Cardiovascular Hemodynamics
Article Sections
Basics of cardiovascular blood flow
The cardiovascular system consists of a continuous circuit of blood vessels that supply oxygen and nutrients to the organs and tissues of the body. The system is powered by 2 pumps:
- The right ventricle (RV) powers the relatively low-pressure pulmonary circulation.
- The left ventricle (LV) powers the relatively high-pressure systemic circulation.
The parameters that govern cardiovascular blood flow are defined as follows.
Stroke volume and cardiac outputCardiac output = stroke volume × heart rate
Cardiac index = cardiac output / total body surface area
- Stroke volume is the volume of blood ejected from the RV or the LV with each contraction. It is typically measured in milliliters. The normal stroke volume for an adult at rest is approximately 70 mL.
- Cardiac output
Continue Learning with UWorld
Get the full Cardiovascular Hemodynamics article plus rich visuals, real-world cases, and in-depth insights from medical experts, all available through the UWorld Medical Library.
Unlock Full AccessFigures
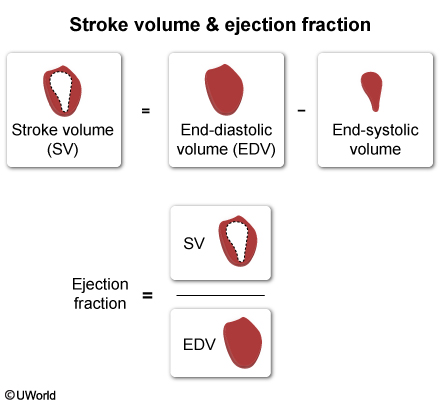
Figure 1
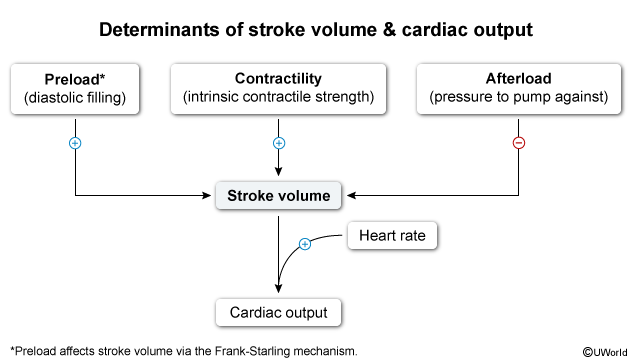
Figure 2
Figure 3
Figure 4
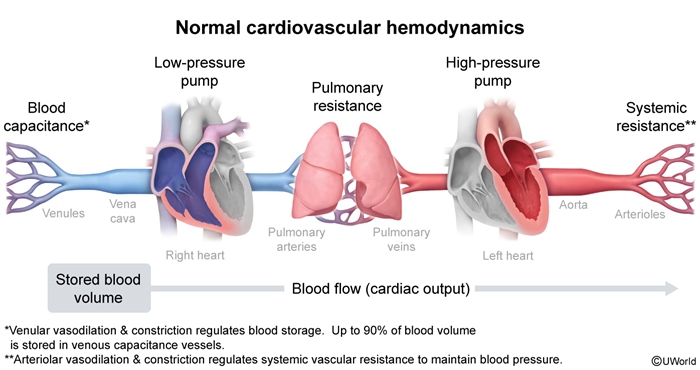
Figure 5
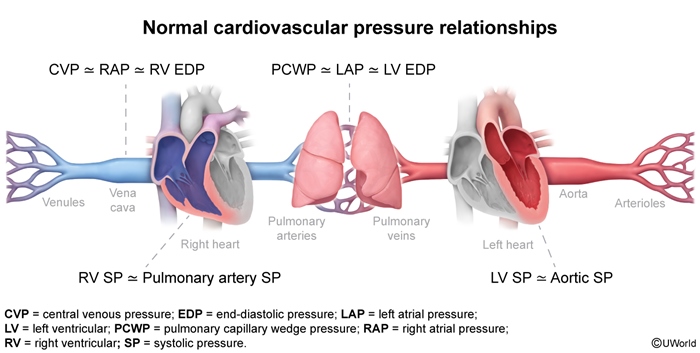
Figure 6