Molluscum Contagiosum
Article Sections
Introduction
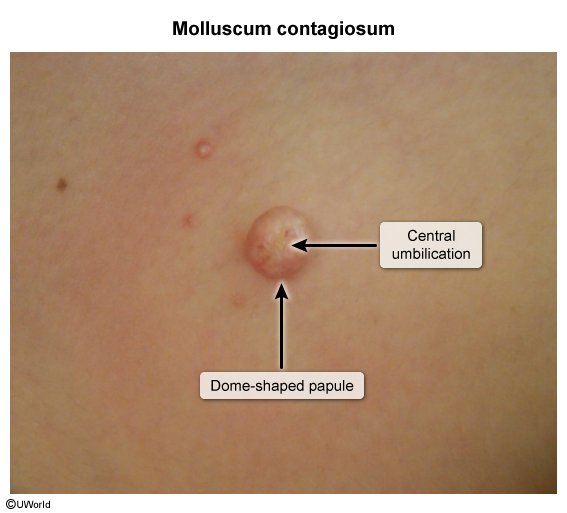
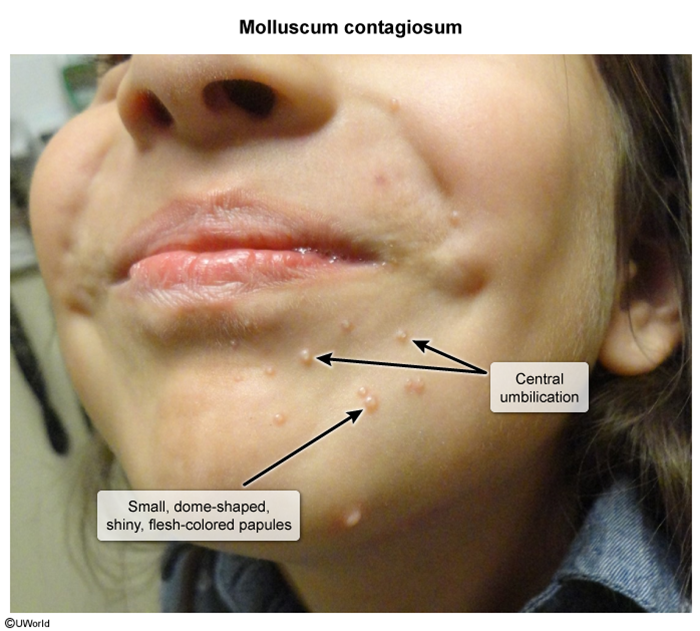
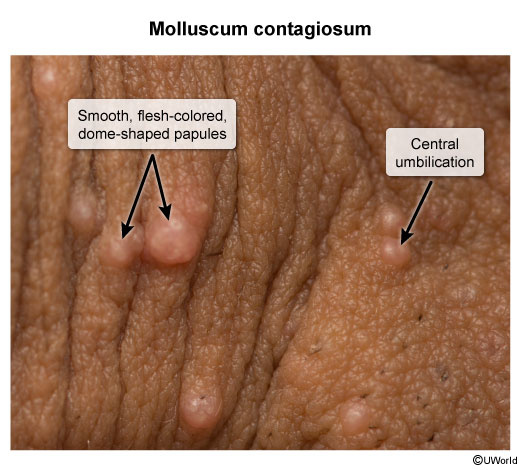
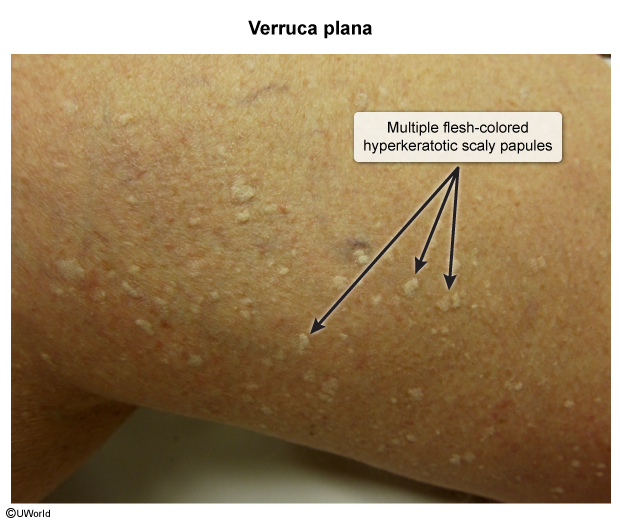
Molluscum contagiosum is a benign viral skin infection that presents with small, dome-shaped, flesh-colored papules with umbilicated centers. Healthy children are most commonly affected, but molluscum contagiosum can also occur in adults, especially those who are immunocompromised or sexually active.
Pathophysiology and risk factors
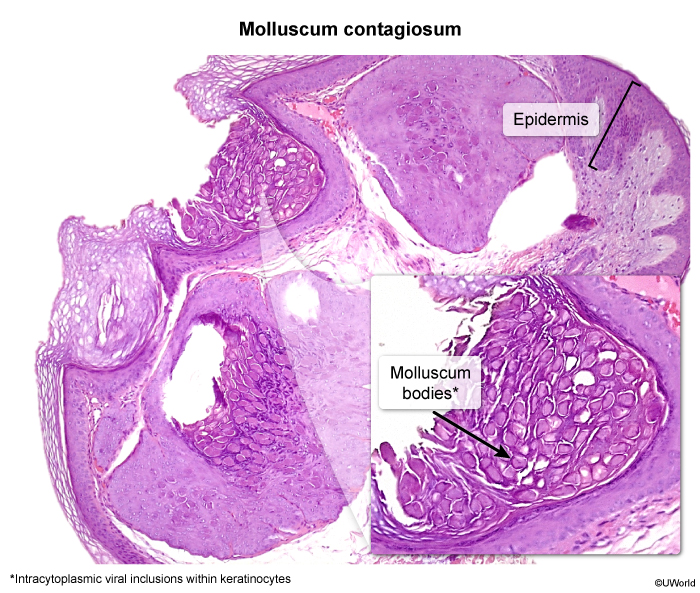
Molluscum contagiosum is a common, benign skin infection caused by a poxvirus. Transmission occurs through skin-to-skin contact or via contaminated fomites (eg, towels), with subsequent autoinoculation to additional sites. The pathophysiology involves viral infection of epidermal cells, with subsequent replication within the cytoplasm. This results in the enlargement of basal keratinocytes and the formation of characteristic intracytoplasmic inclusion bodies.
Risk factors include young age (1-10), participation in contact sports, sexual activity, and cellular immunodeficiency (eg, HIV infection).
Continue Learning with UWorld
Get the full Molluscum Contagiosum article plus rich visuals, real-world cases, and in-depth insights from medical experts, all available through the UWorld Medical Library.
Unlock Full AccessImages