Cardiac Tamponade
Article Sections
Introduction
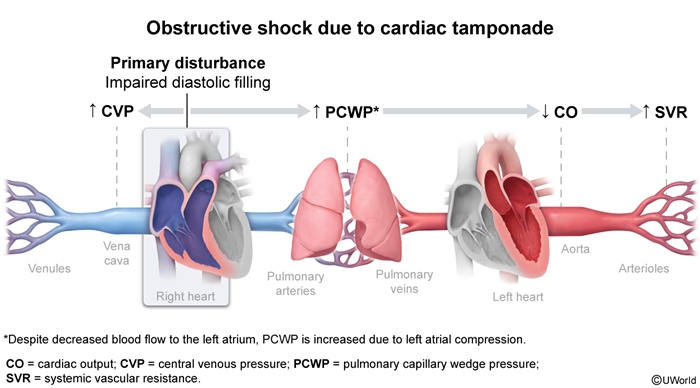
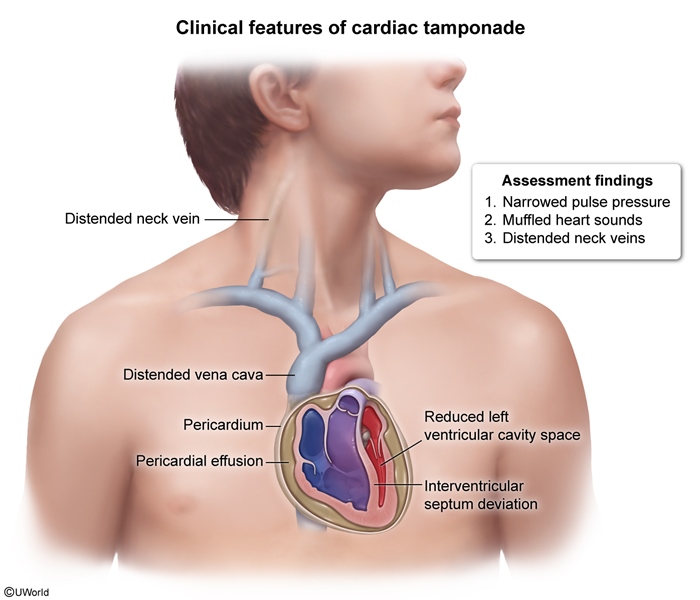
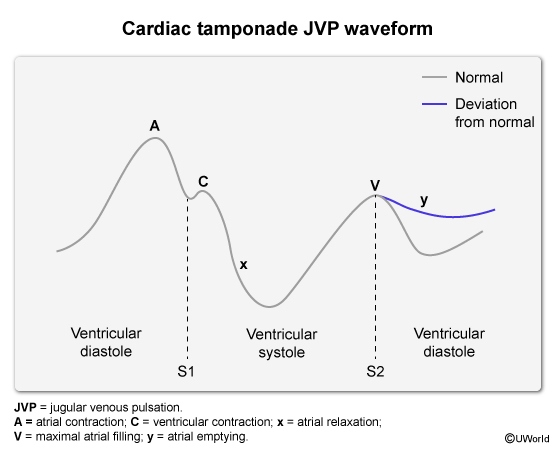
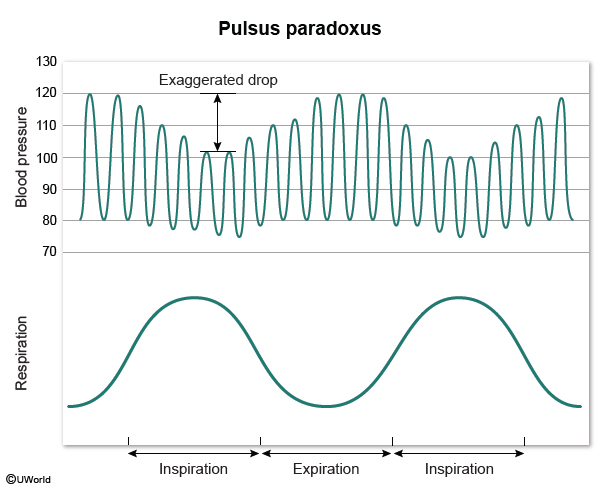
Cardiac tamponade is a life-threatening condition resulting from the accumulation of fluid in the pericardial sac, leading to restricted diastolic filling of the heart, reduced stroke volume, and obstructive shock. It is a medical emergency that requires prompt recognition and intervention.
Risk factors
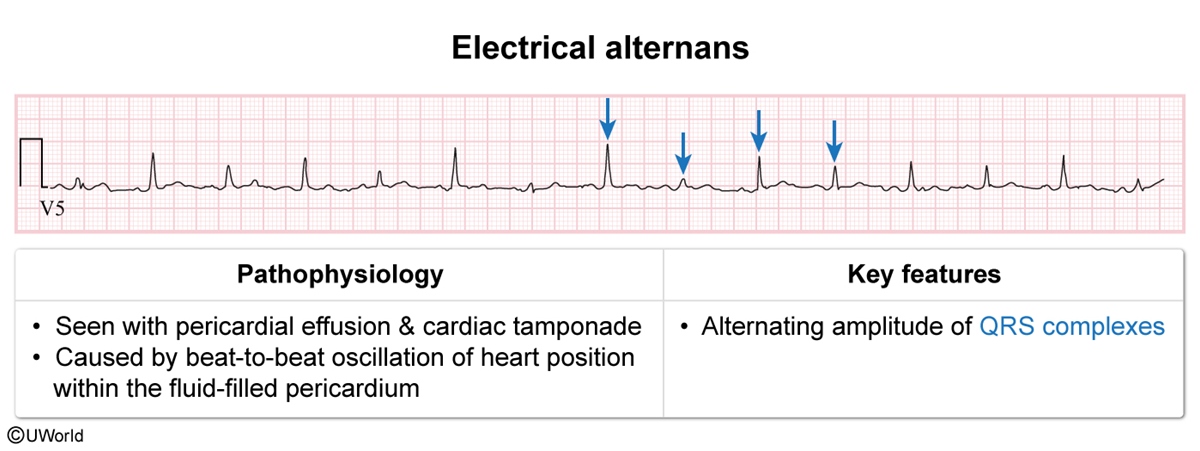
Any condition that causes pericardial effusion can lead to tamponade; this includes all etiologies of pericarditis such as infection (eg, viruses, tuberculosis), uremia, autoimmune disease (eg, systemic lupus erythematosus, rheumatoid arthritis), and malignancy. Hypothyroidism is a rare cause of pericardial effusion and tamponade. In addition, cardiac trauma (eg, injury, free wall rupture) or invasive procedures (eg, cardiac ablation, cardiothoracic surgery) can result in blood accumulation in the pericardial space and lead to tamponade. Aortic dissection with extension into the aortic root and rupture into the pericardial space is an occasional cause of tamponade.
Continue Learning with UWorld
Get the full Cardiac Tamponade article plus rich visuals, real-world cases, and in-depth insights from medical experts, all available through the UWorld Medical Library.
Unlock Full AccessFigures
Images