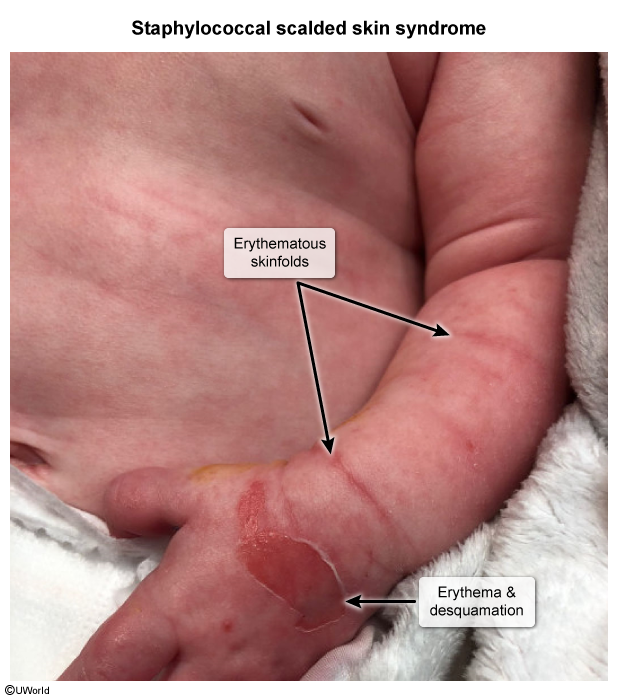
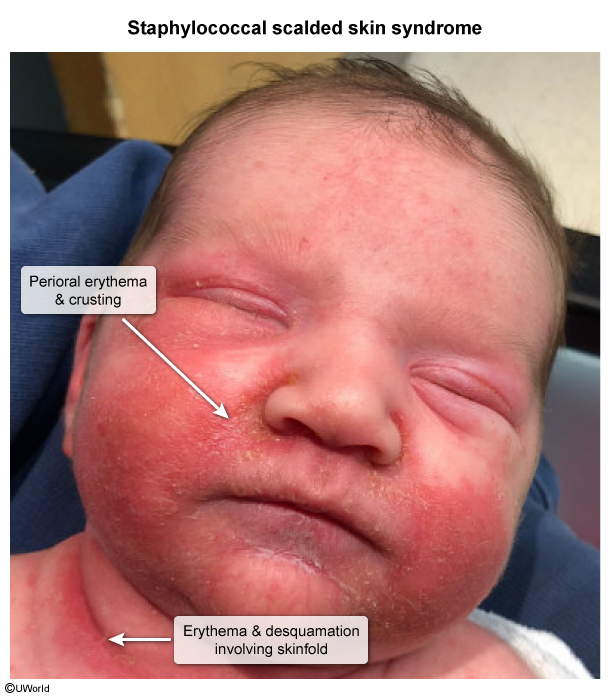
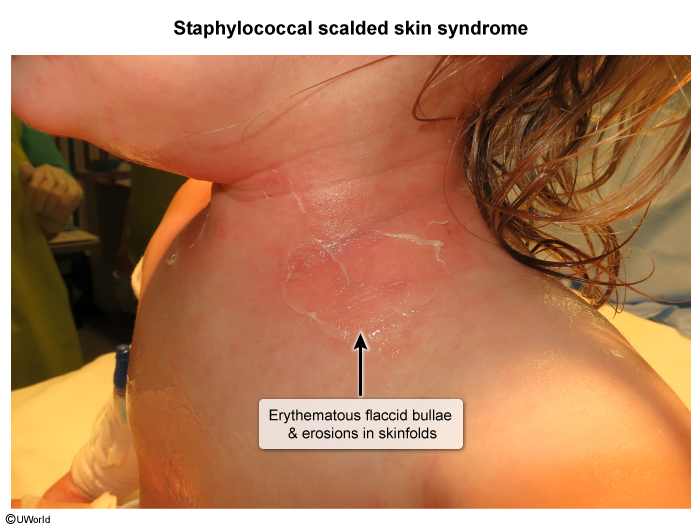
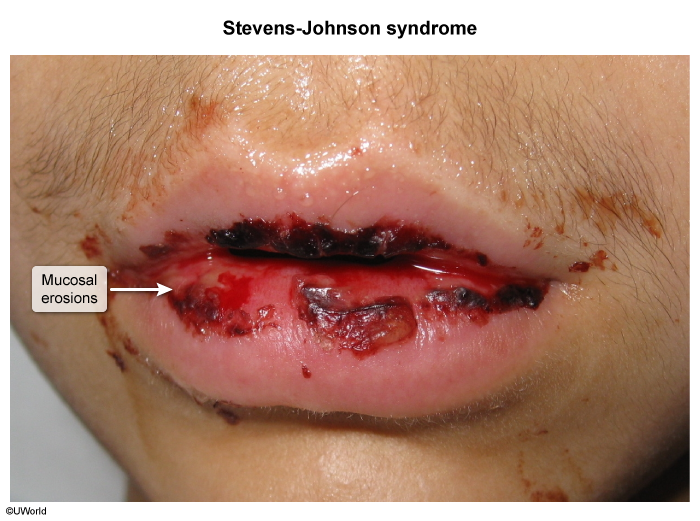
Staphylococcal Scalded Skin Syndrome
Article Sections
Introduction
Staphylococcal scalded skin syndrome (SSSS) is a desquamating skin disorder caused by exfoliative toxins produced by certain strains of Staphylococcus aureus. It primarily affects young children but can occur in adults, particularly in the setting of immunosuppression or renal insufficiency.
Risk factors
Age ≤5 is the greatest risk factor for developing SSSS. This is likely related to a relative lack of toxin-neutralizing antibodies in young children as compared to older children and adults, as well as poor renal toxin clearance due to immature renal function.
In adults, risk factors include immunosuppression (eg, HIV) and renal insufficiency.
Pathophysiology
The pathogenesis of SSSS involves infection with certain strains of S aureus that produce exfoliative toxins. In children, the inciting infection is typically conjunctivitis, impetigo, or umbilical or circumcision site infection, whereas, in adults, abscess or pneumonia is more common.
Continue Learning with UWorld
Get the full Staphylococcal Scalded Skin Syndrome article plus rich visuals, real-world cases, and in-depth insights from medical experts, all available through the UWorld Medical Library.
Unlock Full AccessFigures
Images