Erysipelas
Article Sections
Introduction
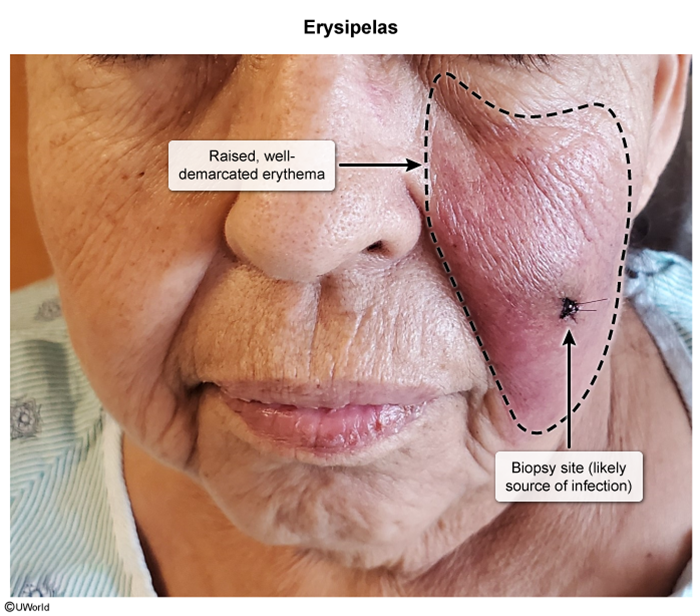
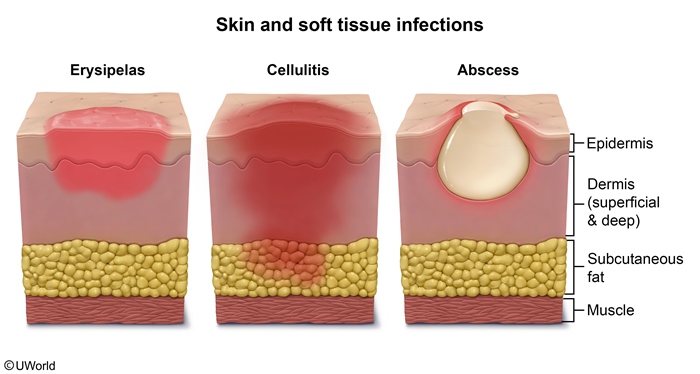
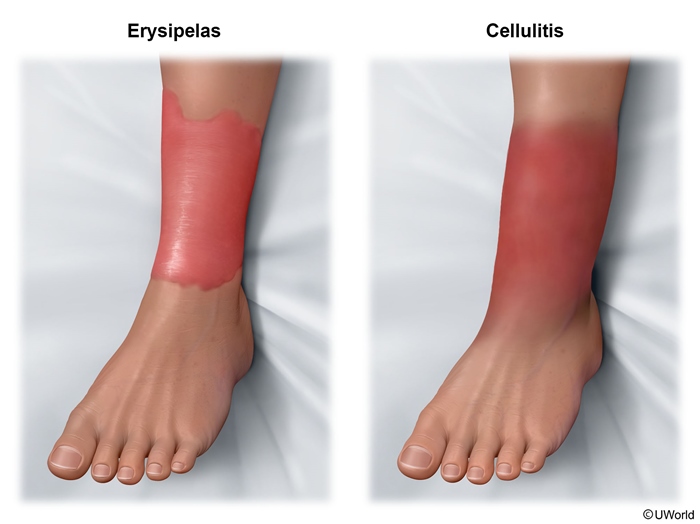
Erysipelas is a rapidly spreading skin infection affecting the upper dermis and superficial lymphatics. It is most commonly caused by Streptococcus pyogenes and classically manifests as tender, warm, well-demarcated erythema of the face or lower extremities.
Pathogenesis
Erysipelas is a rapidly spreading skin infection of the upper dermis and superficial lymphatic system that most commonly occurs in young children and older adults. Infection typically develops in an area of skin disruption (eg, abrasion, insect bite) and is most commonly caused by S pyogenes, or group A Streptococcus (GAS). Less commonly, other beta-hemolytic streptococci (eg, groups C or G streptococci) can cause disease.
The proliferation of S pyogenes with subsequent spread to the superficial lymphatic system leads to immune system activation, causing local erythema, edema, and warmth as well as systemic manifestations of fever and chills.
Continue Learning with UWorld
Get the full Erysipelas article plus rich visuals, real-world cases, and in-depth insights from medical experts, all available through the UWorld Medical Library.
Unlock Full AccessFigures
Images