Impetigo
Article Sections
Introduction
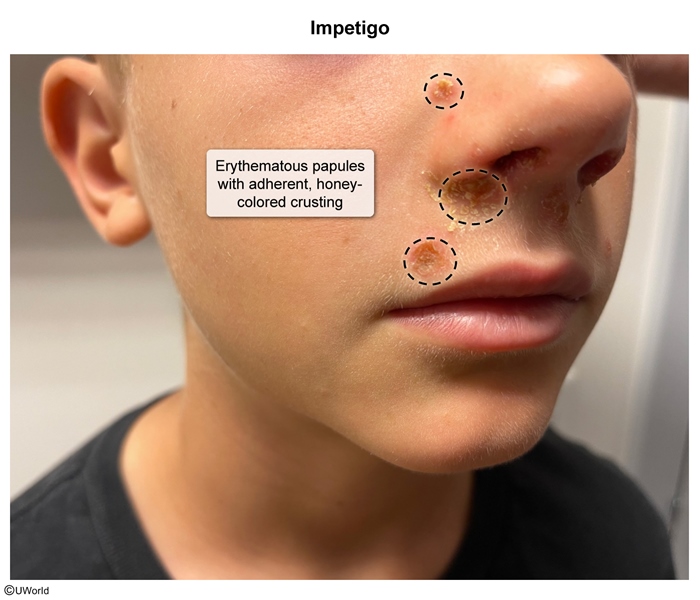
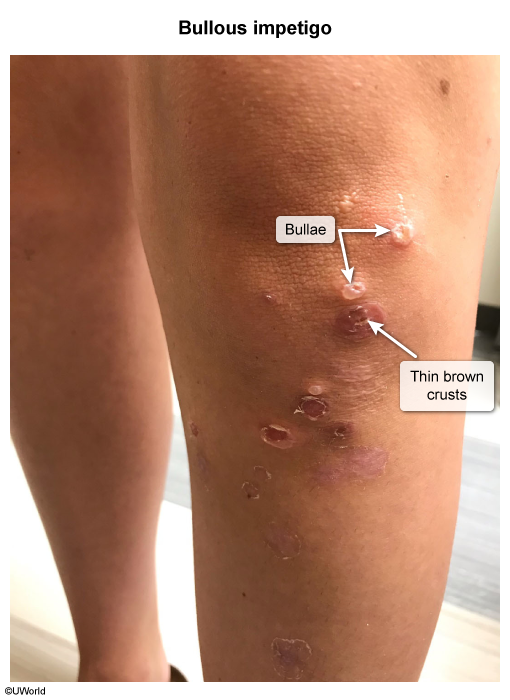
Impetigo is a superficial skin infection that typically occurs in children; it presents with honey-crusted papules and pustules on the face and extremities. The most common causes are Staphylococcus aureus and Streptococcus pyogenes, and management is antimicrobial therapy.
Risk Factors
- Age: most common in children age 2-5
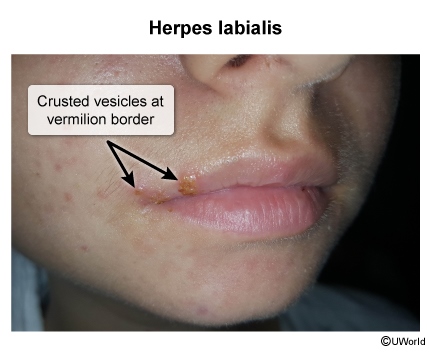
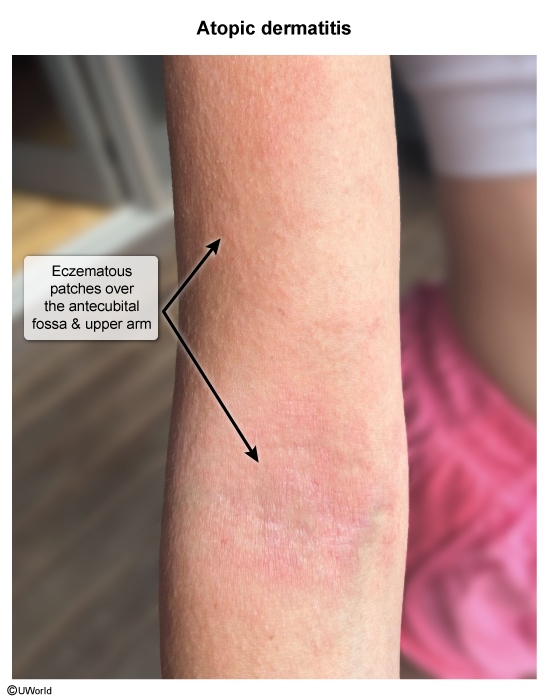
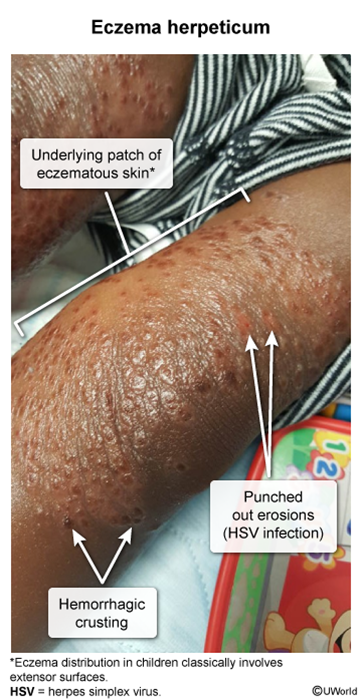
- Preexisting skin trauma/inflammation: wounds (eg, cuts, insect bites), infection (eg, herpes simplex virus [HSV]), or inflammation (eg, eczema, burn)
- Climate: more prevalent in warm, humid regions
- Poor hygiene: increases the likelihood of bacterial colonization
Pathophysiology
Impetigo is an infection of the superficial epidermis most commonly caused by bacterial invasion through a break in the skin barrier, including infection (eg, HSV, varicella virus, scabies), inflammation (eg, eczema, burn), or any open wound (eg, cuts, insect bites). Less commonly, impetigo can be caused by primary infection of previously intact skin.
Continue Learning with UWorld
Get the full Impetigo article plus rich visuals, real-world cases, and in-depth insights from medical experts, all available through the UWorld Medical Library.
Unlock Full AccessImages