Antiplatelet Agents
Article Sections
Introduction
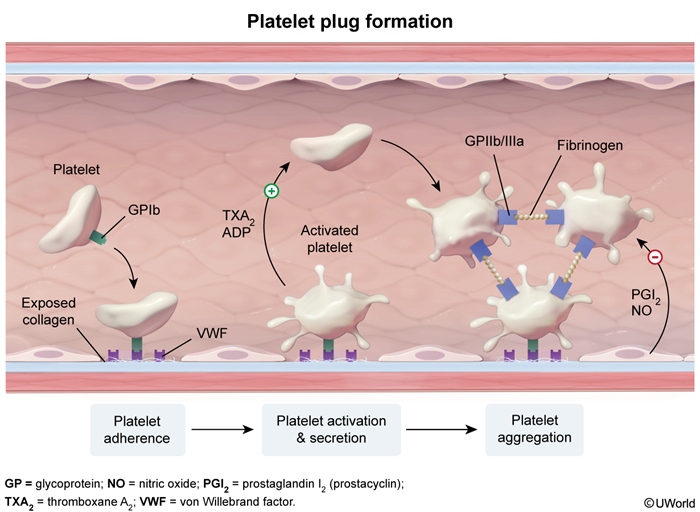
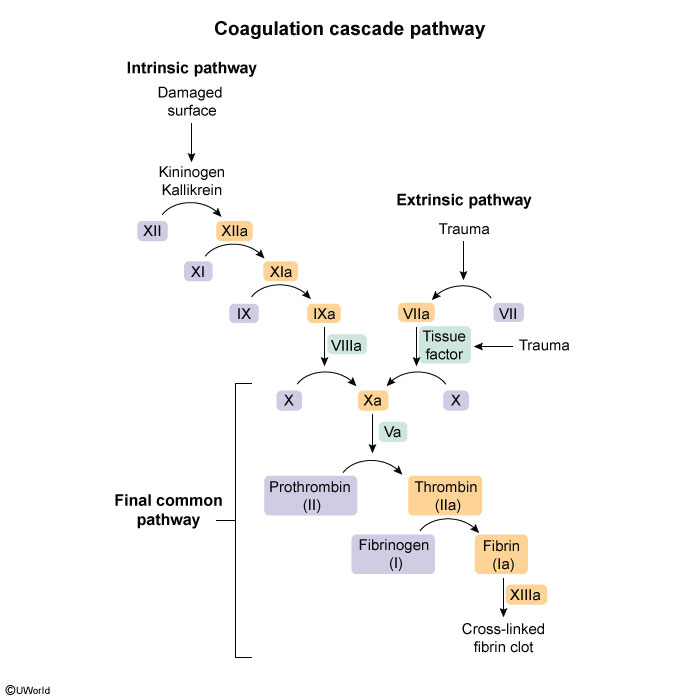
Hemostasis is a physiologic process that occurs in response to vascular injury. The process begins with the formation of a platelet plug at the site of endothelial injury (ie, primary hemostasis) (Figure 1), which is reinforced and stabilized by a cross-linked fibrin mesh formed via the coagulation cascade (ie, secondary hemostasis) (Figure 2).
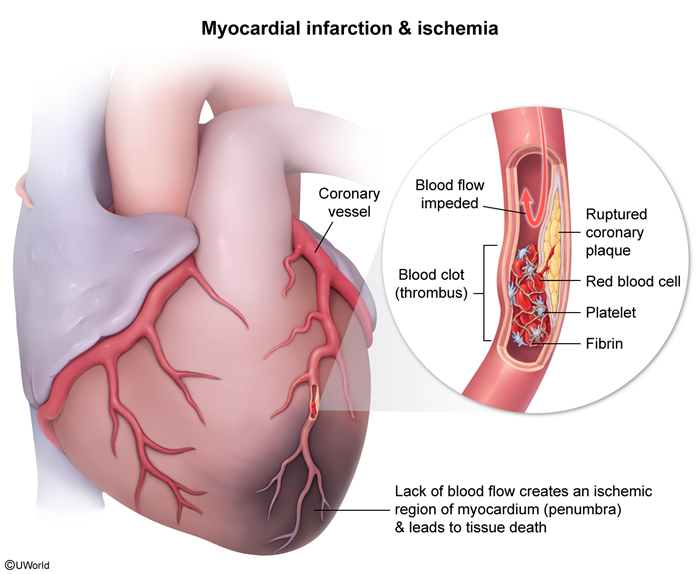
Thrombosis is a pathologic process in which the hemostatic mechanisms are excessively activated, resulting in a clot (thrombus) that obstructs normal blood flow. This can lead to life-threatening complications (eg, myocardial infarction [MI]) (Figure 3).
Several antithrombotic agents have been developed to prevent and treat thromboembolic disease, including:
- Antiplatelet agents (eg, aspirin, clopidogrel): Prevent formation of the platelet plug.
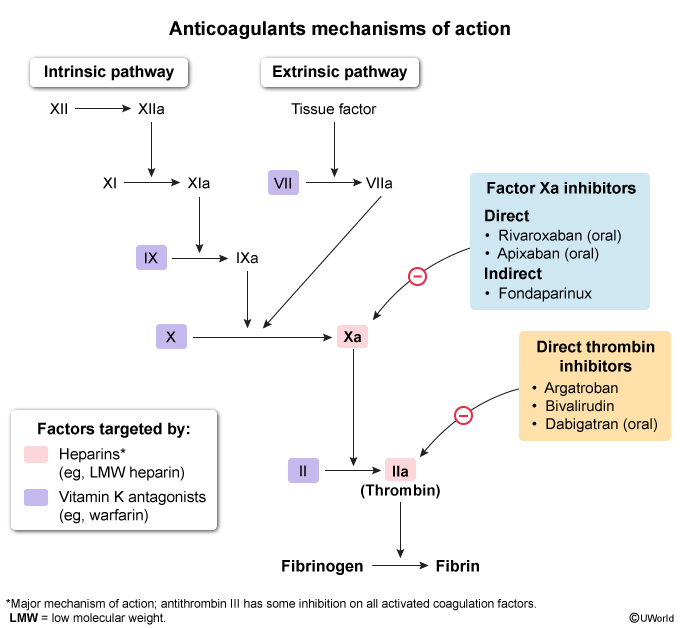
- Anticoagulant agents (eg, warfarin, heparin, dabigatran): Prevent formation of the fibrin mesh by inhibiting various steps in the coagulation cascade (
Continue Learning with UWorld
Get the full Antiplatelet Agents article plus rich visuals, real-world cases, and in-depth insights from medical experts, all available through the UWorld Medical Library.
Unlock Full AccessFigures