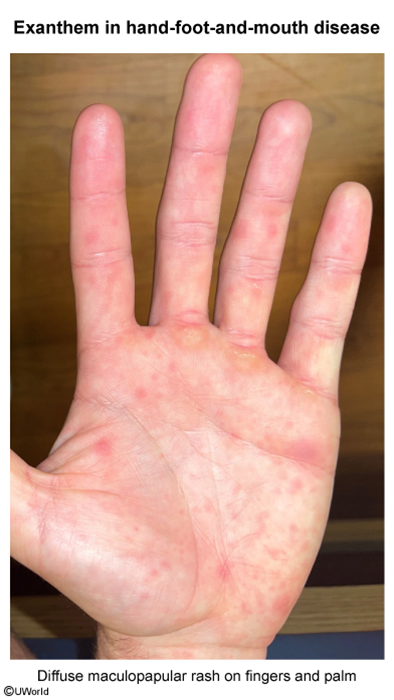
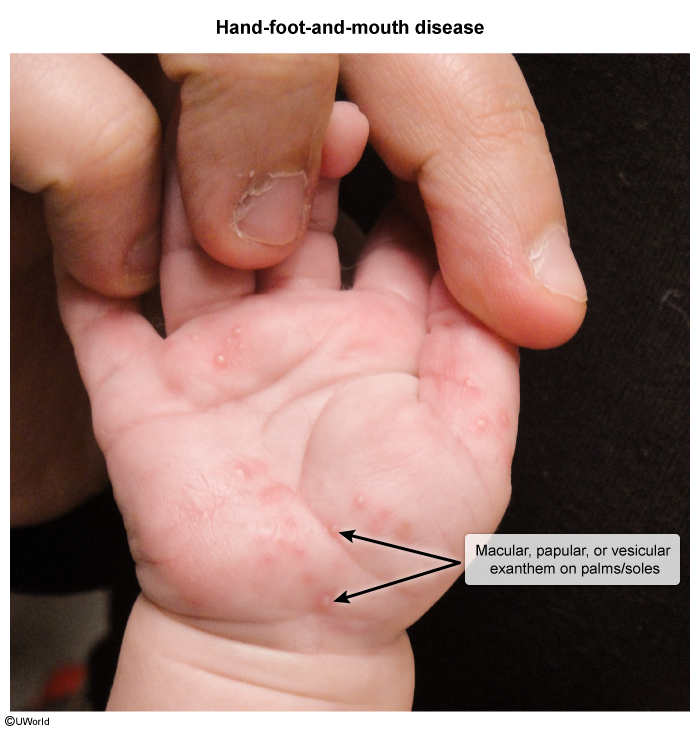
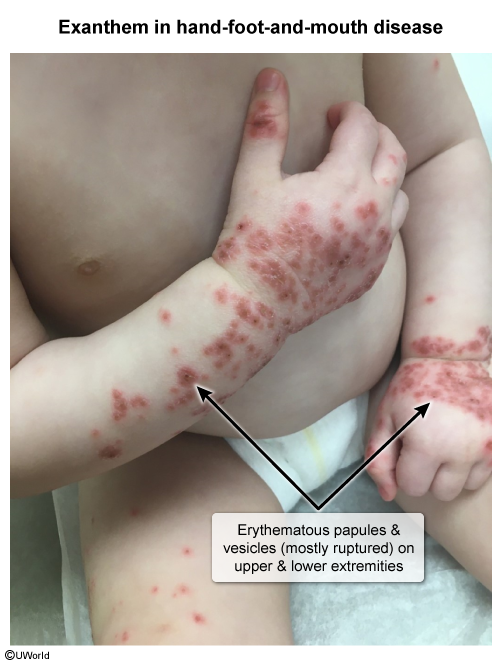
Hand-foot-and-mouth disease (HFMD) is a viral infection characterized by oral ulcers and a rash on the hands and feet. HFMD primarily affects infants and young children and is caused by enteroviruses, most commonly coxsackievirus A serotypes.
Pathophysiology and risk factors
HFMD is caused by enteroviruses (eg, coxsackievirus, enterovirus A71), which enter the body through the ingestion of viral particles from infected individuals. The virus can be shed from respiratory secretions, oral secretions, fecal material, or vesicular fluid. After it enters the body, the incubation period is 3-5 days. During this period, the virus replicates in the gastrointestinal tract and lymphoid tissues before disseminating through the reticuloendothelial system and bloodstream to other organs (eg, heart, liver, brain, skin). The characteristic clinical manifestations result from viral replication and immune-mediated inflammation at these distant sites.
Continue Learning with UWorld
Get the full Hand-Foot-And-Mouth Disease article plus rich visuals, real-world cases, and in-depth insights from medical experts, all available through the UWorld Medical Library.
Unlock Full AccessImages