Chickenpox
Article Sections
Introduction
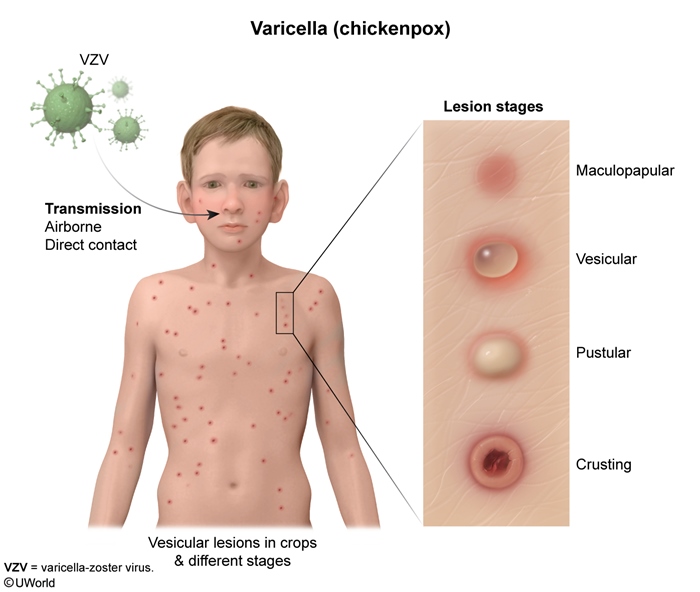
Chickenpox is a primary infection with varicella-zoster virus (VZV), a highly contagious, vaccine-preventable disease. It presents with a pruritic, vesicular rash and can lead to acute complications (eg, pneumonia), especially in immunocompromised patients and adolescents/adults.
Pathophysiology and risk factors
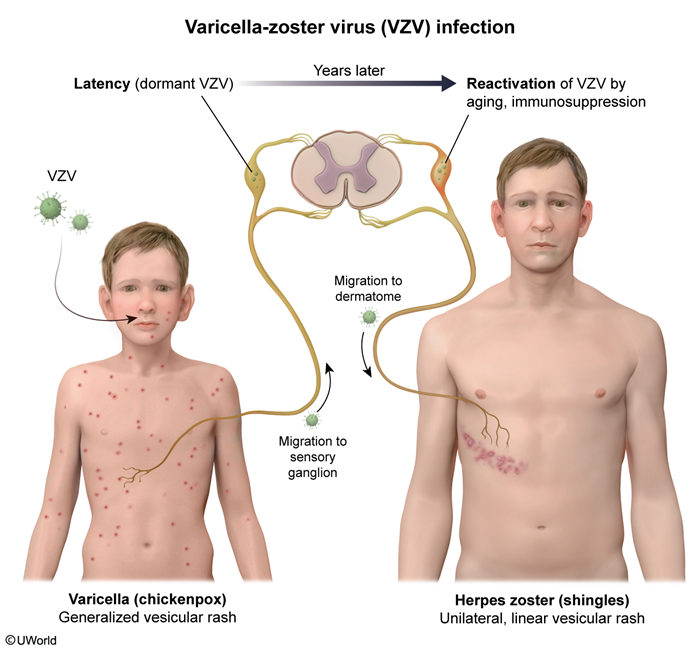
VZV is a double-stranded DNA virus and a member of the herpesvirus family. Transmission occurs primarily via inhalation of infected, airborne respiratory particles and, less commonly, from direct contact with vesicular fluid. Following infection of respiratory epithelial cells, VZV spreads to and replicates in the tonsils and regional lymph nodes, infecting T cells. Viremia subsequently leads to spread of the virus to local sensory ganglia, reticuloendothelial tissues, and skin.
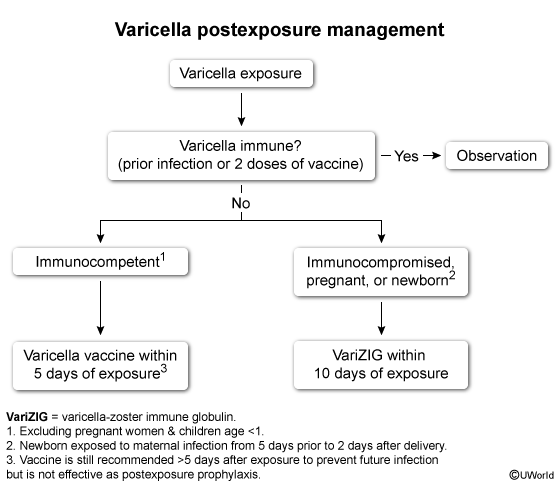
The transmission rate is >90% in susceptible individuals after exposure, with an incubation period of 1-3 weeks.
Continue Learning with UWorld
Get the full Chickenpox article plus rich visuals, real-world cases, and in-depth insights from medical experts, all available through the UWorld Medical Library.
Unlock Full AccessFigures