Overview Of Immunology And Primary Immunodeficiencies
Article Sections
Introduction
The immune system is complex, with overlapping pathways. This article provides an overview of the immune system by conceptualizing it based on 2 major branches:
- Innate immunity refers to a rapid generalized response that remains constant with each exposure. It occurs at the site of infection.
- Adaptive immunity refers to a slower, memory-based response to specific pathogens that improves over time. It begins when antigen-presenting cells (APCs [eg, dendritic cells]) move from the site of infection to the nearest lymphoid tissue (eg, lymph node). The adaptive immune branch is subdivided into 2 categories:
- Cell-mediated immunity (T cells) is characterized by direct killing of intracellularly infected or abnormal cells (cytotoxic T-cell response) and broad assistance of other immune cells (helper T-cell response).
Continue Learning with UWorld
Get the full Overview Of Immunology And Primary Immunodeficiencies article plus rich visuals, real-world cases, and in-depth insights from medical experts, all available through the UWorld Medical Library.
Unlock Full AccessFigures
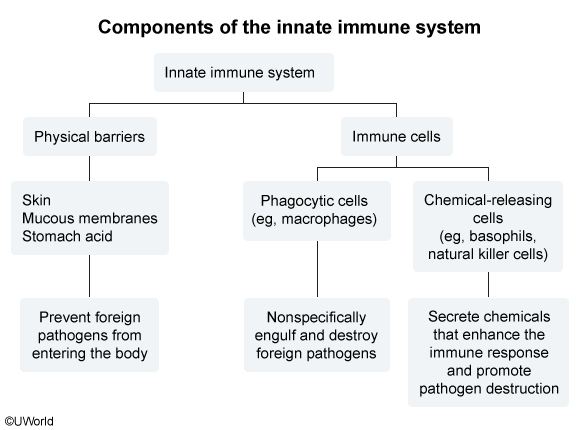
Figure 1
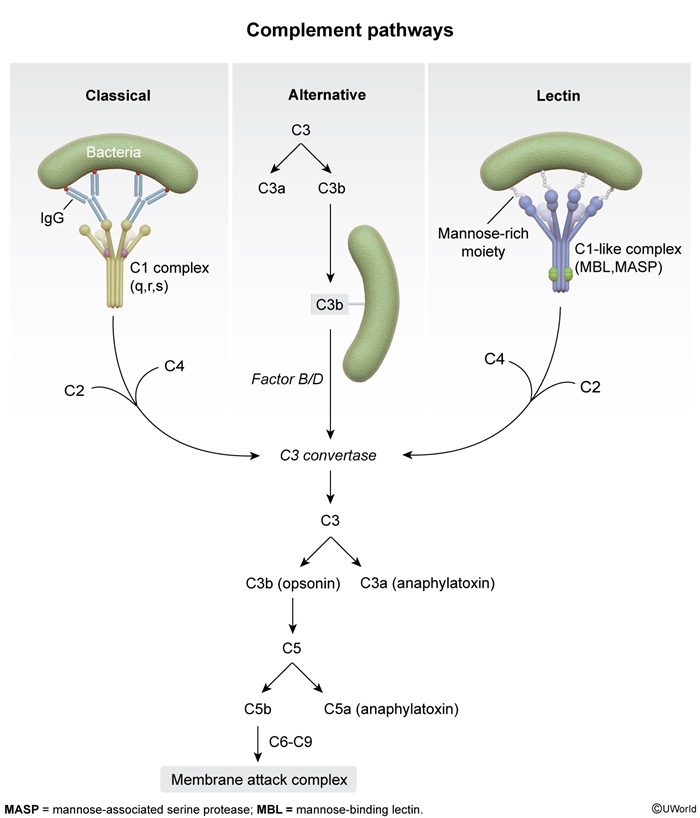
Figure 2
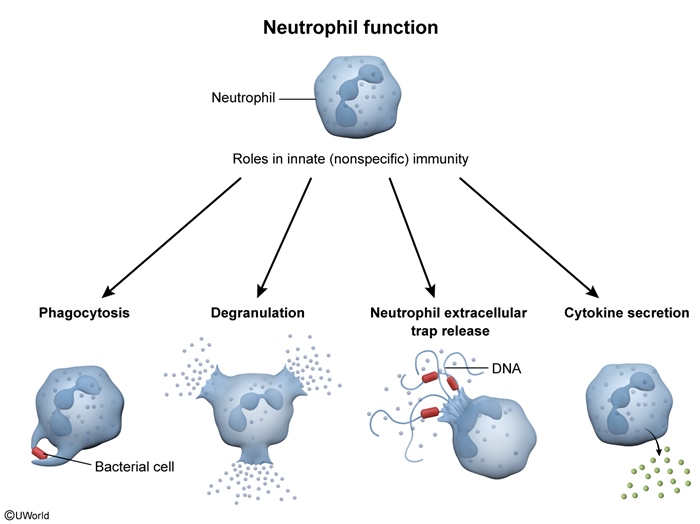
Figure 3
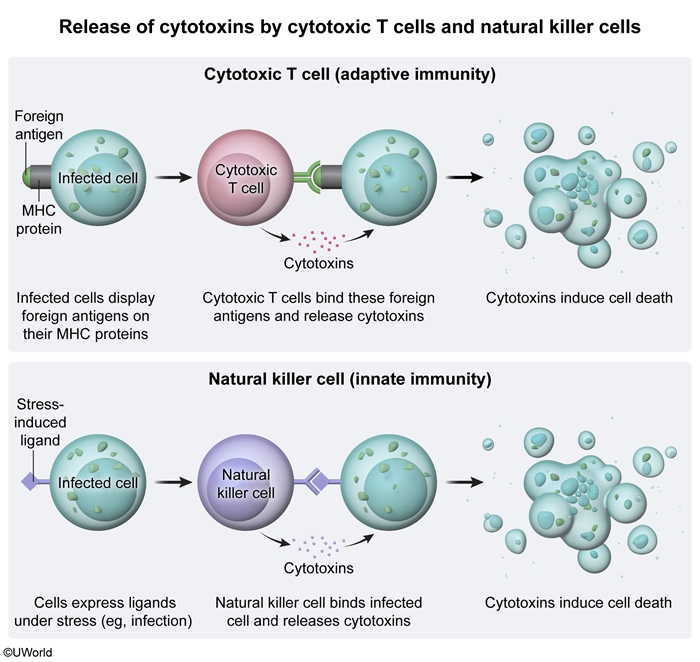
Figure 4
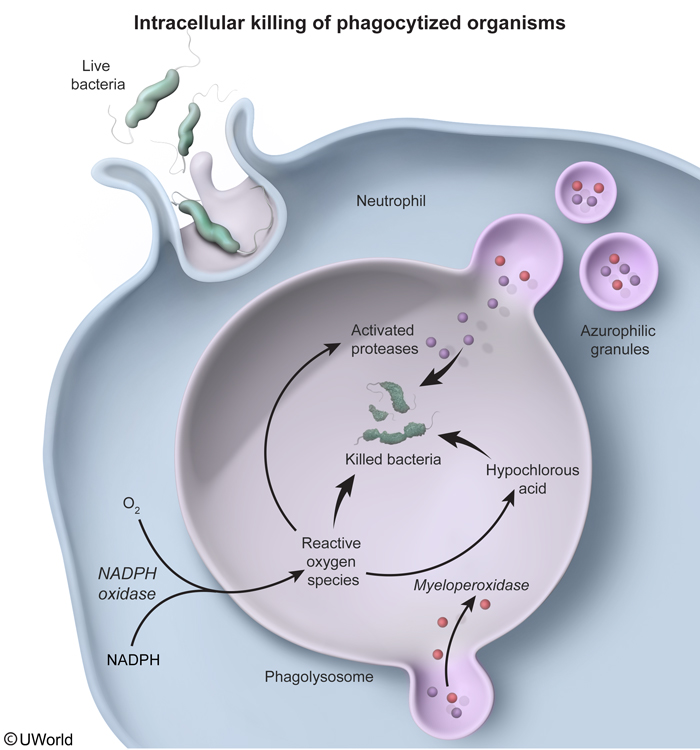
Figure 5
Tables
Table 1