Staphylococcal Toxic Shock Syndrome
Article Sections
Introduction
Staphylococcal toxic shock syndrome (TSS) is a life-threatening condition caused by exotoxins produced by Staphylococcus aureus within a retained foreign body or a wound infection. It is characterized by sudden onset of high fever, rash, hypotension, and multiorgan dysfunction.
Risk factors
Risk factors for the development of staphylococcal TSS include the following:
- Retained foreign body (eg, tampon, nasal/vaginal packing); prolonged, single use increases risk
- Surgical/postpartum wound infection
- Skin and soft tissue infections (eg, mastitis, burns)
Wounds may not appear infected due to a poor local inflammatory response.
Pathophysiology
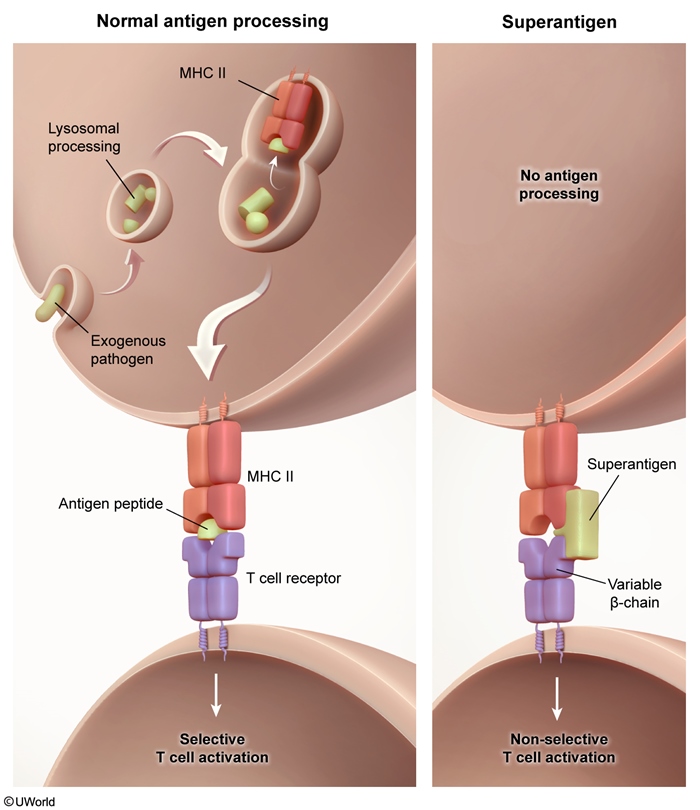
Staphylococcal TSS is an exotoxin-mediated disease. Most cases are linked to prolonged tampon use, nasal wound packing, or wound infections, each of which provide a medium for localized S aureus proliferation and the elaboration of pyrogenic toxin superantigens (eg, TSS toxin-1) into the bloodstream.
Continue Learning with UWorld
Get the full Staphylococcal Toxic Shock Syndrome article plus rich visuals, real-world cases, and in-depth insights from medical experts, all available through the UWorld Medical Library.
Unlock Full AccessFigures