Kaposi Sarcoma
Article Sections
Introduction
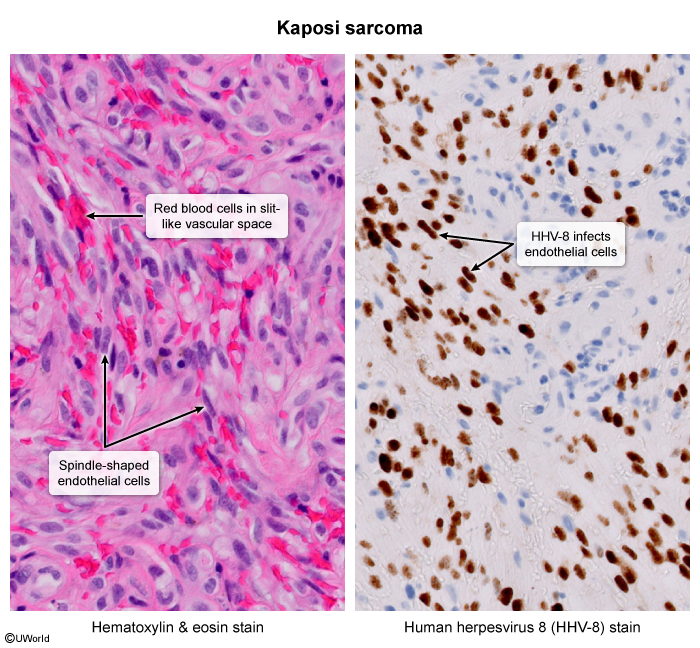
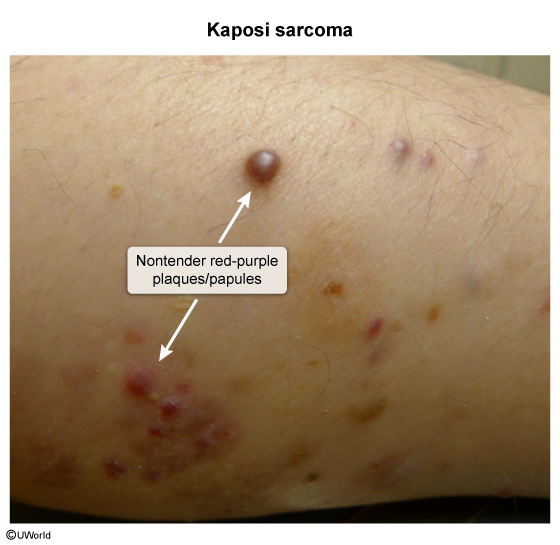
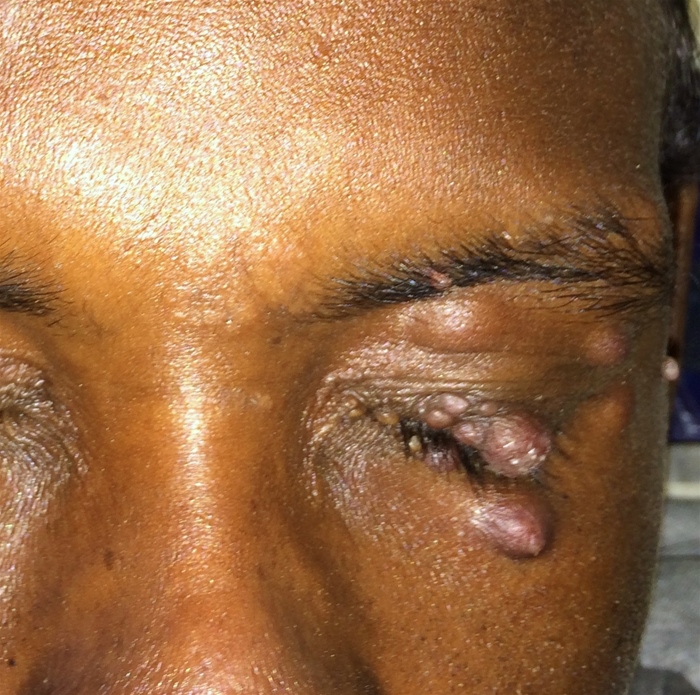
Kaposi sarcoma (KS) is a vascular tumor that is strongly associated with human herpesvirus 8 (HHV-8) as well as HIV. It manifests as violaceous cutaneous and mucosal lesions and can involve internal organs. There are 4 primary forms of KS:
- AIDS-associated (epidemic) KS
- Classic KS
- Endemic (African) KS
- Iatrogenic (immunosuppression-related) KS
AIDS-associated KS is the most common and can be aggressive, particularly in untreated or poorly controlled HIV infection.
Pathophysiology
HHV-8 infects vascular and lymphatic endothelial cells, causing them to differentiate into a mixed phenotype thought to increase oncogenic potential. The viral genome also contains several oncogenes that cause endothelial proliferation (eg, inhibit cell cycle regulation and apoptosis), thus promoting tumorigenesis. In addition, HHV-8 induces production of angiogenic and inflammatory cytokines, creating a favorable environment for cell growth.
Continue Learning with UWorld
Get the full Kaposi Sarcoma article plus rich visuals, real-world cases, and in-depth insights from medical experts, all available through the UWorld Medical Library.
Unlock Full AccessImages