Cutaneous Warts
Article Sections
Introduction
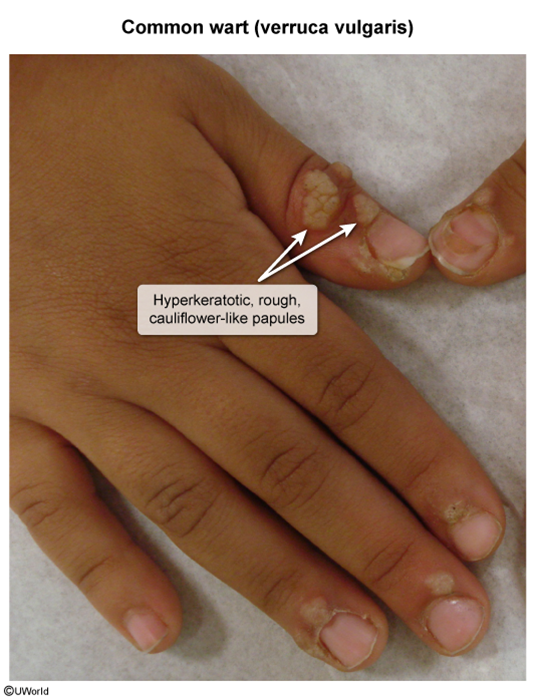
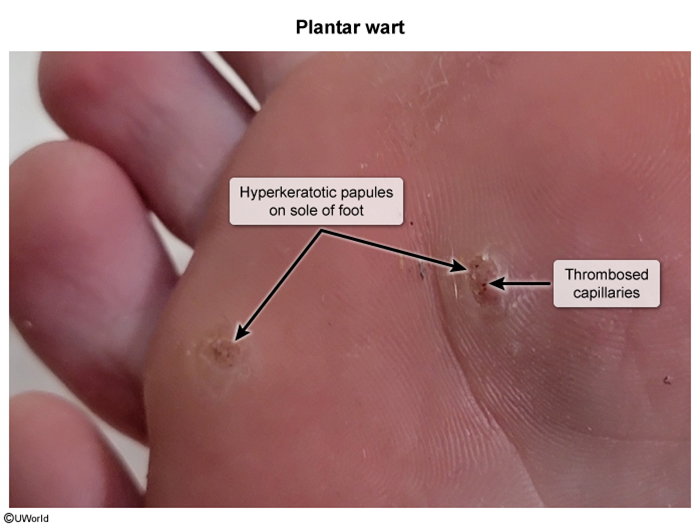
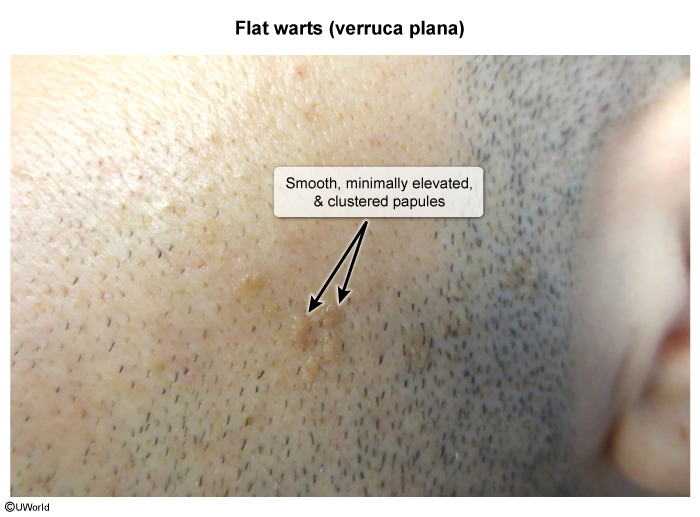
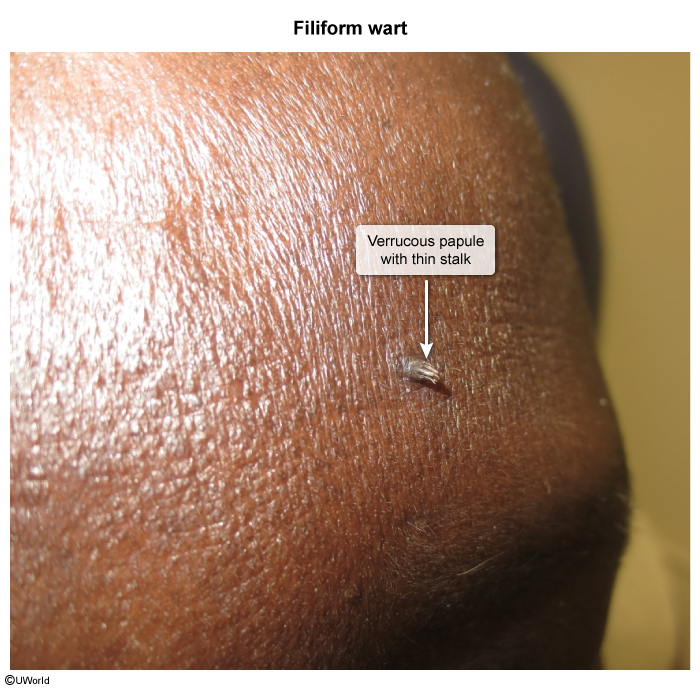
Cutaneous warts are epidermal proliferations caused by human papillomavirus. The most common presentation is hyperkeratotic papules on the hands and feet of children and young adults. Spontaneous resolution can occur, but topical treatment (eg, salicylic acid, cryotherapy) is often administered.
Pathophysiology
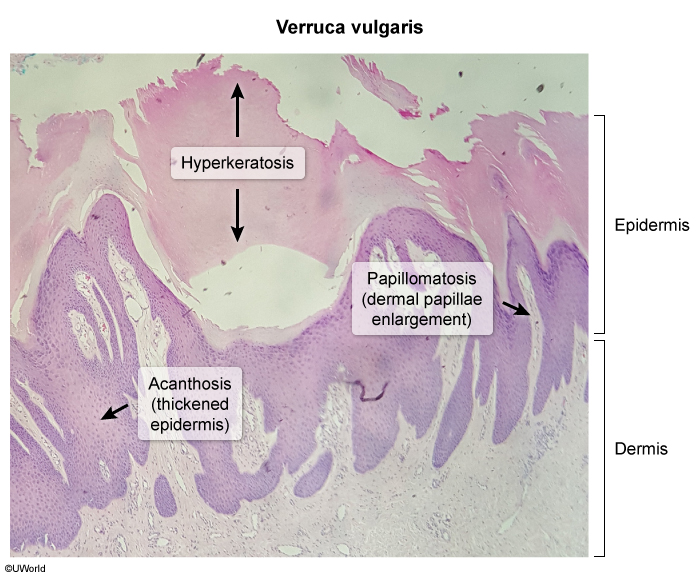
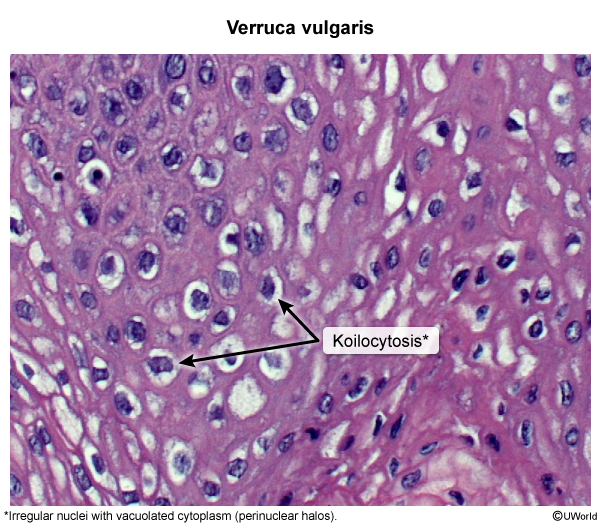
Cutaneous warts are caused by human papillomavirus (HPV), which has many subtypes that have a tendency to infect specific areas of the body and cause distinct disease (eg, HPV 16 and 18 in cervical cancer, HPV 6 and 11 in anogenital warts). In the case of cutaneous warts, which are located anywhere other than the anogenital area, subtypes 1, 2, and 4 are most commonly implicated.
HPV is usually transmitted via direct contact, although fomite transmission may occur. The virus enters through small cuts or abrasions and infects basal keratinocytes. The resulting keratinocyte proliferation leads to the characteristic finding of hyperkeratotic papules. Lesions can develop weeks to months after initial infection, and malignant transformation is rare.
Continue Learning with UWorld
Get the full Cutaneous Warts article plus rich visuals, real-world cases, and in-depth insights from medical experts, all available through the UWorld Medical Library.
Unlock Full AccessImages