Bedbugs
Article Sections
Introduction
Bedbugs (Cimex lectularius, Cimex hemipterus) are small parasitic insects that infest human dwellings and rely on blood meals for survival and reproduction.
Pathophysiology and risk factors
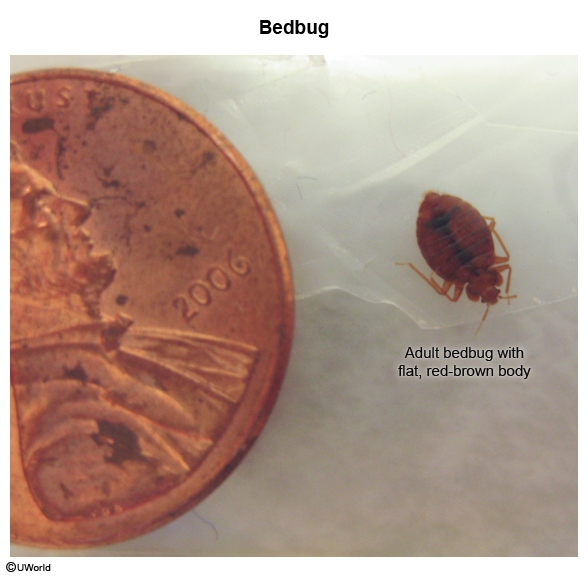
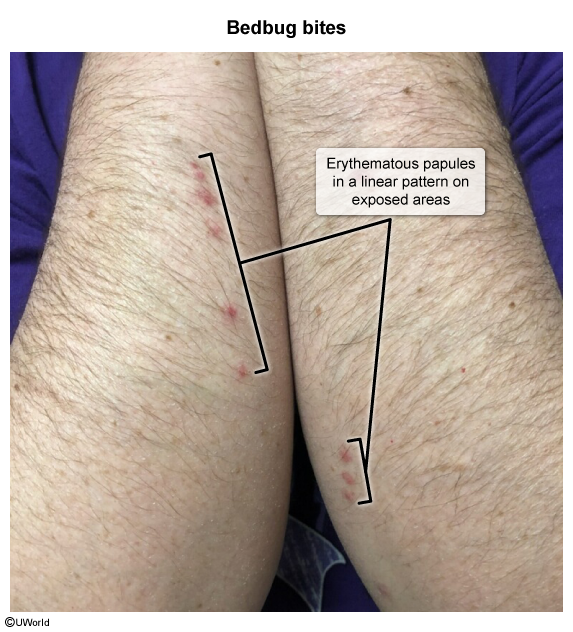
The bedbug life cycle includes 3 stages: egg, nymph, and adult. Adult bedbugs have flat, red-brown bodies (Image 1) and hide in clusters along the periphery and crevices of mattresses, bed frames, and surrounding structures. Bedbugs are nocturnal and attracted to warmth and carbon dioxide, typically feeding while their host sleeps. Bedbugs inject an anticoagulant while feeding, leaving a hemorrhagic punctum at the bite site. A typical blood meal lasts 5-10 minutes, and adult bedbugs can survive for up to a year without feeding.
Bedbug infestations can occur in any environment but are common in areas with high population density. Transmission occurs between colonized objects (eg, cushions, luggage) within a physical living space; human-to-human transmission is rare.
Continue Learning with UWorld
Get the full Bedbugs article plus rich visuals, real-world cases, and in-depth insights from medical experts, all available through the UWorld Medical Library.
Unlock Full AccessImages