Lice
Article Sections
Introduction
Lice infestation, or pediculosis, is a condition in which parasitic insects feed on human blood. There are 3 types of lice that infest humans: head lice (Pediculus humanus capitis), body lice (Pediculus humanus humanus), and pubic lice (Pthirus pubis).
Pathophysiology and risk factors
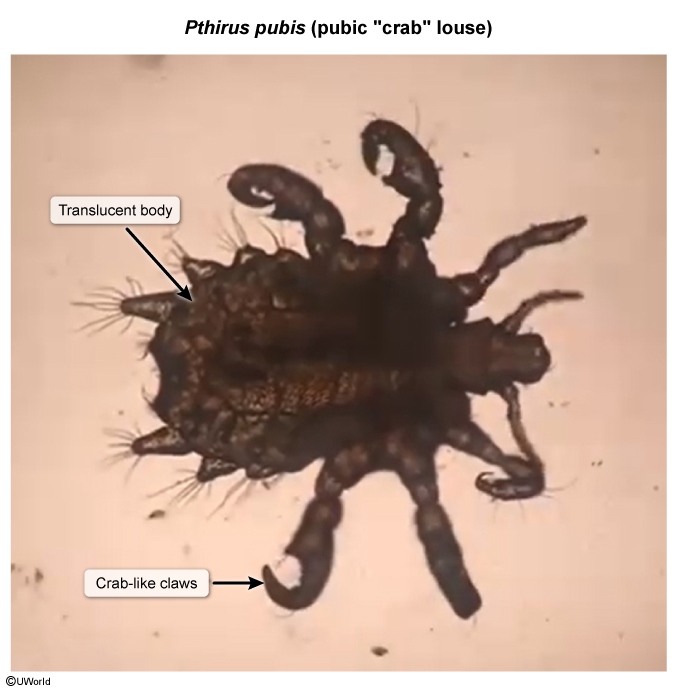
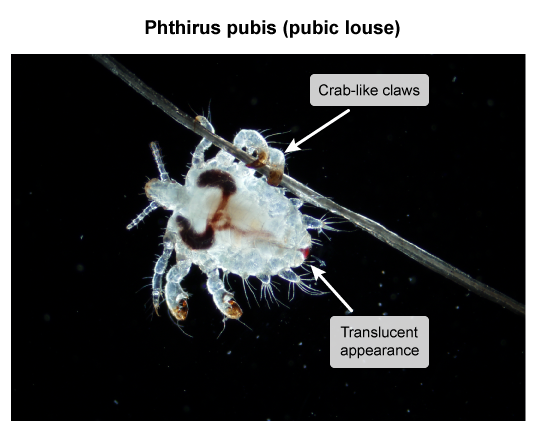
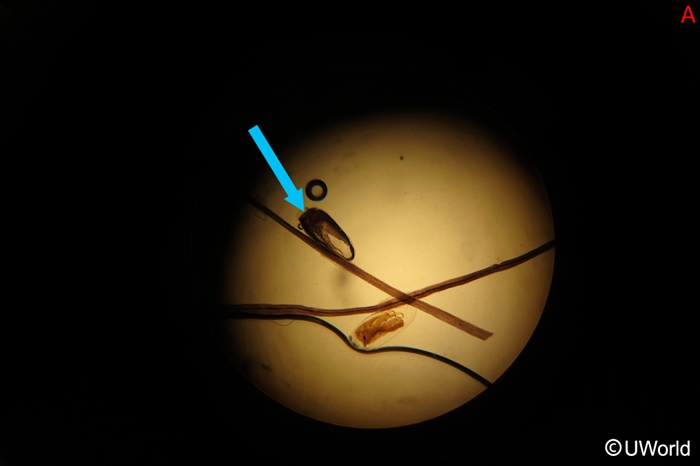
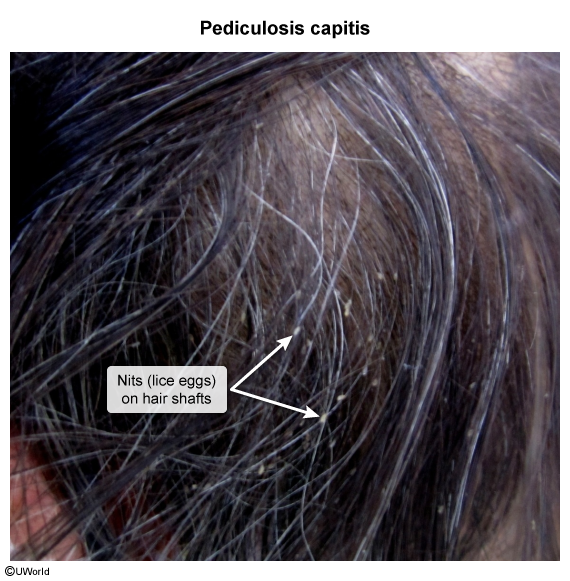
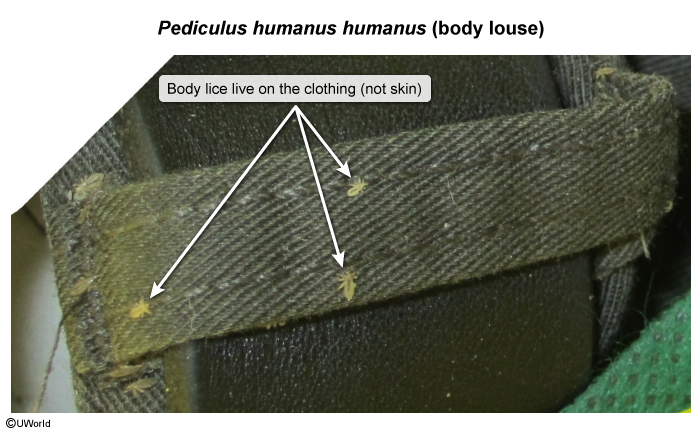
Lice are translucent ectoparasites (Image 1) that depend on human blood for survival. They have "crab-like" claws (Image 2) that help them attach to human hair and specialized mouthparts that pierce human skin. Lice infestation occurs when adult female lice lay eggs, known as nits (Image 3), on either hair shafts (head and pubic lice) or clothing and bedding (body lice). The nits remain firmly attached until they hatch into nymphs in about a week. Nymphs mature into adult lice and live for about a month, feeding on human blood daily. Without a host, lice die in 2-3 days.
Continue Learning with UWorld
Get the full Lice article plus rich visuals, real-world cases, and in-depth insights from medical experts, all available through the UWorld Medical Library.
Unlock Full AccessImages