Cutaneous T-Cell Lymphoma
Article Sections
Introduction
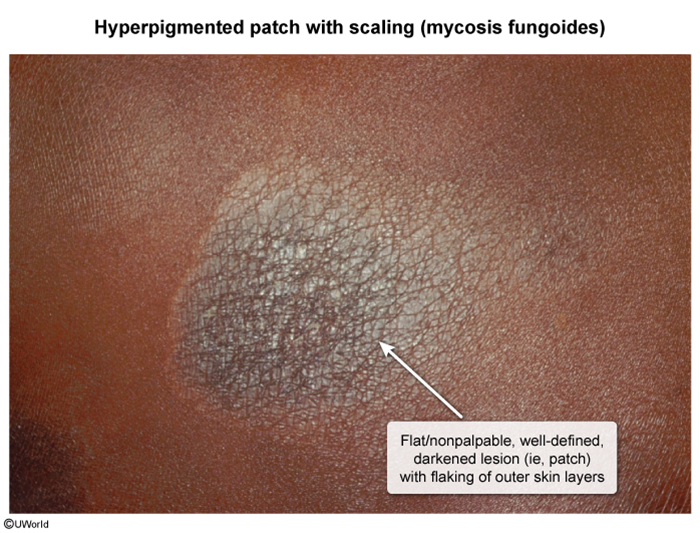
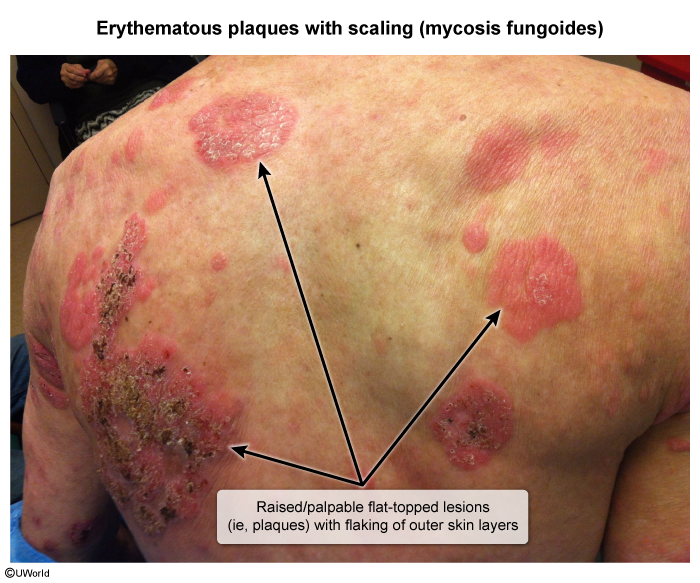
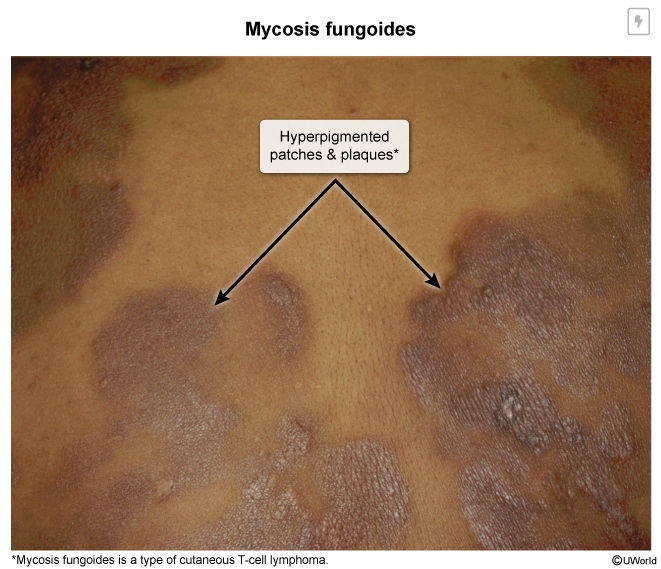
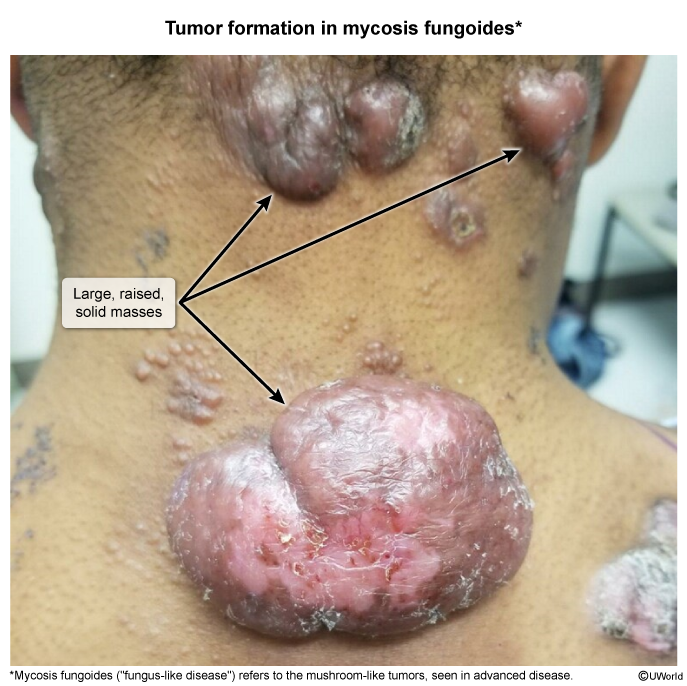
Cutaneous T-cell lymphoma (CTCL) refers to a rare group of neoplasms arising from mature T cells that reside in the skin. CTCL encompasses a variety of subtypes, with mycosis fungoides (MF) being the most common, followed by Sézary syndrome.
Pathogenesis and risk factors
Lymphomas are a diverse group of neoplasms that can be categorized according to the cell of origin and stage of maturation (Table 1). CTCL appears to develop following the accumulation of genetic and epigenetic changes affecting cell growth and survival of mature CD4+ memory T cells that reside on the skin. Although various types of genetic mutations can occur, chromosomal translocations and deletions appear to occur more frequently. Combined with alterations in the tumor microenvironment leading to reduced immune surveillance, which allows for malignant transformation and clonal expansion.
Continue Learning with UWorld
Get the full Cutaneous T-Cell Lymphoma article plus rich visuals, real-world cases, and in-depth insights from medical experts, all available through the UWorld Medical Library.
Unlock Full AccessImages