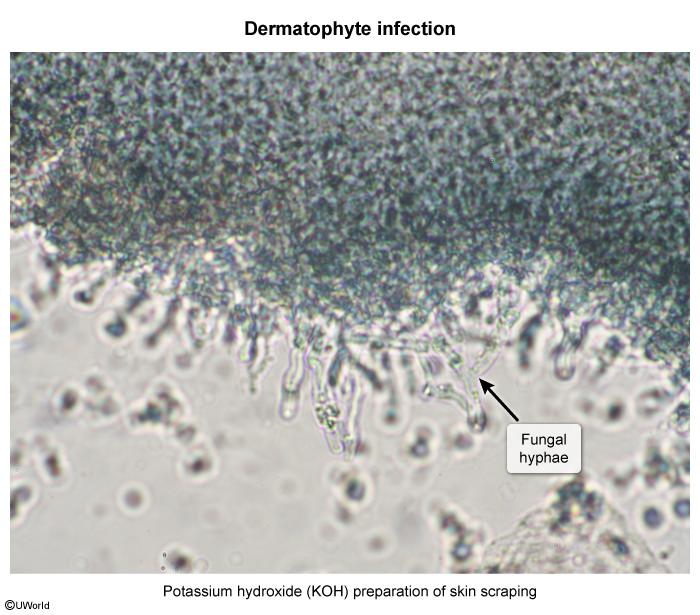
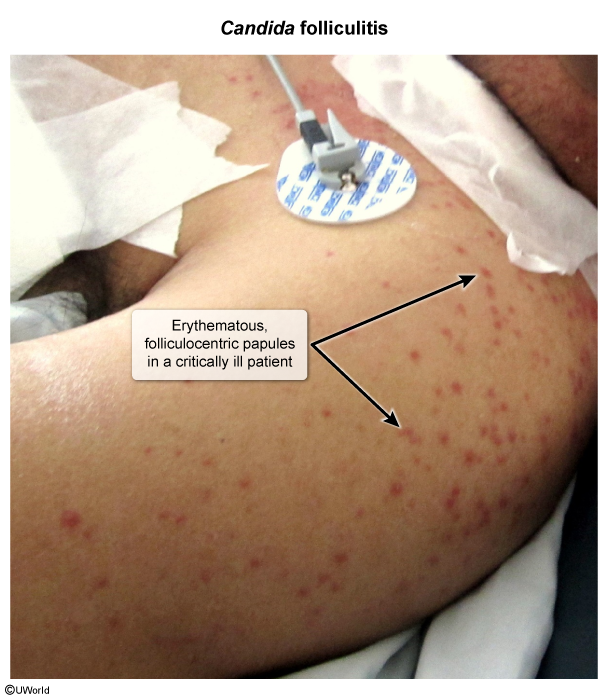
Infectious Folliculitis
Article Sections
Introduction
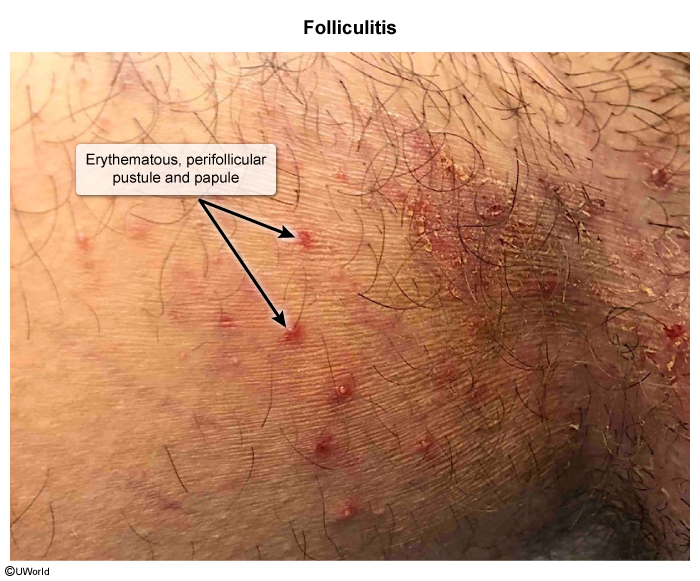
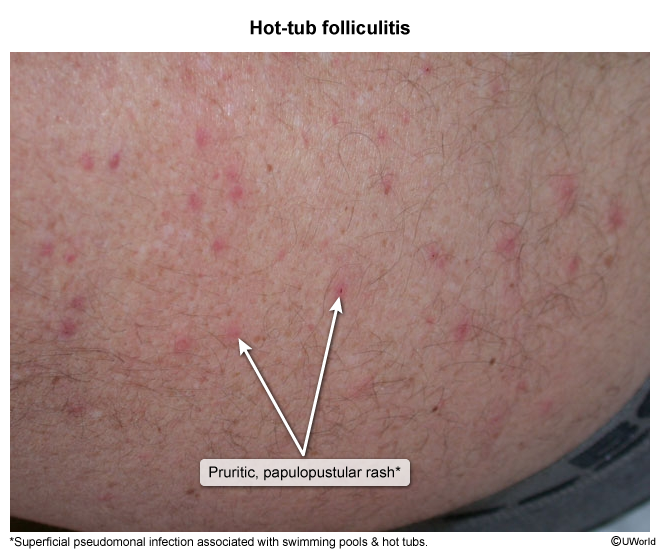
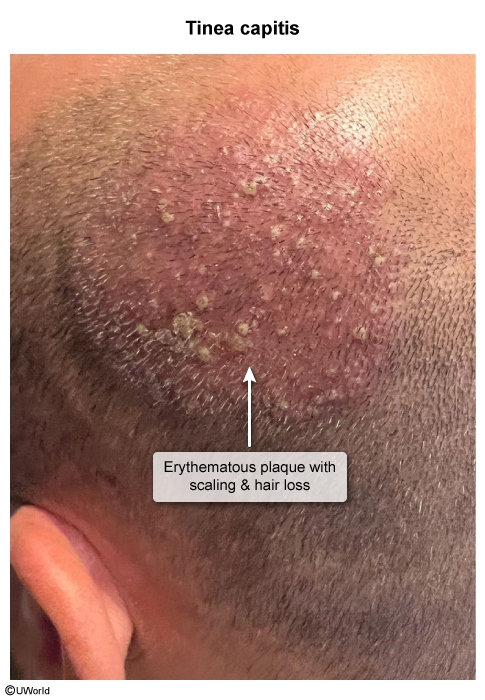
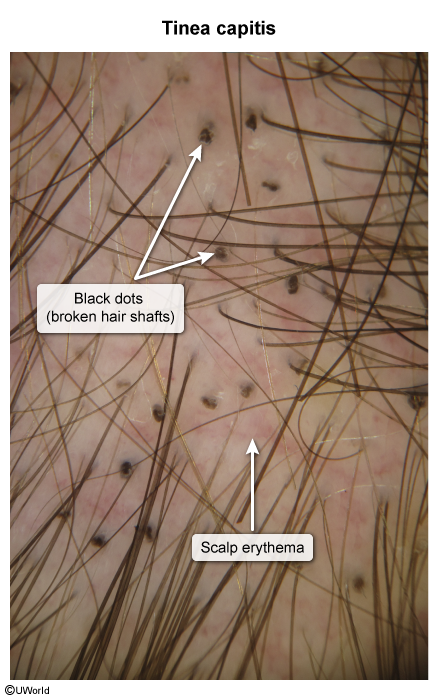
Folliculitis is inflammation of hair follicles; it is most commonly caused by infectious organisms, but it can also be noninfectious (eg, drug-induced folliculitis caused by glucocorticoid therapy). This article focuses on infectious etiologies of folliculitis, including bacterial, fungal, viral, and parasitic.
The first portion of this article provides an overview of infectious folliculitis, highlighting common features across all etiologies. Following this section, each of the infectious etiologies is discussed in greater detail, focusing on distinctive features unique to each.
Overview of infectious folliculitis
Folliculitis occurs when hair follicles become damaged or obstructed, allowing pathogens to penetrate and trigger an inflammatory response. The severity of folliculitis ranges from mild superficial to deep follicular inflammation, potentially forming abscesses.
Risk factorsGeneral risk factors for infectious folliculitis are as follows:
Continue Learning with UWorld
Get the full Infectious Folliculitis article plus rich visuals, real-world cases, and in-depth insights from medical experts, all available through the UWorld Medical Library.
Unlock Full AccessImages