Chagas Disease
Article Sections
Introduction
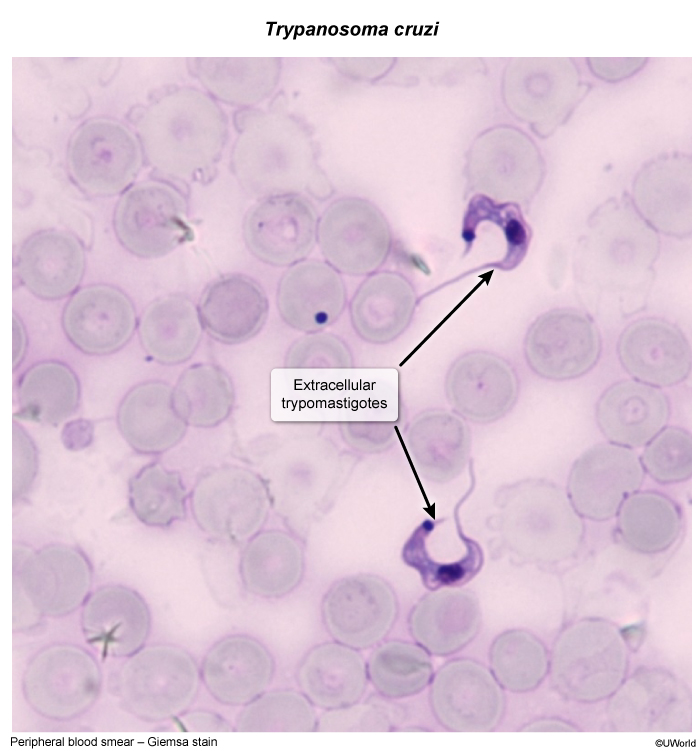
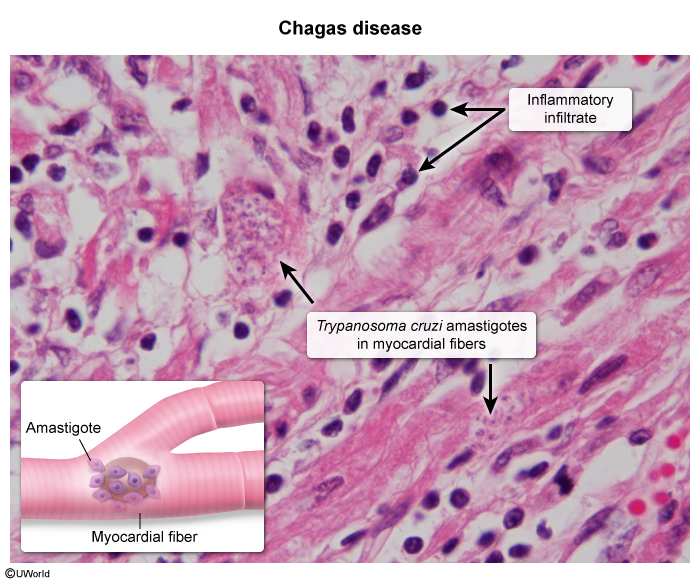
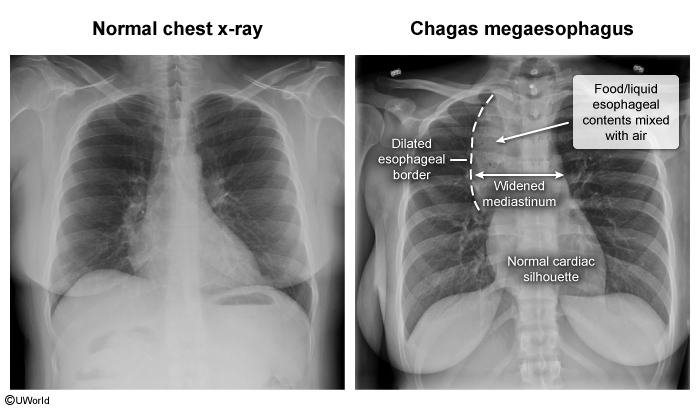
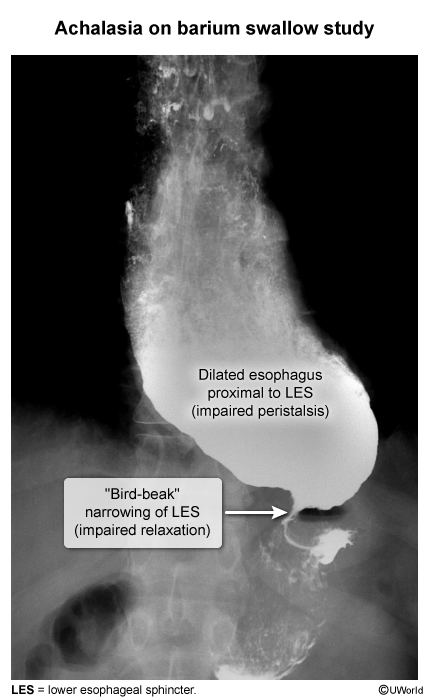
Chagas disease, also known as American trypanosomiasis, is a parasitic infection caused by Trypanosoma cruzi. It is endemic to parts of Central and Latin America but has increasingly been recognized in other regions (eg, southern United States) due to global migration. The disease is transmitted primarily through the bite of triatomine bugs, commonly known as "kissing bugs," but can also be spread congenitally from mother to child and through blood transfusions and organ transplants. The disease presents in 2 main phases, acute and chronic, and carries potentially serious consequences if left untreated.
Epidemiology and transmission
Chagas disease is endemic to rural Central and Latin American regions. Transmission occurs through the following routes:
- Triatomine bug vector: Transmission occurs when the bug feeds on human blood during the night and defecates the underlying pathogen
Continue Learning with UWorld
Get the full Chagas Disease article plus rich visuals, real-world cases, and in-depth insights from medical experts, all available through the UWorld Medical Library.
Unlock Full AccessImages